Related Research Articles

Ravi Shankar was an Indian sitarist and composer. A sitar virtuoso, he became the world's best-known expert of North Indian classical music in the second half of the 20th century, and influenced many musicians in India and throughout the world. Shankar was awarded India's highest civilian honour, the Bharat Ratna, in 1999. He is also the father of American singer Norah Jones.

Carnatic music, known as Karnāṭaka saṃgīta or Karnāṭaka saṅgītam in the South Indian languages, is a system of music commonly associated with South India, including the modern Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and portions of east and south Telangana and southern Odisha. It is one of two main subgenres of Indian classical music that evolved from ancient Hindu texts and traditions, particularly the Samaveda. The other subgenre is Hindustani music, which emerged as a distinct form because of Persian or Islamic influences from Northern India. The main emphasis in Carnatic music is on vocal music; most compositions are written to be sung, and even when played on instruments, they are meant to be performed in gāyaki (singing) style.
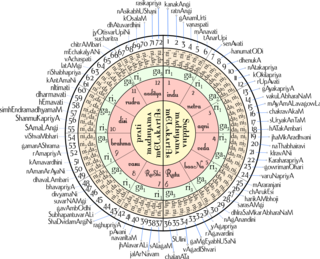
A raga is a melodic framework for improvisation in Indian classical music akin to a melodic mode. Rāga is central to classical Indian music. Each rāga consists of an array of melodic structures with musical motifs; and, from the perspective of the Indian tradition, the resulting music has the ability to "colour the mind" as it engages the emotions of the audience.

Indian Classical Music is the classical music of the Indian subcontinent. It is generally described using terms like Shastriya Sangeet and Marg Sangeet. It has two major traditions: the North Indian classical music known as Hindustani and the South Indian expression known as Carnatic. These traditions were not distinct until about the 15th century. During the period of Mughal rule of the Indian subcontinent, the traditions separated and evolved into distinct forms. Hindustani music emphasizes improvisation and exploration of all aspects of a raga, while Carnatic performances tend to be short composition-based. However, the two systems continue to have more common features than differences. Another unique classical music tradition from the eastern part of India is Odissi music, which has evolved over the last two thousand years.

Hariprasad Chaurasia is an Indian music director and classical flautist, who plays the bansuri, in the Hindustani classical tradition.
Hindustani classical music is the classical music of the Indian subcontinent's northern regions. It may also be called North Indian classical music or Uttar Bhartiya shastriya sangeet. The term shastriya sangeet literally means classical music, and is also used to refer to Indian classical music in general. It is played on instruments like the veena, sitar and sarod. It diverged in the 12th century CE from Carnatic music, the classical tradition of Southern India. While Carnatic music largely uses compositions written in Sanskrit, Kannada, Telugu, Tamil, Malayalam, Hindustani music largely uses compositions written in Hindi, Urdu, Braj, Avadhi, Bhojpuri, Bengali, Rajasthani, Marathi and Punjabi.

The shruti or śruti is the smallest interval of pitch that the human ear can detect and a singer or musical instrument can produce. The concept is found in ancient and medieval Sanskrit texts such as the Natya Shastra, the Dattilam, the Brihaddeshi, and the Sangita Ratnakara. Chandogya Upanishad speaks of the division of the octave in 22 parts.

Jasraj was an Indian classical vocalist, belonging to the Mewati gharana. His musical career spanned 75 years resulting in national and international fame, respect and numerous major awards and accolades. His legacy includes memorable performances of classical and semi-classical vocal music, classical and devotional music, albums and film soundtracks, innovations in various genres including Haveli Sangeeth and popularizing the Mewati Gharana – a school of thought in Hindustani classical music. Pandit Jasraj taught music to amateur and professional students in India, Europe, Canada and the United States.

Pandit Nikhil Ranjan Banerjee was an Indian classical sitarist of the Maihar Gharana. Along with Pandit Ravi Shankar and Ustad Vilayat Khan, he emerged as one of the leading exponents of the sitar. He was a recipient of the Indian civilian honour of the Padma Bhushan.

Ustad Amjad Ali Khan is an Indian classical sarod player, best known for his clear and fast ekhara taans. Khan was born into a classical musical family and has performed internationally since the 1960s. He was awarded India's second highest civilian honor Padma Vibhushan in 2001, India's third highest civilian honor Padma Bhushan in 1991 and Padma Shree in 1975.

Kambhoji or Kambodhi is a popular Raga in Carnatic Music. It is classified as a derived raga from 28th Melakartha, Harikambhoji, and has existed since the 7th century.

Pandit Vishnu Narayan Bhatkhande was an Indian musicologist who wrote the first modern treatise on Hindustani classical music, an art which had been propagated for centuries mostly through oral traditions. During those earlier times, the art had undergone several changes, rendering the raga grammar documented in scant old outdated texts.

Aashish Khan Debsharma is an Indian classical musician, a player of the sarod. He was nominated for a Grammy Award in 2006 for the 'Best Traditional World Music Album' category for his album "Golden Strings of the Sarode". He is also a recipient of the Sangeet Natak Akademi Award. Besides being a performer, composer, and conductor, he is also an adjunct professor of Indian classical music at the California Institute of the Arts, and the University of California at Santa Cruz, in the United States.
Shree is a very old North Indian raga of the Purvi thaat, and has traditionally been associated with Laxmi. It also appears in the Sikh tradition from northern India, and is a part of the Guru Granth Sahib, the holy text of the Sikhs. The Guru Granth Sahib composition comprises 31 ragas where Shree is the first raga to appear. The raga appears first on 14th page of the composition.

The Gundecha Brothers are Indian classical singers of the dhrupad genre of the Dagar vani. From 1985 to 2019 the duo consisted of brothers Umakant Gundecha and Ramakant Gundecha and were awarded the Padma Shri for art for 2012. Following the death of Ramakant Gundecha in 2019, his son Anant began to perform with Umakant in the Gundecha bandhu.

Raga is a 1971 documentary film about the life and music of Indian sitarist Ravi Shankar, produced and directed by Howard Worth. It includes scenes featuring Western musicians Yehudi Menuhin and George Harrison, as well as footage of Shankar returning to Maihar in central India, where as a young man he trained under the mentorship of Allauddin Khan. The film also features a portion of Shankar and tabla player Alla Rakha's acclaimed performance at the 1967 Monterey Pop Festival.
Pandit Ulhas Kashalkar is a Hindustani classical vocalist. He has received training in the Gwalior, Jaipur and Agra gharanas, and is considered one of the finest representative of all three schools.

Rajeev Taranath was an Indian classical musician who played the sarod. Taranath was a disciple of Ali Akbar Khan.

Pandit Manilal Nag is an Indian classical sitar player and an exponent of the Bishnupur gharana of Bengal. He was given the Padma Shri Award, the fourth highest civilian award in India in 2020.

Annavarapu Rama Swamy is an Indian classical violinist from Andhra Pradesh, India.
References
- ↑ Ramakrishnan, M. V. (5 March 2010). "Well done, Superbna!". The Hindu.
- ↑ "Music of Ragas as Expression of Mysticism and Devotion - Times of India". The Times of India . Archived from the original on 4 November 2012. Retrieved 17 January 2022.