Related Research Articles

Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms. Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical study.
In chemistry, chemical synthesis is the artificial execution of chemical reactions to obtain one or several products. This occurs by physical and chemical manipulations usually involving one or more reactions. In modern laboratory uses, the process is reproducible and reliable.
Pyrrole is a heterocyclic, aromatic, organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula C4H4NH. It is a colorless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air. Substituted derivatives are also called pyrroles, e.g., N-methylpyrrole, C4H4NCH3. Porphobilinogen, a trisubstituted pyrrole, is the biosynthetic precursor to many natural products such as heme.
Synthesis or synthesize may refer to:
In organic chemistry, a nitrile is any organic compound that has a −C≡N functional group. The prefix cyano- is used interchangeably with the term nitrile in industrial literature. Nitriles are found in many useful compounds, including methyl cyanoacrylate, used in super glue, and nitrile rubber, a nitrile-containing polymer used in latex-free laboratory and medical gloves. Nitrile rubber is also widely used as automotive and other seals since it is resistant to fuels and oils. Organic compounds containing multiple nitrile groups are known as cyanocarbons.
In organic chemistry, the diazo group is an organic moiety consisting of two linked nitrogen atoms at the terminal position. Overall charge-neutral organic compounds containing the diazo group bound to a carbon atom are called diazo compounds or diazoalkanes and are described by the general structural formula R2C=N+=N−. The simplest example of a diazo compound is diazomethane, CH2N2. Diazo compounds should not be confused with azo compounds or with diazonium compounds.
Dimethylformamide is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NC(O)H. Commonly abbreviated as DMF (although this initialism is sometimes used for dimethylfuran, or dimethyl fumarate), this colourless liquid is miscible with water and the majority of organic liquids. DMF is a common solvent for chemical reactions. Dimethylformamide is odorless, but technical-grade or degraded samples often have a fishy smell due to impurity of dimethylamine. Dimethylamine degradation impurities can be removed by sparging samples with an inert gas such as argon or by sonicating the samples under reduced pressure. As its name indicates, it is structurally related to formamide, having two methyl groups in the place of the two hydrogens. DMF is a polar (hydrophilic) aprotic solvent with a high boiling point. It facilitates reactions that follow polar mechanisms, such as SN2 reactions.
A lactam is a cyclic amide, formally derived from an amino alkanoic acid. The term is a portmanteau of the words lactone + amide.
In organic chemistry, the Knoevenagel condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction named after German chemist Emil Knoevenagel. It is a modification of the aldol condensation.
Clemmensen reduction is a chemical reaction described as a reduction of ketones or aldehydes to alkanes using zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid (HCl). This reaction is named after Erik Christian Clemmensen, a Danish-American chemist.

The Einhorn–Brunner reaction is the designation for the chemical reaction of imides with alkyl hydrazines to form an isomeric mixture of 1,2,4-triazoles. It was initially described by the German chemist Alfred Einhorn in a paper, published in 1905, describing N-methylol compounds of amides. In 1914 chemist Karl Brunner published a paper expanding on Einhorn's research of the reaction pictured below, thus resulting in the naming as the Einhorn-Brunner. Substituted 1,2,4-triazole have been prepared from diverse imides and hydrazines.
The Friedländer synthesis is a chemical reaction of 2-aminobenzaldehydes with ketones to form quinoline derivatives. It is named after German chemist Paul Friedländer (1857–1923).
Oppenauer oxidation, named after Rupert Viktor Oppenauer, is a gentle method for selectively oxidizing secondary alcohols to ketones.

N-Phenethyl-4-piperidinone (NPP) is a derivative of 4-piperidinone with the molecular formula C13H17NO. It is used as an intermediate in the manufacture of chemicals and pharmaceutical drugs such as fentanyl.
In organic chemistry, the Claisen–Schmidt condensation is the reaction between an aldehyde or ketone having an α-hydrogen with an aromatic carbonyl compound lacking an α-hydrogen. It can be considered as a specific variation of the aldol condensation. This reaction is named after two of its pioneering investigators Rainer Ludwig Claisen and J. Gustav Schmidt, who independently published on this topic in 1880 and 1881. An example is the synthesis of dibenzylideneacetone ( -1,5-diphenylpenta-1,4-dien-3-one).

In chemistry, the haloform reaction is a chemical reaction in which a haloform is produced by the exhaustive halogenation of an acetyl group, in the presence of a base. The reaction can be used to transform acetyl groups into carboxyl groups or to produce chloroform, bromoform, or iodoform. Note that fluoroform can't be prepared in this way.
The Petrenko-Kritschenko reaction is a classic multicomponent-name reaction that is closely related to the Robinson–Schöpf tropinone synthesis, but was published 12 years earlier.

2-Piperidinone is a chemical compound classified as a lactam. It is used as an intermediate in the preparation of other chemicals.
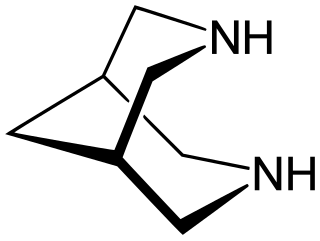
Bispidine (3,7-diazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane) is an organic compound that is classified as a bicyclic diamine. Although synthetic, it is related structurally to natural alkaloid sparteine. It is a white crystalline solid. It has been widely investigated as a chelating agent. Many derivatives are known.
References
- ↑ Petrenko-Kritschenko P, Zoneff N (March 1906). "Ueber die Condensation von Aceton‐dicarbonsäureestern mit Benzaldehyd unter Anwendung von Ammoniak". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft (in German). 39 (2): 1358–61. doi:10.1002/cber.19060390234.