
A plan-relief (French pronunciation: [plɑ̃ʁəljɛf] ) is a scale model of a landscape and buildings produced for military usage, made to visualize building projects on fortifications or campaigns surrounding fortified locations.

A plan-relief (French pronunciation: [plɑ̃ʁəljɛf] ) is a scale model of a landscape and buildings produced for military usage, made to visualize building projects on fortifications or campaigns surrounding fortified locations.
The first examples seem to have been used by the Venetian Republic and more generally by the Italian city-states of the Renaissance era. The wood turner Jakob Sandtner (fl. 1561-1579) produced plans-relief of many Bavarian towns, whilst in France Louis XIV's war minister Louvois initiated a collection of plans-relief of French strongholds on a 1:600 scale in 1688. This collection included 144 examples according to Vauban's 1697 inventory of it and was put on a show at the Palais des Tuileries. Vauban's successors expanded the collection as and when operational necessity demanded, right up until 1870 when they were rendered obsolete by advances in the power of artillery. Some examples from this collection were destroyed and as a whole, it fell into disrepair until being made a Monument historique on 22 July 1927. One hundred examples from this collection survive, of which most are on show in the Museum of Plans-reliefs at Les Invalides and some others in the Palais des Beaux-Arts de Lille, still providing a witness to the towns and fortresses of France at this era.
After the success of the panorama painting, a spin-off of the plan-relief called the "panstereorama" emerged, this time for popular rather than military use. It was designed to offer an approximation of a balloon ride over a given city. No known models survive. [1]

Strasbourg is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France, in the historic region of Alsace. It is the prefecture of the Bas-Rhin department and the official seat of the European Parliament.

Toulon is a city on the French Riviera, famous for its 1793 siege, and a large port on the Mediterranean coast, with a major naval base. Located in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region, and the Provence province, Toulon is the prefecture of the Var department.

Sébastien Le Prestre, seigneur de Vauban, later styling himself as the marquis de Vauban, commonly referred to as Vauban, was a French military engineer and Marshal of France who worked under Louis XIV. He is generally considered the greatest engineer of his time, and one of the most important in European military history.

The Hôtel des Invalides, commonly called Les Invalides, is a complex of buildings in the 7th arrondissement of Paris, France, containing museums and monuments, all relating to the military history of France, as well as a hospital and an Old Soldiers' retirement home, the building's original purpose. The buildings house the Musée de l'Armée, the museum of the Army of France, the Musée des Plans-Reliefs, and the Musée d'Histoire Contemporaine. The complex also includes the Cathedral of Saint-Louis-des-Invalides, the national cathedral of the French military. It is adjacent to the Royal Chapel known as the Dôme des Invalides, the tallest church building in Paris at a height of 107 meters. The latter has been converted into a shrine to some of France's leading military figures, most notably the tomb of Napoleon.

Besançon is the prefecture of the department of Doubs in the region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté. The city is located in Eastern France, close to the Jura Mountains and the border with Switzerland.

The Exposition Universelle of 1900, better known in English as the 1900 Paris Exposition, was a world's fair held in Paris, France, from 14 April to 12 November 1900, to celebrate the achievements of the past century and to accelerate development into the next. It was the sixth of ten major expositions held in the city between 1855 and 1937. It was held at the esplanade of Les Invalides, the Champ de Mars, the Trocadéro and at the banks of the Seine between them, with an additional section in the Bois de Vincennes, and it was visited by more than fifty million people. Many international congresses and other events were held within the framework of the exposition, including the 1900 Summer Olympics.

The Palais Bourbon is the meeting place of the National Assembly, the lower legislative chamber of the French Parliament. It is in the 7th arrondissement of Paris, on the Rive Gauche of the Seine across from the Place de la Concorde.

The Grand Palais des Champs-Élysées, commonly known as the Grand Palais, is a historic site, exhibition hall and museum complex located in the 8th arrondissement of Paris between the Champs-Élysées and the Seine, France. Construction of the Grand Palais began in 1897 following the demolition of the Palais de l'Industrie to prepare for the Universal Exposition of 1900. That exposition also produced the adjacent Petit Palais and Pont Alexandre III.

The Petit Palais is an art museum in the 8th arrondissement of Paris, France.

