Related Research Articles
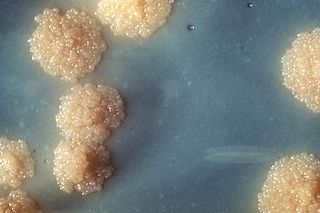
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, also known as Koch's bacillus, is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis. First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, M. tuberculosis has an unusual, waxy coating on its cell surface primarily due to the presence of mycolic acid. This coating makes the cells impervious to Gram staining, and as a result, M. tuberculosis can appear weakly Gram-positive. Acid-fast stains such as Ziehl–Neelsen, or fluorescent stains such as auramine are used instead to identify M. tuberculosis with a microscope. The physiology of M. tuberculosis is highly aerobic and requires high levels of oxygen. Primarily a pathogen of the mammalian respiratory system, it infects the lungs. The most frequently used diagnostic methods for tuberculosis are the tuberculin skin test, acid-fast stain, culture, and polymerase chain reaction.

Mycobacterium is a genus of over 190 species in the phylum Actinomycetota, assigned its own family, Mycobacteriaceae. This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis and leprosy in humans. The Greek prefix myco- means 'fungus', alluding to this genus' mold-like colony surfaces. Since this genus has cell walls with a waxy lipid-rich outer layer that contains high concentrations of mycolic acid, acid-fast staining is used to emphasize their resistance to acids, compared to other cell types.
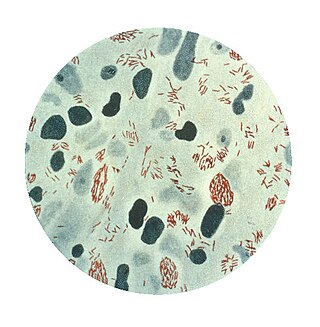
Mycobacterium leprae is one of the two species of bacteria that cause Hansen’s disease (leprosy), a chronic but curable infectious disease that damages the peripheral nerves and targets the skin, eyes, nose, and muscles.

Rifampicin, also known as rifampin, is an ansamycin antibiotic used to treat several types of bacterial infections, including tuberculosis (TB), Mycobacterium avium complex, leprosy, and Legionnaires' disease. It is almost always used together with other antibiotics with two notable exceptions: when given as a "preferred treatment that is strongly recommended" for latent TB infection; and when used as post-exposure prophylaxis to prevent Haemophilus influenzae type b and meningococcal disease in people who have been exposed to those bacteria. Before treating a person for a long period of time, measurements of liver enzymes and blood counts are recommended. Rifampicin may be given either by mouth or intravenously.

Tuberculosis management describes the techniques and procedures utilized for treating tuberculosis (TB).

Mycobacterium smegmatis is an acid-fast bacterial species in the phylum Actinomycetota and the genus Mycobacterium. It is 3.0 to 5.0 µm long with a bacillus shape and can be stained by Ziehl–Neelsen method and the auramine-rhodamine fluorescent method. It was first reported in November 1884 by Lustgarten, who found a bacillus with the staining appearance of tubercle bacilli in syphilitic chancres. Subsequent to this, Alvarez and Tavel found organisms similar to that described by Lustgarten also in normal genital secretions (smegma). This organism was later named M. smegmatis.
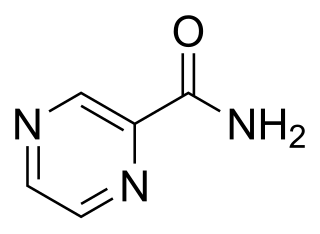
Pyrazinamide is a medication used to treat tuberculosis. For active tuberculosis, it is often used with rifampicin, isoniazid, and either streptomycin or ethambutol. It is not generally recommended for the treatment of latent tuberculosis. It is taken by mouth.

4-Aminosalicylic acid, also known as para-aminosalicylic acid (PAS) and sold under the brand name Paser among others, is an antibiotic primarily used to treat tuberculosis. Specifically it is used to treat active drug resistant tuberculosis together with other antituberculosis medications. It has also been used as a second line agent to sulfasalazine in people with inflammatory bowel disease such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. It is typically taken by mouth.
The rpoB gene encodes the β subunit of bacterial RNA polymerase and the homologous plastid-encoded RNA polymerase (PEP). It codes for 1342 amino acids in E. coli, making it the second-largest polypeptide in the bacterial cell. It is targeted by the rifamycin family of antibacterials, such as rifampin. Mutations in rpoB that confer resistance to rifamycins do so by altering the protein's drug-binding residues, thereby reducing affinity for these antibiotics.

