Related Research Articles
In grammar, tense is a category that expresses time reference. Tenses are usually manifested by the use of specific forms of verbs, particularly in their conjugation patterns.

Latin is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Classical Latin is considered a dead language as it is no longer used to produce major texts, while Vulgar Latin evolved into the Romance Languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins in Latium, the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the early 19th century, when regional vernaculars supplanted it in common academic and political usage—including its own descendants, the Romance languages.
Old English, or Anglo-Saxon, was the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th century, and the first Old English literary works date from the mid-7th century. After the Norman Conquest of 1066, English was replaced for several centuries by Anglo-Norman as the language of the upper classes. This is regarded as marking the end of the Old English era, since during the subsequent period the English language was heavily influenced by Anglo-Norman, developing into what is now known as Middle English in England and Early Scots in Scotland.
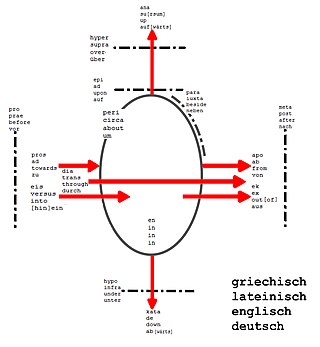
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the stem of a word. Particularly in the study of languages, a prefix is also called a preformative, because it alters the form of the word to which it is affixed.

Volapük is a constructed language created between 1879 and 1880 by Johann Martin Schleyer, a Catholic priest in Baden, Germany, who believed that God told him to create an international language. Notable as the first major constructed international auxiliary language, the grammar comes from European languages and the vocabulary mostly from English. However, the roots are often distorted beyond recognition.
English grammar is the set of structural rules of the English language. This includes the structure of words, phrases, clauses, sentences, and whole texts.

Plywood is a composite material manufactured from thin layers, or "plies", of wood veneer that have been stacked and glued together. It is an engineered wood from the family of manufactured boards, which include plywood, medium-density fibreboard (MDF), oriented strand board (OSB), and particle board.

Latin is a heavily inflected language with largely free word order. Nouns are inflected for number and case; pronouns and adjectives are inflected for number, case, and gender; and verbs are inflected for person, number, tense, aspect, voice, and mood. The inflections are often changes in the ending of a word, but can be more complicated, especially with verbs.
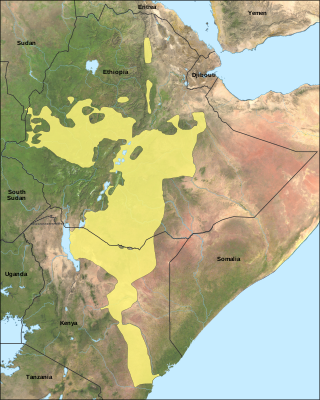
Oromo, historically also called Galla, which is regarded by the Oromo as pejorative, is an Afroasiatic language that belongs to the Cushitic branch. It is native to the Ethiopian state of Oromia and northern Kenya and is spoken predominantly by the Oromo people and neighboring ethnic groups in the Horn of Africa. It is used as a lingua franca particularly in the Oromia Region and northeastern Kenya.
In grammar, a future tense is a verb form that generally marks the event described by the verb as not having happened yet, but expected to happen in the future. An example of a future tense form is the French aimera, meaning "will love", derived from the verb aimer. The "future" expressed by the future tense usually means the future relative to the moment of speaking, although in contexts where relative tense is used it may mean the future relative to some other point in time under consideration.
In grammar, a supine is a form of verbal noun used in some languages. The term is most often used for Latin, where it is one of the four principal parts of a verb. The word refers to a position of lying on one's back, but there exists no widely accepted etymology that explains why or how the term came to be used to also describe this form of a verb.
The perfect tense or aspect is a verb form that indicates that an action or circumstance occurred earlier than the time under consideration, often focusing attention on the resulting state rather than on the occurrence itself. An example of a perfect construction is I have made dinner. Although this gives information about a prior action, the focus is likely to be on the present consequences of that action. The word perfect in this sense means "completed".
A finite verb is a verb that contextually complements either an explicit subject or – in the imperative mood – an implicit subject. A finite transitive verb or a finite intransitive verb can function as the root of an independent clause. Finite verbs are distinguished from non-finite verbs such as infinitives, participles, gerunds etc.
In the textile arts, plying is a process of twisting one or more strings of yarn together to create a stronger yarn. Strands are twisted together in the direction opposite that in which they were spun. Plied yarns will not unravel, break, or degrade as easily as unplied yarns. When enough twist is added to the plies to counter the initial twist of each strand, the resulting yarn is "balanced", having no tendency to twist upon itself.

The Lexikon der indogermanischen Verben is an etymological dictionary of the Proto-Indo-European (PIE) verb. The first edition appeared in 1998, edited by Helmut Rix. A second edition followed in 2001. The book may be seen as an update to the verb entries of the Indogermanisches etymologisches Wörterbuch (IEW) by Julius Pokorny. It was the first dictionary fully utilizing the modern three-laryngeal theory with reconstructions of Indo-European verbal roots.

A scrim is a woven material, either finely woven lightweight fabric widely used in theatre, or a heavy, coarse woven material used for reinforcement in both building and canvas making.
Äiwoo is an Oceanic language spoken on the Santa Cruz Islands and the Reef Islands in the Temotu Province of the Solomon Islands.
In linguistics and literature, periphrasis is the use of a larger number of words, with an implicit comparison to the possibility of using fewer. The comparison may be within a language or between languages. For example, "more happy" is periphrastic in comparison to "happier", and English "I will eat" is periphrastic in comparison to Spanish comeré.
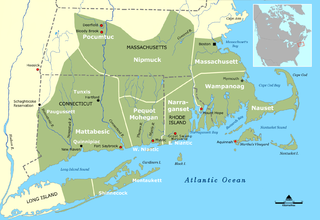
Mohegan-Pequot is an Algonquian language formerly spoken by indigenous peoples in southern present-day New England and eastern Long Island.

A thread is a long strand of material, often composed of several filaments or fibres, used for joining, creating or decorating textiles. Ancient Egyptians were known for creating thread using plant fibers, wool and hair. Today, thread can also be made of many different materials including but not limited to cotton, wool, flax, nylon, silk, polyester etc. There are also metal threads, which can be made of fine wire.