
A pilot station is an onshore headquarters for maritime pilots, or a place where pilots can be hired from. To get from a pilot station to an approaching ship, pilots need to use fast vessels to arrive in time, i.e. a pilot boat.

A pilot station is an onshore headquarters for maritime pilots, or a place where pilots can be hired from. To get from a pilot station to an approaching ship, pilots need to use fast vessels to arrive in time, i.e. a pilot boat.
Historically, pilot stations would often be found on an island or other point at sea near a harbor, giving pilots ample time to transfer to an approaching boat. Two boats would rotate and operate around the clock. Pilot boats would stay at a station for up to a week. It was typical that up to six pilots would be on a boat to board incoming vessels. Pilots would be dropped off at the pilot station after bringing a boat in so they could pick up another outgoing vessel. [1]
Boats working with pilot stations were called station boats. The Cape Cod pilot station and the Boston Light were examples of pilot stations. The station boats stayed inside the line between Race Point Light to the northwest and Highland Light to the south. The Cape Cod Pilot Station was established in 1873. Pilots would have "station duty" where they were expected to patrol an area and not go beyond it. If they did, they could be reported to the Pilot Commissioner. When they were not on station boat duty they could go wherever they wanted and some went 300 miles or more from port. [2]
Modern pilot boats being much faster, most pilot stations are now on the mainland. The Ambrose Pilot Station is an example of a pilot station used today by the Sandy Hook Pilots. [3] Ships will notify the pilot station by radio when they are expected to enter the harbor. The pilot station has a radio and radar so it can talk to the captain of the ship and see the ship as it approaches. The pilot station will then send a pilot to meet the ship and guide it into the harbor. After the pilot is on board the vessel the pilot boat will return to the pilot station. [4]
Occasionally pilot station can refer to a place on the bridge of a ship where a pilot is positioned while guiding a ship, for example a pilothouse, but this use is less common.

A pilot boat is a type of boat used to transport maritime pilots between land and the inbound or outbound ships that they are piloting. Pilot boats were once sailing boats that had to be fast because the first pilot to reach the incoming ship got the business. Today, pilot boats are scheduled by telephoning the ship agents/representatives prior to arrival.

America was a 19th-century racing yacht and first winner of the America's Cup international sailing trophy.

Lightship Ambrose was the name given to multiple lightships that served as the sentinel beacon marking Ambrose Channel, New York Harbor's main shipping channel.

A maritime pilot, marine pilot, harbor pilot, port pilot, ship pilot, or simply pilot, is a mariner who has specific knowledge of an often dangerous or congested waterway, such as harbors or river mouths. Maritime pilots know local details such as depth, currents, and hazards. They board and temporarily join the crew to safely guide the ship's passage, so they must also have expertise in handling ships of all types and sizes. Obtaining the title "maritime pilot" requires being licensed or authorised by a recognised pilotage authority.

Boston Light is a lighthouse located on Little Brewster Island in outer Boston Harbor, Massachusetts. The first lighthouse to be built on the site dates back to 1716, and was the first lighthouse to be built in what is now the United States. The current lighthouse dates from 1783, is the second oldest working lighthouse in the United States, and is the only lighthouse to still be actively staffed by the United States Coast Guard, being automated in 1998 though there is still a keeper acting as tour guide. The structure was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1964.

USS Hope was a 19th-century wooden yacht schooner, designed and built in 1861 by Henry Steers for Captain Thomas B. Ives of Providence, Rhode Island. She was acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was placed into service as a gunboat assigned to support the fleet blockading the ports of the Confederate States of America. However, at times, Hope was assigned extra tasks, such as that of a dispatch boat, supply runner and salvage ship. She was a pilot boat from 1866 to 1891 and in 1891 she was replaced by the Herman Oelrichs, when the Hope was wrecked ashore the Sandy Hook Point.

Sandy Hook Pilots are licensed maritime pilots that are members of the Sandy Hook Pilots Association for the Port of New York and New Jersey, the Hudson River, and Long Island Sound. Sandy Hook pilots guide oceangoing vessels, passenger liners, freighters, and tankers in and out of the harbor. The peninsulas of Sandy Hook, and Rockaway in Lower New York Bay define the southern entrance to the port at the Atlantic Ocean.
Rock Harbor is a man-made harbor on Cape Cod Bay located on the border between Orleans, Massachusetts and Eastham, Massachusetts.

