Related Research Articles

The Niobrara River is a tributary of the Missouri River, approximately 568 miles (914 km) long, running through the U.S. states of Wyoming and Nebraska. The river drains one of the most arid sections of the Great Plains, and has a low flow for a river of its length. The Niobrara's watershed includes the northern tier of Nebraska Sandhills, a small south-central section of South Dakota, as well as a small area of eastern Wyoming.

Elephant Butte Reservoir is a reservoir on the southern part of the Rio Grande in the U.S. state of New Mexico, 5 miles (8.0 km) north of Truth or Consequences. The reservoir is the 84th largest man-made lake in the United States and the largest in New Mexico by total surface area and peak volume. It is the only place in New Mexico that one can find pelicans perched on or alongside the lake. There are also temporary US Coast Guard bases stationed at Elephant Butte. It is impounded by Elephant Butte Dam and is part of the largest state park in New Mexico, Elephant Butte Lake State Park.

Elephant Butte Dam or Elephant Butte Dike, originally Engle Dam, is a concrete gravity dam on the Rio Grande near Truth or Consequences, New Mexico. The dam impounds Elephant Butte Reservoir, which is used mainly for agriculture but also provides for recreation, hydroelectricity, and flood and sediment control. The construction of the dam has reduced the flow of the Rio Grande to a small stream for most of the year, with water being released only during the summer irrigation season or during times of exceptionally heavy snow melt.

Jackson Lake Dam is a concrete and earth-fill dam in the western United States, at the outlet of Jackson Lake in northwestern Wyoming. The lake and dam are situated within Grand Teton National Park in Teton County. The Snake River emerges from the dam and flows about eight hundred miles (1,300 km) through Wyoming, Idaho, Oregon, and Washington to its mouth on the Columbia River in eastern Washington.

Buffalo Bill Dam is a concrete arch-gravity dam on the Shoshone River in the U.S. state of Wyoming. It is named after the famous Wild West figure William "Buffalo Bill" Cody, who founded the nearby town of Cody and owned much of the land now covered by the reservoir formed by its construction. The dam is part of the Shoshone Project, successor to several visionary schemes promoted by Cody to irrigate the Bighorn Basin and turn it from a semi-arid sagebrush-covered plain to productive agricultural land. Known at the time of its construction as Shoshone Dam, it was renamed in 1946 to honor Cody.

Fontenelle Dam was built between 1961 and 1964 on the Green River in southwestern Wyoming. The 139-foot (42 m) high zoned earthfill dam impounds the 345,360-acre-foot (0.42600 km3) Fontenelle Reservoir. The dam and reservoir are the central features of the Seedskadee Project of the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation, which manages the Fontenelle impoundment primarily as a storage reservoir for the Colorado River Storage Project. The dam suffered a significant failure in 1965, when the dam's right abutment developed a leak. Emergency releases from the dam flooded downstream properties, but repairs to the dam were successful. However, in 1983 the dam was rated "poor" under Safety Evaluation of Existing Dams (SEED) criteria, due to continuing seepage, leading to an emergency drawdown. A concrete diaphragm wall was built through the core of the dam to stop leakage.
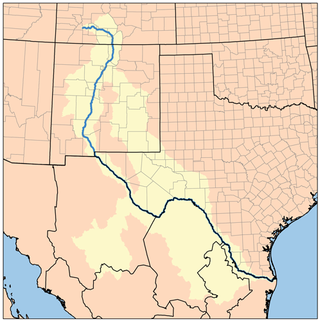
The Rio Grande Project is a United States Bureau of Reclamation irrigation, hydroelectricity, flood control, and interbasin water transfer project serving the upper Rio Grande basin in the southwestern United States. The project irrigates 193,000 acres (780 km2) along the river in the states of New Mexico and Texas. Approximately 60 percent of this land is in New Mexico. Some water is also allotted to Mexico to irrigate some 25,000 acres (100 km2) on the south side of the river. The project was authorized in 1905, but its final features were not implemented until the early 1950s.

