
The Apicomplexa are a large phylum of parasitic alveolates. Most of them possess a unique form of organelle that comprises a type of plastid called an apicoplast, and an apical complex structure. The organelle is an adaptation that the apicomplexan applies in penetration of a host cell.

Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause yellow skin, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin ten to fifteen days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria.

Plasmodium is a genus of unicellular eukaryotes that are obligate parasites of vertebrates and insects. The life cycles of Plasmodium species involve development in a blood-feeding insect host which then injects parasites into a vertebrate host during a blood meal. Parasites grow within a vertebrate body tissue before entering the bloodstream to infect red blood cells. The ensuing destruction of host red blood cells can result in disease, called malaria. During this infection, some parasites are picked up by a blood-feeding insect, continuing the life cycle.

Plasmodium falciparum is a unicellular protozoan parasite of humans, and the deadliest species of Plasmodium that causes malaria in humans. The parasite is transmitted through the bite of a female Anopheles mosquito and causes the disease's most dangerous form, falciparum malaria. It is responsible for around 50% of all malaria cases. P. falciparum is therefore regarded as the deadliest parasite in humans. It is also associated with the development of blood cancer and is classified as Group 2A carcinogen.

Plasmodium vivax is a protozoal parasite and a human pathogen. This parasite is the most frequent and widely distributed cause of recurring malaria. Although it is less virulent than Plasmodium falciparum, the deadliest of the five human malaria parasites, P. vivax malaria infections can lead to severe disease and death, often due to splenomegaly. P. vivax is carried by the female Anopheles mosquito; the males do not bite.

Plasmodium ovale is a species of parasitic protozoa that causes tertian malaria in humans. It is one of several species of Plasmodium parasites that infect humans including Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax which are responsible for most malarial infection. It is rare compared to these two parasites, and substantially less dangerous than P. falciparum.

Plasmodium malariae is a parasitic protozoan that causes malaria in humans. It is one of several species of Plasmodium parasites that infect other organisms as pathogens, also including Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax, responsible for most malarial infection. Found worldwide, it causes a so-called "benign malaria", not nearly as dangerous as that produced by P. falciparum or P. vivax. The signs include fevers that recur at approximately three-day intervals – a quartan fever or quartan malaria – longer than the two-day (tertian) intervals of the other malarial parasites.

Plasmodium knowlesi is a parasite that causes malaria in humans and other primates. It is found throughout Southeast Asia, and is the most common cause of human malaria in Malaysia. Like other Plasmodium species, P. knowlesi has a life cycle that requires infection of both a mosquito and a warm-blooded host. While the natural warm-blooded hosts of P. knowlesi are likely various Old World monkeys, humans can be infected by P. knowlesi if they are fed upon by infected mosquitoes. P. knowlesi is a eukaryote in the phylum Apicomplexa, genus Plasmodium, and subgenus Plasmodium. It is most closely related to the human parasite Plasmodium vivax as well as other Plasmodium species that infect non-human primates.

Plasmodium berghei is a species in the genus Plasmodium subgenus Vinckeia.
Plasmodium chabaudi is a parasite of the genus Plasmodium subgenus Vinckeia. As in all Plasmodium species, P. chabaudi has both vertebrate and insect hosts. The vertebrate hosts for this parasite are rodents.

Laverania is a subgenus of the parasite genus Plasmodium. Infection with these species results in malaria. The subgenus was first described in 1958.
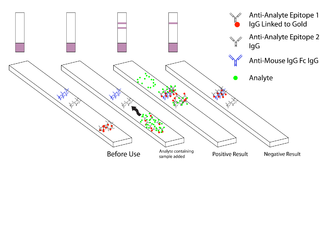
Malaria antigen detection tests are a group of commercially available rapid diagnostic tests of the rapid antigen test type that allow quick diagnosis of malaria by people who are not otherwise skilled in traditional laboratory techniques for diagnosing malaria or in situations where such equipment is not available. There are currently over 20 such tests commercially available. The first malaria antigen suitable as target for such a test was a soluble glycolytic enzyme Glutamate dehydrogenase. None of the rapid tests are currently as sensitive as a thick blood film, nor as cheap. A major drawback in the use of all current dipstick methods is that the result is essentially qualitative. In many endemic areas of tropical Africa, however, the quantitative assessment of parasitaemia is important, as a large percentage of the population will test positive in any qualitative assay.