The Richard K. Fox, first named Lillie, was a 19th-century pilot boat built in 1876 for Boston Pilots. She was designed by model by Dennison J. Lawlor. She was one of the most graceful and attractive of the Boston pilot-boats and represented a trend toward deep-bodied boats. She was later sold to the New York pilots and renamed Richard K. Fox in honor of the famous sportsman and publisher of the Police Gazette. In the age of steam, she was sold in 1896 to the Marine Hospital Service.
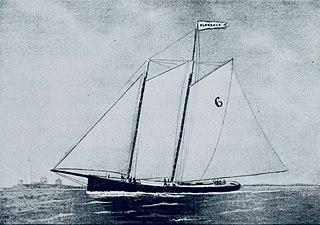
Florence was a 19th-century Boston pilot boat built in 1867 from a model by Dennison J. Lawlor for William C. Fowler. The vessel had a reputation for being fast under sail. She had a long career in the Boston service, skippered by many famous pilots. She was the oldest pilot-boat in the service. In 1897, she was sold to a Portland, Maine group for fishing and yachting excursions. The pilot boat America, No. 1, was launched on April 19, 1897, to replace the Florence.
The Mary Ann, No. 13 was a 19th-century Sandy Hook pilot boat built for the New York pilots. She helped transport maritime pilots between inbound or outbound ships coming into the New York Harbor. In 1860, the Mary Ann, was one of only twenty-one pilot boats in the New York and New Jersey fleet. She went ashore outside Sandy Hook in 1863.

The Nettle was a 19th-century Sandy Hook pilot boat built in 1844 by S. Hall of East Boston, Massachusetts for the New York Pilots. She helped transport maritime pilots between inbound or outbound ships coming into the New York Harbor. In 1868, she found the wreck of the bark Henry Trowbridge, and towed her to Sandy Hook. The Nettle, sank in 1876 in the Pensacola Bay. The sunken wreck was removed in 1878 to improve the Pensacola harbor.

The Caprice was a 19th-century Sandy Hook pilot boat built in 1871 by Brown & Lovell in East Boston, Massachusetts for Peter McEnany and other New York pilots. In 1876, she was run down and sank, off Bay Ridge, Brooklyn, by the steamship New Orleans. She was raised and was one of the pilot boats that survived the Great Blizzard of 1888. The Caprice was last reported sailing off the coast of New York in 1891.
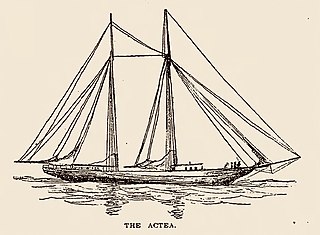
The Actaea, or Actea, was a 19th-century Boston yacht built in 1880 by Weld and David Clark of Kennebunk, Maine for David Sears, Jr., of Montgomery Sears of Boston. She was purchased by a group of New York Sandy Hook Pilots in 1890. She was one of the largest and fastest pilot boats in the fleet. In the age of steam, the Actaea was sold in 1896 to John J. Phelps of the New York Yacht Club and used as a pleasure yacht.

Edmund Blunt was a 19th-century New York pilot boat built in 1858 by Edward F. Williams for the New York Pilots. She helped transport New York City maritime pilots between inbound or outbound ships coming into the New York Harbor. She survived the Great Blizzard of 1888. In the age of steam, the Blunt along with other pilot boats, were replaced with steamboats. She was built to replace the Jacob L. Westervelt, which sank in 1857.

The Friend was a 19th-century pilot boat built by Daniel D. Kelley & Holmes East Boston shipyard in 1848 for Boston pilots. She helped transport Boston maritime pilots between inbound or outbound ships coming into the Boston Harbor. The Friend was one of the last of the low sided, straight sheared schooners built in the 1840s for Boston pilots. The second Boston pilot boat Friend was built in 1887. Her name came from the older Friend that was in the service in the late 1840s. Captain Thomas Cooper sold the Friend to New York pilots in 1893. Cooper replaced the Friend with the pilot-boat Columbia in 1894.

The Mary E. Fish was a 19th-century Sandy Hook pilot boat, built at the Edward F. Williams shipyard of Greenpoint, Brooklyn in 1861 for Richard Brown and the New York Pilots. She was built to replace the Mary Taylor. The Fish was hit and sank by the schooner Frank Harrington in 1885 and replaced by the David Carll.

The Coquette was a 19th-century yacht and pilot boat, built in 1845 by Louis Winde, at the Winde & Clinkard shipyard in Chelsea, Massachusetts for yachtsmen James A. Perkins. Her design was based on a model by shipbuilder Dennison J. Lawlor. The Coquette was a good example of an early American yacht with a clipper bow. As a yacht, she won the attention for outsailing the larger New York yacht Maria at the second New York Yacht Club regatta in 1846. Perkins sold the Coquette to the Boston Pilots' Association for pilot service in 1848. She continued as a pilot boat until 1867 when she was sold as a Blackbirder to be used on the African coast.

The Sandy Hook was a steam pilot boat built in 1902, by Lewis Nixon at the Crescent Shipyard in Elizabeth, New Jersey. In 1914, she was purchased by the New York and New Jersey Sandy Hook Pilots Association to replace the pilot boat New Jersey, that was lost in 1914. She could carry 10 to 12 pilots that would help guide ships through the New York Harbor. The Norwegian America Line Oslofjord, with the Crown Prince Olav of Norway and Princess Märtha of Sweden on board, ran into and sank the Sandy Hook in 1939.

Favorite or Favorita, was a 19th-century New York Sandy Hook pilot boat built in the early 1820s. She helped transport New York City maritime pilots between inbound or outbound ships coming into the New York Harbor. Favorite collided with a United States steamer and sank in 1865 near Barnegat Lighthouse.