
Underground hard-rock mining refers to various underground mining techniques used to excavate "hard" minerals, usually those containing metals, such as ore containing gold, silver, iron, copper, zinc, nickel, tin, and lead. It also involves the same techniques used to excavate ores of gems, such as diamonds and rubies. Soft-rock mining refers to the excavation of softer minerals, such as salt, coal, and oil sands.

Moose River Gold Mines is a Canadian rural community located in Nova Scotia's Halifax Regional Municipality. It is at the junction of Moose River Road and Mooseland Road. No numbered highways run through Moose River Gold Mines. Gold was discovered in the area in 1866 and mining started in the 1870s. Interest waned around 1900 but rose in the 1930s. The community gained international attention in 1936 when three men were trapped in the mine.

The Challenger mine is a gold mine in the Far North of South Australia, 165 km west of the Stuart Highway and 740 km north-west of Adelaide. It was operated by Dominion, Kingsgate and then WPG Resources. The mine is now on Care and Maintenance. The deposit was named by the geologist who discovered it, after his dog.
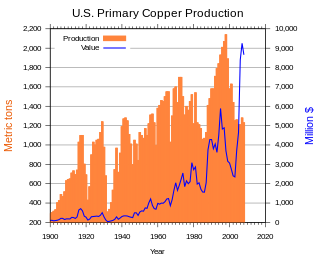
In the United States, copper mining has been a major industry since the rise of the northern Michigan copper district in the 1840s. In 2017, the US produced 1.27 million metric tonnes of copper, worth $8 billion, making it the world's fourth largest copper producer, after Chile, China, and Peru. Copper was produced from 23 mines in the US. Top copper producing states in 2014 were Arizona, Utah, New Mexico, Nevada, and Montana. Minor production also came from Idaho and Missouri. As of 2014, the US had 45 million tonnes of known remaining reserves of copper, the fifth largest known copper reserves in the world, after Chile, Australia, Peru, and Mexico.

In the United States, gold mining has taken place continually since the discovery of gold at the Reed farm in North Carolina in 1799. The first documented occurrence of gold was in Virginia in 1782. Some minor gold production took place in North Carolina as early as 1793, but created no excitement. The discovery on the Reed farm in 1799 which was identified as gold in 1802 and subsequently mined marked the first commercial production.
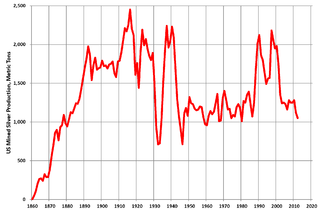
Silver mining in the United States began on a major scale with the discovery of the Comstock Lode in Nevada in 1858. The industry suffered greatly from the demonetization of silver in 1873 by the Coinage Act of 1873, known pejoratively as the "Crime of 73", but silver mining continues today.

Uranium mining in Colorado, United States, goes back to 1872, when pitchblende ore was taken from gold mines near Central City, Colorado. The Colorado uranium industry has seen booms and busts, but continues to this day. Not counting byproduct uranium from phosphate, Colorado is considered to have the third largest uranium reserves of any US state, behind Wyoming and New Mexico.
Gold mining in Alaska, a state of the United States, has been a major industry and impetus for exploration and settlement since a few years after the United States acquired the territory in 1867 from the Russian Empire. Russian explorers discovered placer gold in the Kenai River in 1848, but no gold was produced. Gold mining started in 1870 from placers southeast of Juneau, Alaska.
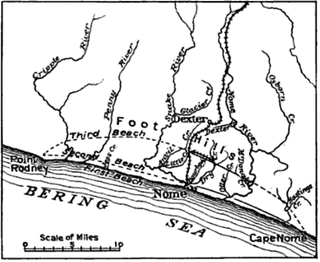
The Nome mining district, also known as the Cape Nome mining district, is a gold mining district in the U.S. state of Alaska. It was discovered in 1898 when Erik Lindblom, Jafet Lindeberg and John Brynteson, the "Three Lucky Swedes", found placer gold deposits on Anvil Creek and on the Snake River few miles from the future site of Nome. Word of the strike caused a major gold rush to Nome in the spring of 1899.
The Admiralty mining district is a mining area in the U.S. state of Alaska which consists of Admiralty Island. Silver and base metals are mined, with gold recovered as a by-product.
Coeur Mining, Inc. is a precious metals mining company listed on the New York Stock exchange. It operates five mines located in North America. Coeur employs 2,200 people and in 2012 it was the world's 9th largest silver producer. In 2013 the company changed its name to Coeur Mining, Inc. from Coeur d'Alene Mines and moved its head office to Chicago, Illinois from Coeur d'Alene, Idaho.

The Sunrise Dam Gold Mine is located 55 km south of Laverton, Western Australia, on the eastern margin of Lake Carey. It is fully owned by AngloGold Ashanti and comprises a large-scale mechanized underground mine with a conventional gravity and leach process plant. In 2015 the mine accounted for 5% of the company's production.
Cortez Gold Mine is a large gold mining and processing facility in Lander and Eureka County, Nevada, United States, located approximately 63 miles (100 km) southwest of Elko. It is owned as a joint venture between Barrick Gold Corporation (61.5%) and Newmont Corporation (38.5%), operated by Barrick, and comprises the Pipeline, Crossroads, and Cortez Hills open pit mines; and the Cortez Hills underground mine. Ore from the mines is treated at an oxide mill at the site and on leach pads, while refractory ore is shipped to Barrick’s Goldstrike operation for processing.

The Bronzewing Gold Mine is a gold mine located approximately 83 km north-east of Leinster, Western Australia. The mine, owned by Navigator Resources Limited, has been in care and maintenance since March 2013, after its owner went into administration.
The Kanowna Belle Gold Mine is a gold mine 19 kilometres (12 mi) north-east of Kalgoorlie, Western Australia, near the ghost town of Kanowna.

Beria is an abandoned town in the Goldfields-Esperance region of Western Australia, located 8 kilometres (5 mi) north of Laverton on the Laverton-Leonora Road.
The Fort Knox Gold Mine is an open pit gold mine, 9 mi (14 km) east of Fox in the Fairbanks mining district of Alaska. It is owned and operated by Toronto-based Kinross Gold. Originally staked in 1913, after very minor mining at the location the property sat idle until being restaked in 1980. Following the initial exploration discovery in 1987, in 1992 the project was purchased by Amax Gold, which brought the mine to production. Amax Gold merged with Kinross Gold in 1998.
Crystal Mine is located near Juneau in the U.S. state of Alaska. The quartz ledge at the Crystal Mine was first discovered in 1895 by B. Heins. It was so named because of the large pyrite cubes which were found occurring in the surface outcrops of the ledge. Gold was extracted till 1905 from quartz using ten-stamp mill and from about 1,000 feet of underground workings yielded 1,210 ounces of gold. Intermittent production of gold is reported till 1925 but there are no records of the yield. The formation was determined as of 54 to 56 Ma age. The gold yielding resources available from the mine were assessed as 9,000 tons of material with yield of 0.21 ounce of gold per ton.

Northern Star Resources is an Australian gold mining company with operations in Western Australia, Northern Territory and Alaska.