Blaye is a commune and subprefecture in the Gironde department in Nouvelle-Aquitaine in southwestern France. For centuries, Blaye was a particularly convenient crossing point for those who came from the north and went to Bordeaux or further south, to Spain and Portugal. Fortified since antiquity, this eminently strategic site located on the bank of a large river, was modernized at the end of the 17th century, thanks to Vauban. In 1685, the Commissaire general des fortifications of Louis XIV proposed the construction of a real lock on the Gironde in order to "take control of the river" and to hold Bordeaux in case of a revolt. It is then that the citadel of Blaye was built, constituting the major element of the estuary control system. Dominating the urban landscape, this imposing building has been listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 2008, as part of a group of structures engineered by Vauban, in testimony to their global influence on military architecture and planning over the next few centuries.

Entrevaux is a commune (municipality), former episcopal seat and Latin Catholic titular see in the Alpes-de-Haute-Provence department in southeastern France. It is a member of Les Plus Beaux Villages de France Association.

Neuf-Brisach is a fortified town and commune of the department of Haut-Rhin in the French region of Alsace. The fortified town was intended to guard the border between France and the Holy Roman Empire and, subsequently, the German states. It was built after the Treaty of Ryswick in 1697 that resulted in France losing the town of Breisach, on the opposite bank of the Rhine. The town's name means New Breisach.

The Musée de l'Armée is a national military museum of France located at Les Invalides in the 7th arrondissement of Paris. It is served by Paris Métro stations Invalides, Varenne and La Tour-Maubourg

An architectural model is a type of scale model made to study aspects of an architectural design or to communicate design intent. They are made using a variety of materials including paper, plaster, plastic, resin, wood, glass, and metal.

The Palais des Beaux-Arts de Lille is a municipal museum dedicated to fine arts, modern art, and antiquities located in Lille. It is one of the largest art museums in France.
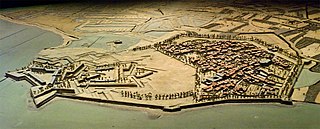
The Musée des Plans-Reliefs is a museum of military models located within the Hôtel des Invalides in the 7th arrondissement of Paris, France.

The Fortifications of Vauban is a UNESCO World Heritage Site made up of 12 groups of fortified buildings and sites along the borders of France. They were designed by renowned military architect Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban (1633–1707) during the reign of King Louis XIV. These sites include a variety of fortifications, ranging from citadels, to mountain batteries and sea fortifications, to bastion walls and towers. In addition, the site includes cities built from scratch by Vauban and communication towers. These sites were chosen because they exemplify Vauban's work, bearing witness to the influence of his designs on military and civilian engineering on a global scale from the 17th century to the 20th century.

The Museum of Fine Arts of Lyon is a municipal museum of fine arts in the French city of Lyon. Located near the Place des Terreaux, it is housed in a former Benedictine convent which was active during the 17th and 18th centuries. It was restored between 1988, and 1998, remaining open to visitors throughout this time despite the ongoing restoration works. Its collections range from ancient Egyptian antiquities to the Modern art period, making the museum one of the most important in Europe. It also hosts important exhibitions of art, for example the exhibitions of works by Georges Braque and Henri Laurens in the second half of 2005, and another on the work of Théodore Géricault from April to July 2006. It is one of the largest art museums in France.

The Citadel of Besançon is a 17th-century fortress in Franche-Comté, France. It is one of the finest masterpieces of military architecture designed by Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban. The Citadel occupies 11 hectares on Mount Saint-Etienne, one of the seven hills that protect Besançon, the capital of Franche-Comté. Mount Saint-Etienne occupies the neck of an oxbow formed by the river Doubs, giving the site a strategic importance that Julius Caesar recognised as early as 58 BC. The Citadel overlooks the old quarter of the city, which is located within the oxbow, and has views of the city and its surroundings.

The Fort du Randouillet, is a fortification in the vicinity of Briançon in the Dauphiné region of southeastern France. Briançon was surveyed by Vauban in 1692. His master plan for the defenses of the city would result in one of the most heavily fortified locales in France over the next forty years. Constructed to Vauban's plan between 1724 and 1734, the site was chosen to protect the lower Fort des Têtes from an enemy on the heights. The position was used by the French Army in the defense of Briançon until 1940, when it was part of the Fortified Sector of the Dauphiné.