A malaria vaccine is a vaccine that is used to prevent malaria. The only approved vaccine as of 2021 is RTS,S, known by the brand name Mosquirix. It requires four injections, and has a relatively low efficacy. Due to this low efficacy, the World Health Organization (WHO) does not recommend the routine use of the RTS,S vaccine in babies between 6 and 12 weeks of age.
The Malaria Atlas Project, abbreviated as MAP, is a non-profit academic group led by Professor Peter Gething, Kerry M Stokes Chair in Child Health, at the Telethon Kids Institute, Perth, Western Australia. The group is funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, with previous funding also coming from the Medical Research Council and the Wellcome Trust. MAP aims to disseminate free, accurate and up-to-date information on malaria and associated topics, organised on a geographical basis. The work of MAP falls into three areas:

Avian malaria is a parasitic disease of birds, caused by parasite species belonging to the genera Plasmodium and Hemoproteus. The disease is transmitted by a dipteran vector including mosquitoes in the case of Plasmodium parasites and biting midges for Hemoproteus. The range of symptoms and effects of the parasite on its bird hosts is very wide, from asymptomatic cases to drastic population declines due to the disease, as is the case of the Hawaiian honeycreepers. The diversity of parasites is large, as it is estimated that there are approximately as many parasites as there are species of hosts. Co-speciation and host switching events have contributed to the broad range of hosts that these parasites can infect, causing avian malaria to be a widespread global disease, found everywhere except Antarctica.
UCSC Malaria Genome Browser is a bioinformatic research tool to study the malaria genome, developed by Hughes Undergraduate Research Laboratory together with the laboratory of Prof. Manuel Ares Jr. at the University of California, Santa Cruz.
Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte membrane protein 1 (PfEMP1) is a family of proteins present on the membrane surface of red blood cells that are infected by the malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum. PfEMP1 is synthesized during the parasite's blood stage inside the RBC, during which the clinical symptoms of falciparum malaria are manifested. Acting as both an antigen and adhesion protein, it is thought to play a key role in the high level of virulence associated with P. falciparum. It was discovered in 1984 when it was reported that infected RBCs had unusually large-sized cell membrane proteins, and these proteins had antibody-binding (antigenic) properties. An elusive protein, its chemical structure and molecular properties were revealed only after a decade, in 1995. It is now established that there is not one but a large family of PfEMP1 proteins, genetically regulated (encoded) by a group of about 60 genes called var. Each P. falciparum is able to switch on and off specific var genes to produce a functionally different protein, thereby evading the host's immune system. RBCs carrying PfEMP1 on their surface stick to endothelial cells, which facilitates further binding with uninfected RBCs, ultimately helping the parasite to both spread to other RBCs as well as bringing about the fatal symptoms of P. falciparum malaria.
Plasmodium billcollinsi is a species of the genus Plasmodium subgenus Laverania.

The Plasmodium helical interspersed subtelomeric proteins (PHIST) or ring-infected erythrocyte surface antigens (RESA) are a family of protein domains found in the malaria-causing Plasmodium species. It was initially identified as a short four-helical conserved region in the single-domain export proteins, but the identification of this part associated with a DnaJ domain in P. falciparum RESA has led to its reclassification as the RESA N-terminal domain. This domain has been classified into three subfamilies, PHISTa, PHISTb, and PHISTc.
Jessica Kissinger is a Distinguished Research Professor at the Franklin College of Arts and Sciences, University of Georgia and director of the Institute of Bioinformatics. Her research focus is on the evolution, assembly and data curation of protozoan parasite genomes, particularly Cryptosporidium, Toxoplasma gondii and Plasmodium.











