
A lathe is a machine tool that rotates a workpiece about an axis of rotation to perform various operations such as cutting, sanding, knurling, drilling, deformation, facing, threading and turning, with tools that are applied to the workpiece to create an object with symmetry about that axis.

A drill is a tool used for making round holes or driving fasteners. It is fitted with a bit, either a drill or driver chuck. Hand-operated types are dramatically decreasing in popularity and cordless battery-powered ones proliferating due to increased efficiency and ease of use.

Taps and dies are tools used to create screw threads, which is called threading. Many are cutting tools; others are forming tools. A tap is used to cut or form the female portion of the mating pair. A die is used to cut or form the male portion of the mating pair. The process of cutting or forming threads using a tap is called tapping, whereas the process using a die is called threading.

A drill bit is a cutting tool used in a drill to remove material to create holes, almost always of circular cross-section. Drill bits come in many sizes and shapes and can create different kinds of holes in many different materials. In order to create holes drill bits are usually attached to a drill, which powers them to cut through the workpiece, typically by rotation. The drill will grasp the upper end of a bit called the shank in the chuck.

Drilling is a cutting process where a drill bit is spun to cut a hole of circular cross-section in solid materials. The drill bit is usually a rotary cutting tool, often multi-point. The bit is pressed against the work-piece and rotated at rates from hundreds to thousands of revolutions per minute. This forces the cutting edge against the work-piece, cutting off chips (swarf) from the hole as it is drilled.
A reamer is a type of rotary cutting tool used in metalworking. Precision reamers are designed to enlarge the size of a previously formed hole by a small amount but with a high degree of accuracy to leave smooth sides. There are also non-precision reamers which are used for more basic enlargement of holes or for removing burrs. The process of enlarging the hole is called reaming. There are many different types of reamer and they may be designed for use as a hand tool or in a machine tool, such as a milling machine or drill press.

A self-tapping screw is a screw that can tap its own hole as it is driven into the material. More narrowly, self-tapping is used only to describe a specific type of thread-cutting screw intended to produce a thread in relatively soft material or sheet materials, excluding wood screws. Other specific types of self-tapping screw include self-drilling screws and thread rolling screws.

A mandrel, mandril, or arbor is a tapered tool against which material can be forged, pressed, stretched or shaped, or a flanged or tapered or threaded bar that grips a workpiece to be machined in a lathe. A flanged mandrel is a parallel bar of a specific diameter with an integral flange towards one end, and threaded at the opposite end. Work is gripped between the flange and a nut on the thread. A tapered mandrel has a taper of approximately 0.005 inches per foot and is designed to hold work by being driven into an accurate hole on the work, gripping the work by friction. A threaded mandrel may have a male or female thread, and work which has an opposing thread is screwed onto the mandrel.
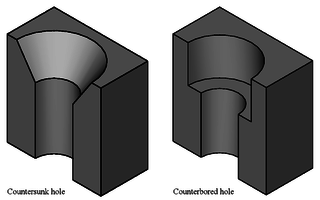
In manufacturing, a countersink is a conical hole cut into a manufactured object, or the cutter used to cut such a hole. A common use is to allow the head of a countersunk bolt, screw or rivet, when placed in the hole, to sit flush with or below the surface of the surrounding material. A countersink may also be used to remove the burr left from a drilling or tapping operation, thereby improving the finish of the product and removing any hazardous sharp edges.

A chuck is a specialized type of clamp used to hold an object with radial symmetry, especially a cylinder. In a drill, a mill and a transmission, a chuck holds the rotating tool; in a lathe, it holds the rotating workpiece.

Turning is a machining process in which a cutting tool, typically a non-rotary tool bit, describes a helix toolpath by moving more or less linearly while the workpiece rotates.

In machining, a metal lathe or metalworking lathe is a large class of lathes designed for precisely machining relatively hard materials. They were originally designed to machine metals; however, with the advent of plastics and other materials, and with their inherent versatility, they are used in a wide range of applications, and a broad range of materials. In machining jargon, where the larger context is already understood, they are usually simply called lathes, or else referred to by more-specific subtype names. These rigid machine tools remove material from a rotating workpiece via the movements of various cutting tools, such as tool bits and drill bits.

A butt joint is a wood joint in which the end of a piece of material is simply placed against another piece. The butt joint is the simplest joint. An unreinforced butt joint is also the weakest joint, as it provides a limited surface area for gluing and lacks any mechanical interlocking to resist external forces.

A hole saw, also known as a hole cutter, is a saw blade of annular (ring) shape, whose annular kerf creates a hole in the workpiece without having to cut up the core material. It is used in a drill. Hole saws typically have a pilot drill bit (arbor) at their center to keep the saw teeth from walking. The fact that a hole saw creates the hole without needing to cut up the core often makes it preferable to twist drills or spade drills for relatively large holes (especially those larger than 25 millimetres. The same hole can be made faster and using less power.
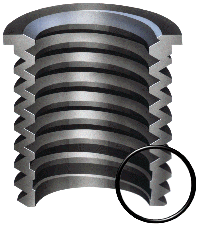
A threaded insert, also known as a threaded bushing, is a fastener element that is inserted into an object to add a threaded hole. They may be used to repair a stripped threaded hole, provide a durable threaded hole in a soft material, place a thread on a material too thin to accept it, mold or cast threads into a work piece thereby eliminating a machining operation, or simplify changeover from unified to metric threads or vice versa.

A caulkin is a blunt projection on a horseshoe or oxshoe that is often forged, welded or brazed onto the shoe. The term may also refer to traction devices screwed into the bottom of a horseshoe, also commonly called shoe studs or screw-in calks. These are usually a blunt spiked cleat, usually placed at the sides of the shoe.

A screw is an externally helical threaded fastener capable of being tightened or released by a twisting force (torque) to the head. The most common uses of screws are to hold objects together and there are many forms for a variety of materials. Screws might be inserted into holes in assembled parts or a screw may form its own thread. The difference between a screw and a bolt is that the latter is designed to be tightened or released by torquing a nut.
In manufacturing, threading is the process of creating a screw thread. More screw threads are produced each year than any other machine element. There are many methods of generating threads, including subtractive methods ; deformative or transformative methods ; additive methods ; or combinations thereof.

A screw extractor is a tool for removing broken or seized screws. There are two types: one has a spiral flute structure, commonly called an easy out after the trademarked name EZ-Out; the other has a straight flute structure.
