The Minidoka Project is a series of public works by the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation to control the flow of the Snake River in Wyoming and Idaho, supplying irrigation water to farmlands in Idaho. One of the oldest Bureau of Reclamation projects in the United States, the project involves a series of dams and canals intended to store, regulate and distribute the waters of the Snake, with electric power generation as a byproduct. The water irrigates more than a million acres (4,000 km²) of otherwise arid land, producing much of Idaho's potato crop. Other crops include alfalfa, fruit and sugar beets. The primary irrigation district lies between Ashton in eastern Idaho and Bliss in the southwestern corner of the state. Five main reservoirs collect water, distributing it through 1,600 miles (2,600 km) of canals and 4,000 miles (6,400 km) of lateral distribution ditches.

Caballo Dam is an earthen dam on the Rio Grande about 15 miles (24 km) downstream from Truth or Consequences, New Mexico, United States. In conjunction with Elephant Butte Dam, which lies about 25 miles (40 km) upstream, it regulates the discharge of the river in the lower Rio Grande Valley of New Mexico. Caballo serves as an afterbay for the Elephant Butte Reservoir, i.e. it stores water released from Elephant Butte for hydroelectricity generation purposes and discharges it in the dry season to provide for irrigation agriculture downstream. The dam is an important part of the Rio Grande Project. A secondary purpose of the dam was to compensate for lost capacity in Elephant Butte Lake due to sedimentation.

Grassy Lake Dam is a small dam operated by the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation in Teton County, Wyoming, immediately to the south of Yellowstone National Park. The dam lies in a corridor of Caribou-Targhee National Forest that runs between Yellowstone and Grand Teton National Parks. The dam structure and outlets are within a few hundred feet of the south boundary of Yellowstone. The zoned earthfill dam was built between 1937 and 1939 as part of the Minidoka Project, which provides water to irrigate farmland in Idaho's Snake River Plain.

Central Oregon Irrigation District is a municipal corporation to provide irrigation water for Central Oregon, U.S. The canals serve agricultural and industrial users in the arid lands between Alfalfa, Bend, Redmond, Terrebonne, and Powell Butte. Among its 4,000 or so individual customer accounts, it also provides municipal water to the city of Redmond, neighboring subdivisions, and parks and schools in Bend. The district manages more than 700 miles (1,100 km) of canals serving about 70.3 square miles (182 km2) of lands within a rough area of 280 square miles (730 km2).

Kirwin Reservoir is a reservoir in Phillips County, Kansas, United States. It is located next to the city of Kirwin in northern Kansas. The U.S. Bureau of Reclamation built it and continues to operate it for the purposes of flood control and area irrigation. The Kirwin National Wildlife Refuge lies on its shores.

Anchor Dam is a dam in Hot Springs County, about 35 miles (56 km) west of Thermopolis, Wyoming.

Lemon Dam is an earthen dam, and is a project of the United States Bureau of Reclamation. It was completed in 1963, at 284 feet (87 m) high and 1,360 feet (410 m) long at its crest. The dam impounds the Florida River for flood control and irrigation water storage, operated by the local Florida Water Conservancy District. 120 kW of hydroelectric power is generated here.
Bull Lake Dam is a dam in Fremont County, Wyoming within the Wind River Indian Reservation.
Box Butte Dam is a dam in the arid northwestern panhandle area of Dawes County, Nebraska.

Bonny Dam is a dam in Yuma County, Colorado, in the eastern part of the state.
Stateline Dam is a dam in Summit County, Utah, less than a half-mile south of the Utah-Wyoming state line.

The Middle Rio Grande Project manages water in the Albuquerque Basin of New Mexico, United States. It includes major upgrades and extensions to the irrigation facilities built by the Middle Rio Grande Conservancy District and modifications to the channel of the Rio Grande to control sedimentation and flooding. The bulk of the work was done by the United States Bureau of Reclamation and the United States Army Corps of Engineers in the 1950s, but construction continued into the 1970s and maintenance is ongoing. The project is complementary to the San Juan–Chama Project, which transfers water from the San Juan River in the Colorado River Basin to the Rio Grande. Although distribution of water from the two projects is handled through separate allotments and contracts, there is some sharing of facilities including the river itself. The ecological impact on the river and the riparian zone was the subject of extended litigation after a group of environmentalists filed Rio Grande Silvery Minnow v. Bureau of Reclamation in 1999.
References
- ↑ "Dam details - Pilot Butte Dam". Bureau of Reclamation. Archived from the original on September 27, 2012. Retrieved September 25, 2012.
- ↑ "Pilot Butte". Archived from the original on October 11, 2012. Retrieved September 25, 2012.
- ↑ "Pilot Butte Reservoir, Wyoming".