
In geology and related fields, a stratum is a layer of rock or sediment characterized by certain lithologic properties or attributes that distinguish it from adjacent layers from which it is separated by visible surfaces known as either bedding surfaces or bedding planes. Prior to the publication of the International Stratigraphic Guide, older publications have defined a stratum as either being either equivalent to a single bed or composed of a number of beds; as a layer greater than 1 cm in thickness and constituting a part of a bed; or a general term that includes both bed and lamina.
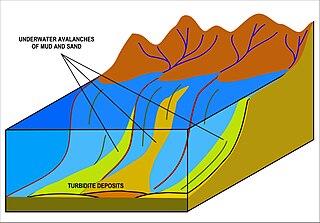
A turbidite is the geologic deposit of a turbidity current, which is a type of amalgamation of fluidal and sediment gravity flow responsible for distributing vast amounts of clastic sediment into the deep ocean.
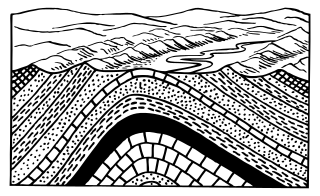
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex up in which the hinge or crest is the location where the curvature is greatest, and the limbs are the sides of the fold that dip away from the hinge. Anticlines can be recognized and differentiated from antiforms by a sequence of rock layers that become progressively older toward the center of the fold. Therefore, if age relationships between various rock strata are unknown, the term antiform should be used.
A petroleum reservoir or oil and gas reservoir is a subsurface accumulation of hydrocarbons contained in porous or fractured rock formations.
The Windermere Supergroup is a geological unit formed during the Ordovician to Silurian periods ~450 million years ago, and exposed in northwest England, including the Pennines and correlates along its strike, in the Isle of Man and Ireland, and down-dip in the Southern Uplands and Welsh Borderlands. It underlies much of north England's younger cover, extending south to East Anglia. It formed as a foreland basin, in a similar setting to the modern Ganges basin, fronting the continent of Avalonia as the remains of the attached Iapetus ocean subducted under Laurentia.
A petroleum geologist is an earth scientist who works in the field of petroleum geology, which involves all aspects of oil discovery and production. Petroleum geologists are usually linked to the actual discovery of oil and the identification of possible oil deposits, gas caps, or leads. It can be a very labor-intensive task involving several different fields of science and elaborate equipment. Petroleum geologists look at the structural and sedimentary aspects of the stratum/strata to identify possible oil traps or tight shale plays.
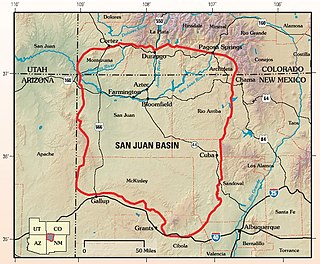
The San Juan Basin is a geologic structural basin located near the Four Corners region of the Southwestern United States. The basin covers 7,500 square miles and resides in northwestern New Mexico, southwestern Colorado, and parts of Utah and Arizona. Specifically, the basin occupies space in the San Juan, Rio Arriba, Sandoval, and McKinley counties in New Mexico, and La Plata and Archuleta counties in Colorado. The basin extends roughly 100 miles (160 km) N-S and 90 miles (140 km) E-W.

The Bend Arch–Fort Worth Basin Province is a major petroleum producing geological system which is primarily located in North Central Texas and southwestern Oklahoma. It is officially designated by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) as Province 045 and classified as the Barnett-Paleozoic Total Petroleum System (TPS).
Onlap or overlap is the geological phenomenon of successively wedge-shaped younger rock strata extending progressively further across an erosion surface cut in older rocks. It is generally associated with a marine transgression. It is a more general term than overstep, in which the younger beds overlap onto successively older beds. The opposite is offlap, in which each younger rock bed pinches out short of the full extent of the underlying older bed, typically due to a marine regression.

In petroleum geology, a trap is a geological structure affecting the reservoir rock and caprock of a petroleum system allowing the accumulation of hydrocarbons in a reservoir. Traps can be of two types: stratigraphic or structural. Structural traps are the most important type of trap as they represent the majority of the world's discovered petroleum resources.