Ethionamide is an antibiotic used to treat tuberculosis. Specifically it is used, along with other antituberculosis medications, to treat active multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. It is no longer recommended for leprosy. It is taken by mouth.
Mycobacterium microti is a member of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC) known as the 'Vole bacillus', first described as a pathogen of field voles in England.
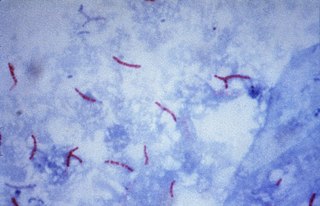
Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) is a form of tuberculosis (TB) infection caused by bacteria that are resistant to treatment with at least two of the most powerful first-line anti-TB medications (drugs): isoniazid and rifampin. Some forms of TB are also resistant to second-line medications, and are called extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR-TB).

Bedaquiline, sold under the brand name Sirturo, is a medication used to treat active tuberculosis. Specifically, it is used to treat multi-drug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) along with other medications for tuberculosis. It is used by mouth.

Isocitrate lyase, or ICL, is an enzyme in the glyoxylate cycle that catalyzes the cleavage of isocitrate to succinate and glyoxylate. Together with malate synthase, it bypasses the two decarboxylation steps of the tricarboxylic acid cycle and is used by bacteria, fungi, and plants.
The Xpert MTB/RIF is a cartridge-based nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) for simultaneous rapid tuberculosis diagnosis and rapid antibiotic sensitivity test. It is an automated diagnostic test that can identify Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) DNA and resistance to rifampicin (RIF). It was co-developed by the laboratory of Professor David Alland at the University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey (UMDNJ), Cepheid Inc. and Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics, with additional financial support from the US National Institutes of Health (NIH).
The Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex is a genetically related group of Mycobacterium species that can cause tuberculosis in humans or other animals.
MUBII-TB-DB is a database that focuses on tuberculosis antibiotic resistance genes. It is a highly structured, text-based database focusing on Mycobacterium tuberculosis at seven different mutation loci: rpoB, pncA, katG; mabA(fabG1)-inhA, gyrA, gyrB, and rrs. MUBII analyzes the query using two parallel strategies: 1). A BLAST search against previously mutated sequences. 2). Alignment of query sequences with wild-type sequences. MUBII outputs graphs of alignments and description of the mutation and therapeutic significance. Therapeutically relevant mutations are tagged as "High-Confident" based on the criteria set by Sandgren et al. MUBII-TB-DB provides a platform that is easy to use for even users that are not trained in bioinformatics.

François Balloux is the director of the UCL Genetics Institute, and a professor of computational biology at University College London.
KatG is an enzyme that functions as both catalase and peroxidase. Its mutation is the cause for Mycobacterium resistance with the drug isoniazid, which targets the mycolic acids within the tuberculosis bacteria. Due to both its catalase and peroxidase activity, this enzyme protects M. Tuberculosis against reactive oxygen species. M. tuberculosis' survival within macrophages depends on the KatG enzyme.
References
- ↑ Scorpio A, Zhang Y (June 1996). "Mutations in pncA, a gene encoding pyrazinamidase/nicotinamidase, cause resistance to the antituberculous drug pyrazinamide in tubercle bacillus". Nat. Med. 2 (6): 662–7. doi:10.1038/nm0696-662. PMID 8640557. S2CID 8579133.
- ↑ Whitfield, Michael G.; Soeters, Heidi M.; Warren, Robin M.; York, Talita; Sampson, Samantha L.; Streicher, Elizabeth M.; Helden, Paul D. van; Rie, Annelies van (2015-07-28). "A Global Perspective on Pyrazinamide Resistance: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis". PLOS ONE. 10 (7): e0133869. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1033869W. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133869 . ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 4517823 . PMID 26218737.
- ↑ Juréen, Pontus; Werngren, Jim; Toro, Juan-Carlos; Hoffner, Sven (2016-12-15). "Pyrazinamide Resistance and pncA Gene Mutations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 52 (5): 1852–1854. doi:10.1128/AAC.00110-08. ISSN 0066-4804. PMC 2346646 . PMID 18316515.