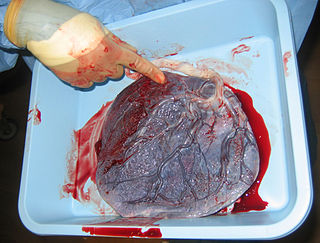
The placenta is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas and waste exchange between the physically separate maternal and fetal circulations, and is an important endocrine organ, producing hormones that regulate both maternal and fetal physiology during pregnancy. The placenta connects to the fetus via the umbilical cord, and on the opposite aspect to the maternal uterus in a species-dependent manner. In humans, a thin layer of maternal decidual (endometrial) tissue comes away with the placenta when it is expelled from the uterus following birth. Placentas are a defining characteristic of placental mammals, but are also found in marsupials and some non-mammals with varying levels of development.

Chorionic villus sampling (CVS), sometimes called "chorionic villous sampling", is a form of prenatal diagnosis done to determine chromosomal or genetic disorders in the fetus. It entails sampling of the chorionic villus and testing it for chromosomal abnormalities, usually with FISH or PCR. CVS usually takes place at 10–12 weeks' gestation, earlier than amniocentesis or percutaneous umbilical cord blood sampling. It is the preferred technique before 15 weeks.

Gestational hypertension or pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH) is the development of new hypertension in a pregnant woman after 20 weeks' gestation without the presence of protein in the urine or other signs of pre-eclampsia. Gestational hypertension is defined as having a blood pressure greater than 140/90 on two occasions at least 6 hours apart.

The trophoblast is the outer layer of cells of the blastocyst. Trophoblasts are present four days after fertilization in humans. They provide nutrients to the embryo and develop into a large part of the placenta. They form during the first stage of pregnancy and are the first cells to differentiate from the fertilized egg to become extraembryonic structures that do not directly contribute to the embryo. After blastulation, the trophoblast is contiguous with the ectoderm of the embryo and is referred to as the trophectoderm. After the first differentiation, the cells in the human embryo lose their totipotency because they can no longer form a trophoblast. They become pluripotent stem cells.

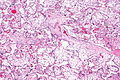
Choriocarcinoma is a malignant, trophoblastic cancer, usually of the placenta. It is characterized by early hematogenous spread to the lungs. It belongs to the malignant end of the spectrum in gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD). It is also classified as a germ cell tumor and may arise in the testis or ovary.
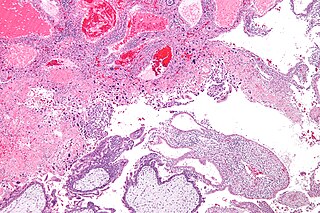
Gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) is a term used for a group of pregnancy-related tumours. These tumours are rare, and they appear when cells in the womb start to proliferate uncontrollably. The cells that form gestational trophoblastic tumours are called trophoblasts and come from tissue that grows to form the placenta during pregnancy.

Intrauterine hypoxia occurs when the fetus is deprived of an adequate supply of oxygen. It may be due to a variety of reasons such as prolapse or occlusion of the umbilical cord, placental infarction, maternal diabetes and maternal smoking. Intrauterine growth restriction may cause or be the result of hypoxia. Intrauterine hypoxia can cause cellular damage that occurs within the central nervous system. This results in an increased mortality rate, including an increased risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). Oxygen deprivation in the fetus and neonate have been implicated as either a primary or as a contributing risk factor in numerous neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders such as epilepsy, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, eating disorders and cerebral palsy.

Human placental lactogen (hPL), also called human chorionic somatomammotropin (hCS) or human chorionic somatotropin, is a polypeptide placental hormone, the human form of placental lactogen. Its structure and function are similar to those of human growth hormone. It modifies the metabolic state of the mother during pregnancy to facilitate energy supply to the fetus. hPL has anti-insulin properties. hPL is a hormone secreted by the syncytiotrophoblast during pregnancy. Like human growth hormone, hPL is encoded by genes on chromosome 17q22-24. It was identified in 1963.

"Cytotrophoblast" is the name given to both the inner layer of the trophoblast or the cells that live there. It is interior to the syncytiotrophoblast and external to the wall of the blastocyst in a developing embryo.
Hofbauer cells are oval eosinophilic histiocytes with granules and vacuoles found in the placenta, which are of mesenchymal origin, in mesoderm of the chorionic villus, particularly numerous in early pregnancy.

Velamentous cord insertion is a complication of pregnancy where the umbilical cord is inserted in the fetal membranes. It is a major cause of antepartum hemorrhage that leads to loss of fetal blood and associated with high perinatal mortality. In normal pregnancies, the umbilical cord inserts into the middle of the placental mass and is completely encased by the amniotic sac. The vessels are hence normally protected by Wharton's jelly, which prevents rupture during pregnancy and labor. In velamentous cord insertion, the vessels of the umbilical cord are improperly inserted in the chorioamniotic membrane, and hence the vessels traverse between the amnion and the chorion towards the placenta. Without Wharton's jelly protecting the vessels, the exposed vessels are susceptible to compression and rupture.

A placental disease is any disease, disorder, or pathology of the placenta.

Placentitis is an inflammation of the placenta. The main forms of placentitis are:
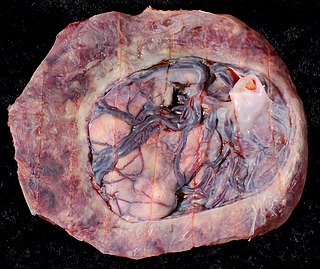
Circumvallate placenta is a rare condition affecting about 1-2% of pregnancies, in which the amnion and chorion fetal membranes essentially "double back" on the fetal side around the edges of the placenta. After delivery, a circumvallate placenta has a thick ring of membranes on its fetal surface. Circumvallate placenta is a placental morphological abnormality associated with increased fetal morbidity and mortality due to the restricted availability of nutrients and oxygen to the developing fetus.
Theca lutein cyst is a type of bilateral functional ovarian cyst filled with clear, straw-colored fluid. These cysts result from exaggerated physiological stimulation due to elevated levels of beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (beta-hCG) or hypersensitivity to beta-hCG. On ultrasound and MRI, theca lutein cysts appear in multiples on ovaries that are enlarged.

Intermediate trophoblast is a distinct subtype of trophoblastic tissue that arises from the cytotrophoblast.

Chorangiosis is a placental pathology characterized by an abundance of blood vessels within the chorionic villi.
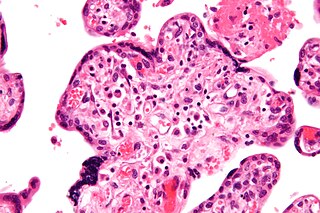
Villitis of unknown etiology (VUE), also known as chronic villitis, is a placental injury. VUE is an inflammatory condition involving the chorionic villi. VUE is a recurrent condition and can be associated with intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR). IUGR involves the poor growth of the foetus, stillbirth, miscarriage, and premature delivery. VUE recurs in about 1/3 of subsequent pregnancies.

A placental infarction results from the interruption of blood supply to a part of the placenta, causing its cells to die.
Massive perivillous fibrin deposition refers to excessive deposition of fibrous tissue around the chorionic villi of the placenta. It causes reduced growth of the foetus, and leads to miscarriage in nearly 1 in 3 pregnancies affected. There are typically no symptoms, and it is rarely detected before birth. The cause is unknown, but may be autoimmune. Diagnosis is based on the histology of the placenta. There are currently no known treatments. MPFD is very rare, but recurrence is around 18% in those affected.