
Prairies are ecosystems considered part of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome by ecologists, based on similar temperate climates, moderate rainfall, and a composition of grasses, herbs, and shrubs, rather than trees, as the dominant vegetation type. Temperate grassland regions include the Pampas of Argentina, Brazil and Uruguay, and the steppe of Ukraine, Russia and Kazakhstan. Lands typically referred to as "prairie" tend to be in North America. The term encompasses the area referred to as the Interior Lowlands of Canada, the United States, and Mexico, which includes all of the Great Plains as well as the wetter, hillier land to the east.

Agronomy is the science and technology of producing and using plants in agriculture for food, fuel, fiber, recreation, and land restoration. Agronomy has come to encompass work in the areas of plant genetics, plant physiology, meteorology, and soil science. It is the application of a combination of sciences like biology, chemistry, economics, ecology, earth science, and genetics. Professionals in the field of agronomy are called agronomists.

The Corn Belt is a region of the Midwestern United States that, since the 1850s, has dominated corn production in the United States. In the United States, "corn" is the common word for "maize". More generally, the concept of the "Corn Belt" connotes the area of the Midwest dominated by farming and agriculture.

The Texas Blackland Prairies are a temperate grassland ecoregion located in Texas that runs roughly 300 miles (480 km) from the Red River in North Texas to San Antonio in the south. The prairie was named after its rich, dark soil.

Corn stover consists of the leaves, stalks, and cobs of maize (corn) plants left in a field after harvest. Such stover makes up about half of the yield of a corn crop and is similar to straw from other cereal grasses; in Britain it is sometimes called corn straw. Corn stover is a very common agricultural product in areas of large amounts of corn production. As well as the non-grain part of harvested corn, the stover can also contain other weeds and grasses. Field corn and sweet corn, two different types of maize, have relatively similar corn stover.

The Finger Lakes National Forest is a United States National Forest that encompasses 16,259 acres (65.80 km2) of Seneca and Schuyler counties, nestled between Seneca Lake and Cayuga Lake in the Finger Lakes Region of the State of New York. It has over 30 miles (50 km) of interconnecting trails that traverse gorges, ravines, pastures, and woodlands.

Originally mapped in Cecil County, Maryland in 1899, more than 10 million acres (40,000 km²) of the Cecil soil series are now mapped in the Piedmont region of the southeastern United States. It extends from Virginia through North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia and Alabama, with the typic Cecil pedon actually located in Franklin County, NC.

Rain gardens, also called bioretention facilities, are one of a variety of practices designed to treat polluted stormwater runoff. Rain gardens are designed landscape sites that reduce the flow rate, total quantity, and pollutant load of runoff from impervious urban areas like roofs, driveways, walkways, parking lots, and compacted lawn areas. Rain gardens rely on plants and natural or engineered soil medium to retain stormwater and increase the lag time of infiltration, while remediating and filtering pollutants carried by urban runoff. Rain gardens provide a method to reuse and optimize any rain that falls, reducing or avoiding the need for additional irrigation. A benefit of planting rain gardens is the consequential decrease in ambient air and water temperature, a mitigation that is especially effective in urban areas containing an abundance of impervious surfaces that absorb heat in a phenomenon known as the heat-island effect.

The Yazoo National Wildlife Refuge is a 12,941 acre (52.4 km2) National Wildlife Refuge located in Washington County, Mississippi. Named after the Yazoo tribe, it was established to provide waterfowl and other migratory birds in the Mississippi Flyway with nesting, feeding, brooding, and resting habitat.

San Joaquin is an officially designated state insignia, the state soil of the U.S. state of California.
Narragansett soils are loamy soils occurring in the northeastern United States. It is the state soil of Rhode Island.

Antigo soils are among the most extensive soils in Wisconsin. They occur on about 300,000 acres (1,200 km²) in the northern part of the State. Antigo soils are well-drained and formed under northern hardwood forests in loess and loamy sediments over stratified sandy outwash. The average annual precipitation ranges from 28 to 33 inches, and the average annual air temperature ranges from 39 to 45 °F. The soil series was named after the city of Antigo, Wisconsin.
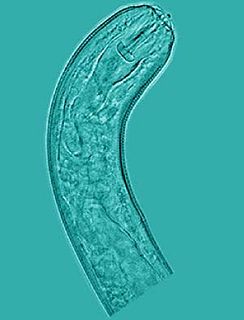
Pratylenchus is a genus of nematodes known commonly as lesion nematodes. They are parasitic on plants and are responsible for root lesion disease on many taxa of host plants in temperate regions around the world. Lesion nematodes are migratory endoparasites that feed and reproduce in the root and move around, unlike the cyst or root-knot nematodes, which may stay in one place. They usually only feed on the cortex of the root. Species are distinguished primarily by the morphology of the stylets.
Blandford soil series is the name given to a loam or sandy loam soil which has developed on glacial till in parts of southern Quebec and northern New England. It belongs to the brown podzolic soil group and occurs in hilly areas of the Green Mountains in Vermont plus the adjoining Sutton Mountains in Quebec. In recent years the USDA has deactivated this series, which remains on active status in Canada.
Berkshire soil series is the name given to a well-drained loam or sandy loam soil which has developed on glacial till in parts of southern Quebec, eastern New York State and New England south to Massachusetts. It belongs to the podzol soil group and is one of the most important soils in its area of occurrence, supporting extensive forests and a fair number of farms. Many Berkshire soils lack the eluvial (E) horizon characteristic of podzols because they have a history of being cleared for cultivation.

Viruá National Park is a national park in the state of Roraima, Brazil. It protects an area with very infertile sandy soil, periodically flooded, that has no economic value but has exceptionally high biodiversity.

The Lost Forest Research Natural Area is a designated forest created by the Bureau of Land Management to protect an ancient stand of ponderosa pine in the remote high desert county of northern Lake County, in the south central area of the U.S. state of Oregon. Lost Forest is an isolated area of pine trees separated from the nearest contiguous forest land by forty miles of arid desert. There are no springs or surface water in Lost Forest, and much of the southwest portion of the natural area is covered by large shifting sand dunes that are slowly encroaching on the forest.

Hagerman National Wildlife Refuge (HNWR), a haven for migratory birds and other wildlife, lies in northwestern Grayson County, Texas, on the Big Mineral Arm of Lake Texoma, on the Red River between Oklahoma and Texas. This National Wildlife Refuge is made up of water, marsh, and upland habitat. Visitors can hike, observe wildlife, hunt, and fish throughout the year.

The Mississippi Alluvial Plain is a Level III ecoregion designated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in seven U.S. states, though predominantly in Arkansas, Louisiana, and Mississippi. It parallels the Mississippi River from the Midwestern United States to the Gulf of Mexico.
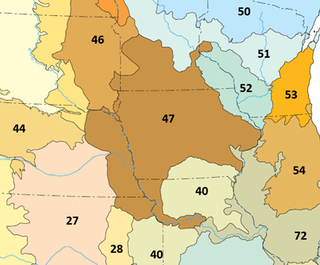
The Western Corn Belt Plains is a Level III ecoregion designated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in seven U.S. states, though predominantly in Iowa.