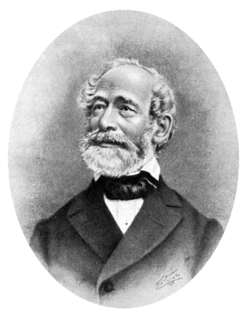A planetarium is a theatre built primarily for presenting educational and entertaining shows about astronomy and the night sky, or for training in celestial navigation.

Jena is a German city and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and Weimar, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 inhabitants, while the city itself has a population of about 110,000. Jena is a centre of education and research; the Friedrich Schiller University was founded in 1558 and had 18,000 students in 2017 and the Ernst-Abbe-Fachhochschule Jena counts another 5,000 students. Furthermore, there are many institutes of the leading German research societies.
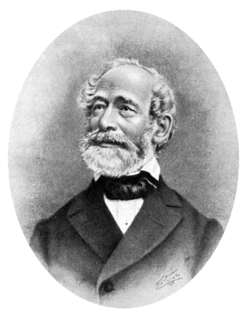
Carl Zeiss was a German scientific instrument maker, optician and businessman. In 1846 he founded his workshop, which is still in business as Carl Zeiss AG. Zeiss gathered a group of gifted practical and theoretical opticians and glass makers to reshape most aspects of optical instrument production. His collaboration with Ernst Abbe revolutionized optical theory and practical design of microscopes. Their quest to extend these advances brought Otto Schott into the enterprises to revolutionize optical glass manufacture. The firm of Carl Zeiss grew to one of the largest and most respected optical firms in the world.

Carl Zeiss AG, branded as ZEISS, is a German manufacturer of optical systems and optoelectronics, founded in Jena, Germany in 1846 by optician Carl Zeiss. Together with Ernst Abbe and Otto Schott he laid the foundation for today's multi-national company. The current company emerged from a reunification of Carl Zeiss companies in East and West Germany with a consolidation phase in the 1990s. ZEISS is active in four business segments with approximately equal revenue, Industrial Quality and Research, Medical Technology, Consumer Markets and Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology in almost 50 countries, has 30 production sites and around 25 development sites worldwide.

Ernst Karl Abbe HonFRMS was a German physicist, optical scientist, entrepreneur, and social reformer. Together with Otto Schott and Carl Zeiss, he developed numerous optical instruments. He was also a co-owner of Carl Zeiss AG, a German manufacturer of scientific microscopes, astronomical telescopes, planetariums, and other advanced optical systems.

Schott AG is a German multinational glass company specializing in the manufacture of glass and glass-ceramics. Headquartered in Mainz, Germany, it is owned by the Carl Zeiss Foundation. The company's founder and namesake, Otto Schott, is credited with the invention of borosilicate glass.

The JenTower is a skyscraper in Jena, Germany.

FC Carl Zeiss Jena is a German football club based in Jena, Thuringia. Formed in 1903 and initially associated with the Carl Zeiss AG factory, they were one of the strongest clubs in East Germany from the 1960s to the 1980s, winning the DDR-Oberliga and the FDGB-Pokal three times each and reaching the 1981 European Cup Winners' Cup Final. Since German reunification in 1990, the club have competed no higher than the second tier. In the 2020–21 season, Jena played in the Regionalliga Nordost.
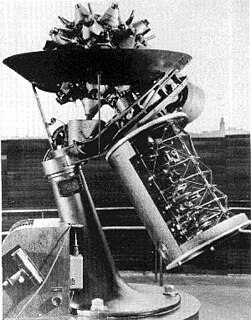
A Zeiss projector is one of a line of planetarium projectors manufactured by the Carl Zeiss Company.

The Deutsches Optisches Museum Jena is a science and technology museum displaying optical instruments from eight centuries. It gives a technical and cultural-historical survey of the development of optical instruments. The development of the city Jena to the centre of the optical industries since the mid-19th-century is integrated in the exhibition, connected with the lifeworks of Ernst Abbe, Carl Zeiss and Otto Schott.

A planetarium projector, also known as a star projector, is a device used to project images of celestial objects onto the dome in a planetarium.

Walther Bauersfeld was a German engineer.

Franz Dischinger was a pioneering German civil and structural engineer, responsible for the development of the modern cable-stayed bridge. He was also a pioneer of the use of prestressed concrete, patenting the technique of external prestressing in 1934.

The Drebach Observatory is a planetarium and astronomical observatory (obs. code: 113) located in the municipality of Drebach, in Saxony, Germany. The planetarium uses a ZKP-3 Skymaster Zeiss projector. The observatory is equipped with a 50-centimetre Cassegrain reflector.
Bryan-Gooding Planetarium in the Alexander Brest Science Theatre is a planetarium in the Museum of Science and History in Jacksonville, Florida, U.S. It was built in 1988 and featured a 60-foot-diameter (18 m) dome-shaped projection screen, JBL stereo sound system, and a Zeiss Jena Optical mechanical planetarium star projector. The facility has seating for 200, and approximately 60,000 people see a planetarium show each year.

The Planetarium of the Royal Observatory of Belgium is a Belgian planetarium on the Heysel Plateau in Brussels and part of the institutions of the Belgian Federal Science Policy Office.
Zeiss or Zeiß may refer to:
Seiler Instrument & Mfg. Co. is a full service contract manufacturer specializing in optical fire control equipment as well as a major distributor of surveying software and instruments, microscopes, and Zeiss planetariums. There are several main divisions within the company which include Manufacturing, Geospatial-Survey, Medical, Seiler Design Solutions, LLC., and Planetarium. The company is headquartered in St. Louis, Missouri with Geospatial-Survey sales offices located in Kansas City, Illinois, Nebraska, Indiana, Michigan, and Wisconsin.

The Buhl Planetarium and Institute of Popular Science Building, also known as the "People's Observatory", is located at 10 Children's Way in the Allegheny Center neighborhood of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.

The Zeiss Major Planetarium is a planetarium in Berlin and one of the largest modern stellar theatres in Europe. It was opened in 1987 on the borders of the Ernst-Thälmann-Park housing estates in the Prenzlauer Berg locality of Berlin.