The Marcellus Formation or the Marcellus Shale is a Middle Devonian age unit of sedimentary rock found in eastern North America. Named for a distinctive outcrop near the village of Marcellus, New York, in the United States, it extends throughout much of the Appalachian Basin.
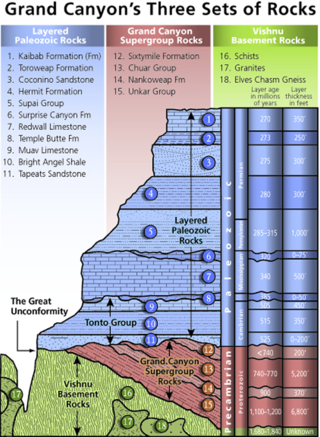
A stratigraphic column is a representation used in geology and its subfield of stratigraphy to describe the vertical location of rock units in a particular area. A typical stratigraphic column shows a sequence of sedimentary rocks, with the oldest rocks on the bottom and the youngest on top.

The Nikanassin Formation is a stratigraphic unit of Late Jurassic (Portlandian) to Early Cretaceous (Barremian) age. It is present along the western edge of the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin in western Alberta and northeastern British Columbia. Its name was first proposed by D.B. Dowling in 1909 (Coal Fields South of Grand Trunk Pacific Railway, in the foothills of the Rocky Mountain, Alberta Page 140 paragraph 4 " to this it is proposed to give the name Nikanassin, from the Cree word meaning outer range" Also it is noted on the map by D.B. Dowling.(Geological Survey of Canada. Incorrect info follows: It was named by B.R. MacKay in 1929 for the Nikanassin Range of the front-central ranges of the Canadian Rockies. Mackay did not designate a type locality for the formation, although he described outcrops near the hamlet of Brûlé, north of the Yellowhead Highway outside of Jasper National Park.

The Vaqueros Formation is a sedimentary geologic unit primarily of Upper Oligocene and Lower Miocene age, which is widespread on the California coast and coastal ranges in approximately the southern half of the state. It is predominantly a medium-grained sandstone unit, deposited in a shallow marine environment. Because of its high porosity and nearness to petroleum source rocks, in many places it is an oil-bearing unit, wherever it has been configured into structural or stratigraphic traps by folding and faulting. Being resistant to erosion, it forms dramatic outcrops in the coastal mountains. Its color ranges from grayish-green to light gray when freshly broken, and it weathers to a light brown or buff color.

The Tres Hermanos Formation is a geologic formation in central and west-central New Mexico. It contains fossils characteristic of the Turonian Age of the late Cretaceous.

The Cozy Dell Shale is a geologic formation of middle Eocene age that crops out in the Santa Ynez Mountains and Topatopa Mountains of California, extending from north of Fillmore in Ventura County westward to near Point Arguello, north of Santa Barbara. Because the Cozy Dell easily weathers to a clay-rich soil, it crops out infrequently and generally forms dense stands of chaparral in saddles between peaks and ridges of the more resistant Matilija and Coldwater formations.

The Cathedral Formation is a stratigraphic unit in the southern Canadian Rockies of Alberta and British Columbia, on the western edge of the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin. It is a thick sequence of carbonate rocks of Middle Cambrian age. It was named for Cathedral Mountain in Yoho National Park by Charles Doolittle Walcott, the discoverer of the Burgess shale fossils.

The Lewis Shale is a geologic formation in the Western United States. It preserves fossils dating back to the Campanian to Maastrichtian stages of the late Cretaceous period.

The Salitral Formation is a Late Triassic geologic formation found in north-central New Mexico, primarily the northwestern Jemez Mountains. It is an older subunit of the Chinle Group, overlying the Shinarump Conglomerate and underlying the Poleo Formation.

The West Siberian petroleum basin is the largest hydrocarbon basin in the world covering an area of about 2.2 million km², and is also the largest oil and gas producing region in Russia.

















