Mains electricity or utility power, power grid, domestic power, and wall power, or, in some parts of Canada, hydro, is a general-purpose alternating-current (AC) electric power supply. It is the form of electrical power that is delivered to homes and businesses through the electrical grid in many parts of the world. People use this electricity to power everyday items by plugging them into a wall outlet.

DMX512 is a standard for digital communication networks that are commonly used to control lighting and effects. It was originally intended as a standardized method for controlling stage lighting dimmers, which, prior to DMX512, had employed various incompatible proprietary protocols. It quickly became the primary method for linking controllers to dimmers and special effects devices such as fog machines and intelligent lights.

The DIN connector is an electrical connector that was standardized by the Deutsches Institut für Normung (DIN), the German Institute for Standards, in the mid 1950's, initial with 3 pins for mono, but when stereo connections and gear appeared in late 1950's, versions with 5 pins or more were launched. The male DIN connectors (plugs) feature a 13.2 mm diameter metal shield with a notch that limits the orientation in which plug and socket can mate. The range of DIN connectors, different only in the configuration of the pins, have been standardized as DIN 41524 / IEC/DIN EN 60130-9 ; DIN 45322 ; DIN 45329 / IEC/DIN EN 60130–9 ; and DIN 45326 / IEC/DIN EN 60130-9.

Pro Tools is a digital audio workstation (DAW) developed and released by Avid Technology for Microsoft Windows and macOS. It is used for music creation and production, sound for picture and, more generally, sound recording, editing, and mastering processes.

AlliedSignal was an American aerospace, automotive and engineering company created through the 1985 merger of Allied Corp. and The Signal Companies. It subsequently purchased Honeywell for $14.8 billion in 1999, and thereafter adopted the Honeywell name and identity.

The Electricity Supply Board is a state owned electricity company operating in the Republic of Ireland. While historically a monopoly, the ESB now operates as a commercial semi-state concern in a "liberalised" and competitive market. It is a statutory corporation whose members are appointed by the government of Ireland.
AC power plugs and sockets connect electric equipment to the alternating current (AC) mains electricity power supply in buildings and at other sites. Electrical plugs and sockets differ from one another in voltage and current rating, shape, size, and connector type. Different standard systems of plugs and sockets are used around the world.

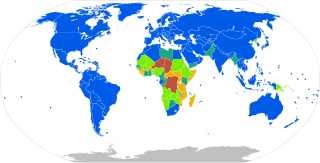
Mains electricity by country includes a list of countries and territories, with the plugs, voltages and frequencies they commonly use for providing electrical power to low voltage appliances, equipment, and lighting typically found in homes and offices. Some countries have more than one voltage available. For example, in North America, a unique split-phase system is used to supply to most premises that works by center tapping a 240 volts transformer. This system is able to concurrently provide 240 volts and 120 volts. Most sockets are connected to 120 V for the use of small appliances and electronic devices. While larger appliances such as dryer, electric oven, range and EV charger use dedicated 240 V sockets. Different sockets are mandated for different voltage or current levels. Consequently, residents are able to wire up any 240 V or 120 V circuits as they wish
In electricity supply design, a ring circuit is an electrical wiring technique in which sockets and the distribution point are connected in a ring. It is contrasted with the usual radial circuit, in which sockets and the distribution point are connected in a line with the distribution point at one end.

Industrial and multiphase plugs and sockets provide a connection to the electrical mains rated at higher voltages and currents than household plugs and sockets. They are generally used in polyphase systems, with high currents, or when protection from environmental hazards is required. Industrial outlets may have weatherproof covers, waterproofing sleeves, or may be interlocked with a switch to prevent accidental disconnection of an energized plug. Some types of connectors are approved for hazardous areas such as coal mines or petrochemical plants, where flammable gas may be present.

Main components found on a typical steam locomotive include:

Architectural lighting design is a field of work or study that is concerned with the design of lighting systems within the built environment, both interior and exterior. It can include manipulation and design of both daylight and electric light or both, to serve human needs.

A light fixture, light fitting, lamp, or luminaire is an electrical device containing an electrical component called a lamp that provides illumination. All light fixtures have a fixture body and one or more lamps. The lamps may be in sockets for easy replacement—or, in the case of some LED fixtures, hard-wired in place.

Energy conversion efficiency (η) is the ratio between the useful output of an energy conversion machine and the input, in energy terms. The input, as well as the useful output may be chemical, electric power, mechanical work, light (radiation), or heat. The resulting value, η (eta), ranges between 0 and 1.

A wireless light switch is a light switch that commands a light or home appliance to turn itself off or on, instead of interrupting the power line going to the light fixture. There are different ways to communicate between the switch and the fixture:
- Using radio transmission: A radio receiver is typically wired or screwed into a fixture or device, wired or otherwise connected to the electrical system of the building or plugged into an outlet. The radio receiver's memory is programmed by any number of means to respond to certain selected "switches" or remote control transmitters.
- Using the existing power lines : A receiver is plugged into an outlet and a device is then plugged into the receiver. The plug-in receiver is then programmed to the switches. Some devices are hard wired into ceiling light fittings, making for a hidden system.

Track lighting is a method of lighting where light fixtures are attached anywhere on a continuous track device which contains electrical conductors. This is in contrast to directly routing electrical wiring to individual light positions. Tracks can either be mounted to ceilings or walls, lengthwise down beams, or crosswise across rafters or joists. They can also be hung with rods from especially high places like vaulted ceilings.
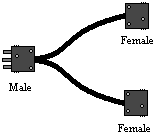
A twofer is a cabling device used in theatrical stage lighting. It allows two stage lighting instruments to be connected to one circuit. It is wired in parallel, such that voltage is unchanged in the twofer, and current is split and divided over two connectors. Twofers are used in conjunction with cables with the same types of connectors. The name is a corruption of the phrase "Two For One".

An automobile auxiliary power outlet in an automobile was initially designed to power an electrically heated cigarette lighter, but became a de facto standard DC connector to supply electrical power for portable accessories used in or near an automobile directly from the vehicle's electrical system. Such include mobile phone chargers, cooling fans, portable fridges, electric air pumps, and power inverters.

The Carcel lamp was an efficient lighting device used in the nineteenth century for domestic purposes and in France as the standard measure for illumination.

Plugs and sockets for electrical appliances not hardwired to mains electricity originated in the United Kingdom in the 1870s and were initially two-pin designs. These were usually sold as a mating pair, but gradually de facto and then official standards arose to enable the interchange of compatible devices. British standards have proliferated throughout large parts of the former British Empire.

















