Related Research Articles

The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority is the public agency responsible for operating most public transportation services in Greater Boston, Massachusetts. Earlier modes of public transportation in Boston were independently owned and operated; many were first folded into a single agency with the formation of the Metropolitan Transit Authority (MTA) in 1947. The MTA was replaced in 1964 with the present-day MBTA, which was established as an individual department within the Commonwealth of Massachusetts before becoming a division of the Massachusetts Department of Transportation (MassDOT) in 2009.

The Long Island Railroad, often abbreviated as the LIRR, is a commuter rail system in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of New York, stretching from Manhattan to the eastern tip of Suffolk County on Long Island. With an average weekday ridership of 354,800 passengers in 2016, it is the busiest commuter railroad in North America. It is also one of the world's few commuter systems that runs 24 hours a day, seven days a week, year-round. It is publicly owned by the Metropolitan Transportation Authority, which refers to it as MTA Long Island Rail Road.

The Boston transportation system includes roadway, subway, regional rail, air, and sea options for passenger and freight transit in Boston, Massachusetts. The Massachusetts Port Authority (Massport) operates the Port of Boston, which includes a container shipping facility in South Boston, and Logan International Airport, in East Boston. The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) operates bus, subway, short-distance rail, and water ferry passenger services throughout the city and region. Amtrak operates passenger rail service to and from major northeastern cities. A major bus terminal at South Station is served by varied intercity bus companies. The city is bisected by major highways I-90 and I-93, the intersection of which has undergone a major renovation, nicknamed the Big Dig.

The New York City Subway is a rapid transit system owned by the City of New York and leased to the New York City Transit Authority, a subsidiary agency of the state-run Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA). Opened in 1904, the New York City Subway is one of the world's oldest public transit systems, one of the most-used, and the one with the most stations. The New York City Subway is the largest rapid transit system in the world by number of stations, with 472 stations in operation. Stations are located throughout the boroughs of Manhattan, Brooklyn, Queens, and the Bronx.

The New York City Transit Authority is a public authority in the U.S. state of New York that operates public transportation in New York City. Part of the Metropolitan Transportation Authority, the busiest and largest transit system in North America, the NYCTA has a daily ridership of 8 million trips.

The Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA) is a public benefit corporation responsible for public transportation in the U.S. state of New York, serving 12 counties in Downstate New York, along with two counties in southwestern Connecticut under contract to the Connecticut Department of Transportation, carrying over 11 million passengers on an average weekday systemwide, and over 850,000 vehicles on its seven toll bridges and two tunnels per weekday. The MTA is the largest public transit authority in the United States.
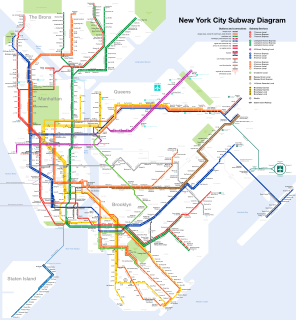
The New York City Subway is a rapid transit system that serves four of the five boroughs of New York City, New York: the Bronx, Brooklyn, Manhattan, and Queens. Its operator is the New York City Transit Authority, which is itself controlled by the Metropolitan Transportation Authority of New York. In 2015, an average of 5.65 million passengers used the system daily, making it the busiest rapid transit system in the United States and the seventh busiest in the world.

The New York Transit Museum is a museum that displays historical artifacts of the New York City Subway, bus, and commuter rail systems in the greater New York City metropolitan region. The main museum is located in the decommissioned Court Street subway station in Downtown Brooklyn and Brooklyn Heights in the New York City borough of Brooklyn. There is a smaller satellite Museum Annex in Grand Central Terminal in Midtown Manhattan. The museum is a self-supporting division of the Metropolitan Transportation Authority.

The transportation system of New York City is a network of complex infrastructural systems. New York City, being the most populous city in the United States, has a transportation system which includes one of the largest subway systems in the world; the world's first mechanically ventilated vehicular tunnel; and an aerial tramway. New York City is also home to an extensive bus system in each of the five boroughs; citywide and Staten Island ferry systems; and numerous yellow taxis and boro taxis throughout the city. Private cars are less used compared to other cities in the rest of the United States.

Brookline Village is a light rail stop on the MBTA Green Line "D" Branch, located in the Brookline Village neighborhood of Brookline, Massachusetts, United States. It was originally a commuter rail station on the Boston and Albany Railroad's Highland Branch; it closed with the rest of the line in 1958 and reopened on July 4, 1959 as a light rail station. With 3,230 daily boardings, it is the third-busiest surface station on the "D" Branch and the sixth-busiest surface station overall.

86th Street, also known as Gravesend–86th Street, is a local station on the BMT Sea Beach Line of the New York City Subway, located at the intersection of 86th Street and West Seventh Street in Gravesend, Brooklyn. It is served by the N train at all times, and by limited rush hour W trains. This station is the southern terminus for W trains.
A transit district or transit authority is a government agency or a public-benefit corporation created for the purpose of providing public transportation within a specific region.

Nearly every major type of transportation serves Long Island, including three major airports, railroads and subways, and several major highways. The New York City Subway only serves the New York City boroughs of Brooklyn and Queens. There are historic and modern bridges, recreational and commuter trails, and ferries, that connect the boroughs of Queens and Brooklyn to Manhattan, the south shore with Fire Island and Long Island's north shore and east end with the state of Connecticut.
MTA Arts & Design, formerly known as Arts for Transit and Urban Design, is a commissioned art program directed by the Metropolitan Transportation Authority for the transportation systems serving New York City and the surrounding region. Since 1985, the program has installed art in more than 260 transit stations. The art is intended to be site-specific and to improve the journey for New Yorkers and visitors alike.

MTA Bus Time, stylized as BusTime, is a Service Interface for Real Time Information, automatic vehicle location (AVL), and passenger information system provided by the Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA) of New York City for customers of its bus operations under the New York City Bus and MTA Bus Company brands. First tested in late 2010 and officially launched in early 2011, MTA Bus Time was installed in all MTA bus routes in New York City by 2014.

Physical accessibility on the Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA) is incomplete. Although accessibility on all buses is provided in compliance with the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 (ADA), much of the MTA's rail system, including its rapid transit and commuter rail services, were built before wheelchair access was a requirement under the ADA. As a side effect, many stations were not designed to be accessible to people with disabilities.
OMNY is a contactless fare payment system, currently being implemented for use on public transit in New York City and the surrounding area. When OMNY is completely rolled out, it will replace the MetroCard on the New York City Subway, the Staten Island Railway, PATH trains, MTA buses, Bee-Line buses, and NICE buses. OMNY will also expand beyond the current scope of the MetroCard to the Long Island Rail Road and Metro-North Railroad.
References
- ↑ Kennedy, Randy (March 6, 2001). "Tunnel Vision; Gatekeeper Shifts Gears From Rails To Poetry". The New York Times.
- ↑ Thomas, Jeffrey (September 7, 2007). "Program Brings Poetry to Mass Transit Systems". America.gov. Archived from the original on February 28, 2010.
- ↑ Smith, Michelle R. (September 11, 2017), "Poetry for the masses: Transit poems spread to Rhode Island", The Seattle Times, AP, retrieved 2019-11-08
- ↑ "Ten Years of Poetry In Motion". Metropolitan Transportation Authority. Archived from the original on 2010-05-14. Retrieved 2008-02-09.
- ↑ Austern, David (November 5, 2002). "'Poetry in Motion' includes some of America's best poets". The Michigan Daily.
- ↑ Sternbergh, Adam (December 13, 2009). "21. Because We Fight Over Poetry". New York Magazine.