
Electrical discharge machining (EDM), also known as spark machining, spark eroding, die sinking, wire burning or wire erosion, is a metal fabrication process whereby a desired shape is obtained by using electrical discharges (sparks). Material is removed from the work piece by a series of rapidly recurring current discharges between two electrodes, separated by a dielectric liquid and subject to an electric voltage. One of the electrodes is called the tool-electrode, or simply the tool or electrode, while the other is called the workpiece-electrode, or work piece. The process depends upon the tool and work piece not making physical contact.

A spark gap consists of an arrangement of two conducting electrodes separated by a gap usually filled with a gas such as air, designed to allow an electric spark to pass between the conductors. When the potential difference between the conductors exceeds the breakdown voltage of the gas within the gap, a spark forms, ionizing the gas and drastically reducing its electrical resistance. An electric current then flows until the path of ionized gas is broken or the current reduces below a minimum value called the "holding current". This usually happens when the voltage drops, but in some cases occurs when the heated gas rises, stretching out and then breaking the filament of ionized gas. Usually, the action of ionizing the gas is violent and disruptive, often leading to sound, light and heat.
The multipactor effect is a phenomenon in radio-frequency (RF) amplifier vacuum tubes and waveguides, where, under certain conditions, secondary electron emission in resonance with an alternating electric field leads to exponential electron multiplication, possibly damaging and even destroying the RF device.
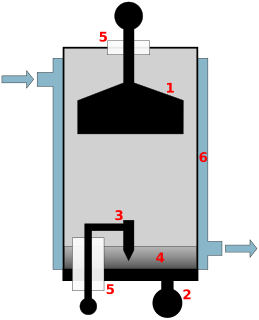
An ignitron is a type of gas-filled tube used as a controlled rectifier and dating from the 1930s. Invented by Joseph Slepian while employed by Westinghouse, Westinghouse was the original manufacturer and owned trademark rights to the name "Ignitron". Ignitrons are closely related to mercury-arc valves but differ in the way the arc is ignited. They function similarly to thyratrons; a triggering pulse to the igniter electrode turns the device "on", allowing a high current to flow between the cathode and anode electrodes. After it is turned on, the current through the anode must be reduced to zero to restore the device to its nonconducting state. They are used to switch high currents in heavy industrial applications.

Electrical breakdown or dielectric breakdown is a process that occurs when an electrical insulating material, subjected to a high enough voltage, suddenly becomes an electrical conductor and electric current flows through it. All insulating materials undergo breakdown when the electric field caused by an applied voltage exceeds the material's dielectric strength. The voltage at which a given insulating object becomes conductive is called its breakdown voltage and depends on its size and shape. Under sufficient electrical potential, electrical breakdown can occur within solids, liquids, gases or vacuum. However, the specific breakdown mechanisms are different for each kind of dielectric medium.

An electric arc, or arc discharge, is an electrical breakdown of a gas that produces a prolonged electrical discharge. The current through a normally nonconductive medium such as air produces a plasma; the plasma may produce visible light. An arc discharge is characterized by a lower voltage than a glow discharge and relies on thermionic emission of electrons from the electrodes supporting the arc. An archaic term is voltaic arc, as used in the phrase "voltaic arc lamp".

