
Piezoelectricity is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solid materials—such as crystals, certain ceramics, and biological matter such as bone, DNA, and various proteins—in response to applied mechanical stress. The word piezoelectricity means electricity resulting from pressure and latent heat. It is derived from Ancient Greek πιέζω (piézō) 'to squeeze or press' and ἤλεκτρον (ḗlektron) 'amber'. The German form of the word (Piezoelektricität) was coined in 1881 by the German physicist Wilhelm Gottlieb Hankel; the English word was coined in 1883.

Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. The charge remains until it can move away by an electric current or electrical discharge. The word "static" is used to differentiate it from current electricity, where an electric charge flows through an electrical conductor.

A lighter is a portable device which uses mechanical or electrical means to create a controlled flame, and can be used to ignite a variety of flammable items, such as cigarettes, butane gas, fireworks, candles, or campfires. A lighter typically consists of a metal or plastic container filled with a flammable liquid, a compressed flammable gas, or in rarer cases a flammable solid ; a means of ignition to produce the flame; and some provision for extinguishing the flame or else controlling it to such a degree that the user may extinguish it with their breath. Alternatively, a lighter can be one which uses electricity to create an electric arc utilizing the created plasma as the source of ignition or a heating element can be used in a similar vein to heat the target to its ignition temperatures, as first formally utilized by Friedrich Wilhelm Schindler to light cigars and now more commonly seen incorporated into the automobile auxiliary power outlet to ignite the target material. Different lighter fuels have different characteristics which is the main influence behind the creation and purchasing of a variety of lighter types.
Piezo is derived from the Greek πιέζω, which means to squeeze or press, and may refer to:
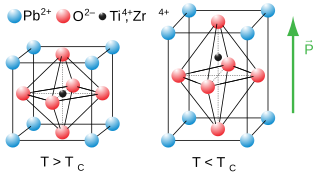
Lead zirconate titanate, also called lead zirconium titanate and commonly abbreviated as PZT, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Pb[ZrxTi1−x]O3(0 ≤ x ≤ 1).. It is a ceramic perovskite material that shows a marked piezoelectric effect, meaning that the compound changes shape when an electric field is applied. It is used in a number of practical applications such as ultrasonic transducers and piezoelectric resonators. It is a white to off-white solid.
Energy harvesting (EH) – also known as power harvesting,energy scavenging, or ambient power – is the process by which energy is derived from external sources, then stored for use by small, wireless autonomous devices, like those used in wearable electronics, condition monitoring, and wireless sensor networks.

An electronic component is any basic discrete electronic device or physical entity part of an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. Electronic components are mostly industrial products, available in a singular form and are not to be confused with electrical elements, which are conceptual abstractions representing idealized electronic components and elements. A datasheet for an electronic component is a technical document that provides detailed information about the component's specifications, characteristics, and performance. Discrete circuits are made of individual electronic components that only perform one function each as packaged, which are known as discrete components, although strictly the term discrete component refers to such a component with semiconductor material such as individual transistors.

A piezoelectric sensor is a device that uses the piezoelectric effect to measure changes in pressure, acceleration, temperature, strain, or force by converting them to an electrical charge. The prefix piezo- is Greek for 'press' or 'squeeze'.
Plasma activation is a method of surface modification employing plasma processing, which improves surface adhesion properties of many materials including metals, glass, ceramics, a broad range of polymers and textiles and even natural materials such as wood and seeds. Plasma functionalization also refers to the introduction of functional groups on the surface of exposed materials. It is widely used in industrial processes to prepare surfaces for bonding, gluing, coating and painting. Plasma processing achieves this effect through a combination of reduction of metal oxides, ultra-fine surface cleaning from organic contaminants, modification of the surface topography and deposition of functional chemical groups. Importantly, the plasma activation can be performed at atmospheric pressure using air or typical industrial gases including hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen. Thus, the surface functionalization is achieved without expensive vacuum equipment or wet chemistry, which positively affects its costs, safety and environmental impact. Fast processing speeds further facilitate numerous industrial applications.

A piezoelectric accelerometer is an accelerometer that employs the piezoelectric effect of certain materials to measure dynamic changes in mechanical variables.
A piezo switch is an electrical switch based on the piezoelectric effect.
A gas lighter is a device used to ignite a gas stove burner. It is used for gas stoves which do not have automatic ignition systems. It uses a physical phenomenon which is called the piezo-electric effect to generate an electric spark that ignites the combustible gas from the stove’s burner.

This is an alphabetized glossary of terms pertaining to lighting fires, along with their definitions. Firelighting is the process of starting a fire artificially. Fire was an essential tool in early human cultural development. The ignition of any fire, whether natural or artificial, requires completing the fire triangle, usually by initiating the combustion of a suitably flammable material.
Oxygen compatibility is the issue of compatibility of materials for service in high concentrations of oxygen. It is a critical issue in space, aircraft, medical, underwater diving and industrial applications. Aspects include effects of increased oxygen concentration on the ignition and burning of materials and components exposed to these concentrations in service.
Piezoelectric direct discharge (PDD) plasma is a type of cold non-equilibrium plasma, generated by a direct gas discharge of a high voltage piezoelectric transformer. It can be ignited in air or other gases in a wide range of pressures, including atmospheric. Due to the compactness and the efficiency of the piezoelectric transformer, this method of plasma generation is particularly compact, efficient and cheap. It enables a wide spectrum of industrial, medical and consumer applications.
A complex oxide is a chemical compound that contains oxygen and at least two other elements. Complex oxide materials are notable for their wide range of magnetic and electronic properties, such as ferromagnetism, ferroelectricity, and high-temperature superconductivity. These properties often come from their strongly correlated electrons in d or f orbitals.

A piezoelectric speaker is a loudspeaker that uses the piezoelectric effect for generating sound. The initial mechanical motion is created by applying a voltage to a piezoelectric material, and this motion is typically converted into audible sound using diaphragms and resonators. The prefix piezo- is Greek for 'press' or 'squeeze'.
This article provides information on the following six methods of producing electric power.
- Friction: Energy produced by rubbing two material together.
- Heat: Energy produced by heating the junction where two unlike metals are joined.
- Light: Energy produced by light being absorbed by photoelectric cells, or solar power.
- Chemical: Energy produced by chemical reaction in a voltaic cell, such as an electric battery.
- Pressure: Energy produced by compressing or decompressing specific crystals.
- Magnetism: Energy produced in a conductor that cuts or is cut by magnetic lines of force.
A piezoelectric microelectromechanical system (piezoMEMS) is a miniature or microscopic device that uses piezoelectricity to generate motion and carry out its tasks. It is a microelectromechanical system that takes advantage of an electrical potential that appears under mechanical stress. PiezoMEMS can be found in a variety of applications, such as switches, inkjet printer heads, sensors, micropumps, and energy harvesters.