Corona treatment is a surface modification technique that uses a low temperature corona discharge plasma to impart changes in the properties of a surface. The corona plasma is generated by the application of high voltage to an electrode that has a sharp tip. The plasma forms at the tip. A linear array of electrodes is often used to create a curtain of corona plasma. Materials such as plastics, cloth, or paper may be passed through the corona plasma curtain in order to change the surface energy of the material. All materials have an inherent surface energy. Surface treatment systems are available for virtually any surface format including dimensional objects, sheets and roll goods that are handled in a web format. Corona treatment is a widely used surface treatment method in the plastic film, extrusion, and converting industries.
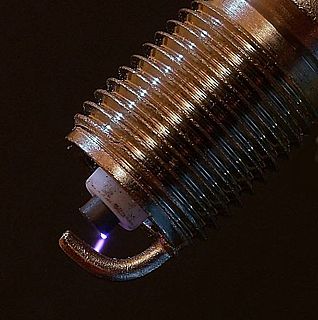
An electric spark is an abrupt electrical discharge that occurs when a sufficiently high electric field creates an ionized, electrically conductive channel through a normally-insulating medium, often air or other gases or gas mixtures. Michael Faraday described this phenomenon as "the beautiful flash of light attending the discharge of common electricity".
A nonthermal plasma, cold plasma or non-equilibrium plasma is a plasma which is not in thermodynamic equilibrium, because the electron temperature is much hotter than the temperature of heavy species. As only electrons are thermalized, their Maxwell-Boltzmann velocity distribution is very different than the ion velocity distribution. When one of the velocities of a species does not follow a Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution, the plasma is said to be non-Maxwellian.
Plasma activation is a method of surface modification employing plasma processing, which improves surface adhesion properties of many materials including metals, glass, ceramics, a broad range of polymers and textiles and even natural materials such as wood and seeds. Plasma functionalization also refers to the introduction of functional groups on the surface of exposed materials. It is widely used in industrial processes to prepare surfaces for bonding, gluing, coating and painting. Plasma processing achieves this effect through a combination of reduction of metal oxides, ultra-fine surface cleaning from organic contaminants, modification of the surface topography and deposition of functional chemical groups. Importantly, the plasma activation can be performed at the atmospheric pressure using air or typical industrial gases including hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen. Thus, the surface functionalization is achieved without expensive vacuum equipment or wet chemistry, which positively affects its costs, safety and environmental impact. Fast processing speeds further facilitate numerous industrial applications.
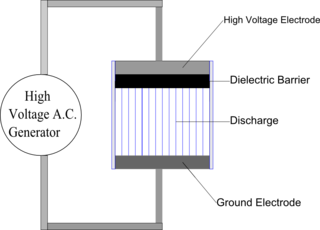
Dielectric-barrier discharge (DBD) is the electrical discharge between two electrodes separated by an insulating dielectric barrier. Originally called silent (inaudible) discharge and also known as ozone production discharge or partial discharge, it was first reported by Ernst Werner von Siemens in 1857. On right, the schematic diagram shows a typical construction of a DBD wherein one of the two electrodes is covered with a dielectric barrier material. The lines between the dielectric and the electrode are representative of the discharge filaments, which are normally visible to the naked eye. Below this, the photograph shows an atmospheric DBD discharge occurring in between two steel electrode plates, each covered with a dielectric (mica) sheet. The filaments are columns of conducting plasma, and the foot of each filament is representative of the surface accumulated charge.
Scanning capacitance microscopy (SCM) is a variety of scanning probe microscopy in which a narrow probe electrode is positioned in contact or close proximity of a sample's surface and scanned. SCM characterizes the surface of the sample using information obtained from the change in electrostatic capacitance between the surface and the probe.
A microplasma is a plasma of small dimensions, ranging from tens to thousands of micrometers. Microplasmas can be generated at a variety of temperatures and pressures, existing as either thermal or non-thermal plasmas. Non-thermal microplasmas that can maintain their state at standard temperatures and pressures are readily available and accessible to scientists as they can be easily sustained and manipulated under standard conditions. Therefore, they can be employed for commercial, industrial, and medical applications, giving rise to the evolving field of microplasmas.

The Wingless Electromagnetic Air Vehicle (WEAV) is a heavier than air flight system developed at the University of Florida, funded by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research. The WEAV was invented in 2006 by Dr. Subrata Roy (scientist),, plasma physicist, aerospace engineering professor at the University of Florida, and has been a subject of several patents. The WEAV employs no moving parts, and combines the aircraft structure, propulsion, energy production and storage, and control subsystems into one integrated system.

Plasma is one of the four fundamental states of matter, and was first described by chemist Irving Langmuir in the 1920s. It consists of a gas of ions – atoms which have some of their orbital electrons removed – and free electrons. Plasma can be artificially generated by heating a neutral gas or subjecting it to a strong electromagnetic field to the point where an ionized gaseous substance becomes increasingly electrically conductive. The resulting charged ions and electrons become influenced by long-range electromagnetic fields, making the plasma dynamics more sensitive to these fields than a neutral gas.

Plasma actuators are a type of actuator currently being developed for aerodynamic flow control. Plasma actuators impart force in a similar way to ionocraft.
Plasma medicine is an emerging field that combines plasma physics, life sciences and clinical medicine. It is being studied in disinfection, healing, and cancer. Most of the research is in vitro and in animal models.

Mounir Laroussi, is a Tunisian-American scientist. He is known for his work in plasma science, especially low temperature plasmas and their biomedical applications.
Plasma-activated bonding is a derivative, directed to lower processing temperatures for direct bonding with hydrophilic surfaces. The main requirements for lowering temperatures of direct bonding are the use of materials melting at low temperatures and with different coefficients of thermal expansion (CTE).

A streamer discharge, also known as filamentary discharge, is a type of transient electrical discharge which forms at the surface of a conductive electrode carrying a high voltage in an insulating medium such as air. Streamers are luminous writhing branching sparks, plasma channels composed of ionized air molecules, which repeatedly strike out from the electrode into the air.













