An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the power of a signal. It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a proportionally greater amplitude signal at its output. The amount of amplification provided by an amplifier is measured by its gain: the ratio of output voltage, current, or power to input. An amplifier is a circuit that has a power gain greater than one.
In telecommunications, RS-232, Recommended Standard 232 refers to a standard originally introduced in 1960 for serial communication transmission of data. It formally defines signals connecting between a DTE such as a computer terminal, and a DCE, such as a modem. The standard defines the electrical characteristics and timing of signals, the meaning of signals, and the physical size and pinout of connectors. The current version of the standard is TIA-232-F Interface Between Data Terminal Equipment and Data Circuit-Terminating Equipment Employing Serial Binary Data Interchange, issued in 1997. The RS-232 standard had been commonly used in computer serial ports.

A circulator is a passive, non-reciprocal three- or four-port device, in which a microwave or radio-frequency signal entering any port is transmitted to the next port in rotation (only). A port in this context is a point where an external waveguide or transmission line, connects to the device. For a three-port circulator, a signal applied to port 1 only comes out of port 2; a signal applied to port 2 only comes out of port 3; a signal applied to port 3 only comes out of port 1, so to up to a phase-factor, the scattering matrix for an ideal three-port circulator is
Push-to-type operation: In telegraph or data transmission systems, that method of communication in which the operator at a station must keep a switch operated in order to send messages.

In telecommunications, a repeater is an electronic device that receives a signal and retransmits it. Repeaters are used to extend transmissions so that the signal can cover longer distances or be received on the other side of an obstruction.

Time-division multiplexing (TDM) is a method of transmitting and receiving independent signals over a common signal path by means of synchronized switches at each end of the transmission line so that each signal appears on the line only a fraction of time in an alternating pattern. It is used when the bit rate of the transmission medium exceeds that of the signal to be transmitted. This form of signal multiplexing was developed in telecommunications for telegraphy systems in the late 19th century, but found its most common application in digital telephony in the second half of the 20th century.

A transmission medium is a material substance that can propagate energy waves. For example, the transmission medium for sounds is usually a gas, but solids and liquids may also act as a transmission medium for sound.
The U interface or U reference point is a Basic Rate Interface (BRI) in the local loop of an Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN). It is characterized by the use of a 2-wire transmission system that connects the network termination type 1 (NT1) on the customer's premises and the line termination (LT) in the carrier's local exchange. It is not as distance sensitive as a service using an S interface or T interface.

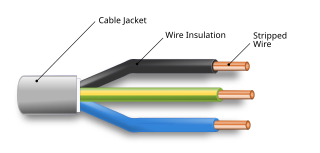
Coaxial cable, or coax is a type of electrical cable that has an inner conductor surrounded by a tubular insulating layer, surrounded by a tubular conducting shield. Many coaxial cables also have an insulating outer sheath or jacket. The term coaxial comes from the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing a geometric axis. Coaxial cable was invented by English physicist, engineer, and mathematician Oliver Heaviside, who patented the design in 1880.

Direct current (DC) is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. A battery is a good example of a DC power supply. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or even through a vacuum as in electron or ion beams. The electric current flows in a constant direction, distinguishing it from alternating current (AC). A term formerly used for this type of current was galvanic current.

A high-voltage, direct current (HVDC) electric power transmission system uses direct current for the bulk transmission of electrical power, in contrast with the more common alternating current (AC) systems. For long-distance transmission, HVDC systems may be less expensive and suffer lower electrical losses. For underwater power cables, HVDC avoids the heavy currents required to charge and discharge the cable capacitance each cycle. For shorter distances, the higher cost of DC conversion equipment compared to an AC system may still be justified, due to other benefits of direct current links. HVDC currently uses voltages between 100 kV and 800 kV, with an 1,100 kV link in China due to become operational in 2019.

In computer networking, Fast Ethernet physical layers carry traffic at the nominal rate of 100 Mbit/s. The prior Ethernet speed was 10 Mbit/s. Of the Fast Ethernet physical layers, 100BASE-TX is by far the most common.

In radio engineering, an antenna is the interface between radio waves propagating through space and electric currents moving in metal conductors, used with a transmitter or receiver. In transmission, a radio transmitter supplies an electric current to the antenna's terminals, and the antenna radiates the energy from the current as electromagnetic waves. In reception, an antenna intercepts some of the power of a radio wave in order to produce an electric current at its terminals, that is applied to a receiver to be amplified. Antennas are essential components of all radio equipment.

The Schottky diode, also known as Schottky barrier diode or hot-carrier diode, is a semiconductor diode formed by the junction of a semiconductor with a metal. It has a low forward voltage drop and a very fast switching action. The cat's-whisker detectors used in the early days of wireless and metal rectifiers used in early power applications can be considered primitive Schottky diodes.

A residual-current device (RCD), or residual-current circuit breaker (RCCB), is a device that quickly breaks an electrical circuit to prevent serious harm from an ongoing electric shock. Injury may still occur in some cases, for example if a human falls after receiving a shock, or if the person touches both conductors at the same time.

An Earth-leakage circuit breaker (ELCB) is a safety device used in electrical installations with high Earth impedance to prevent shock. It detects small stray voltages on the metal enclosures of electrical equipment, and interrupts the circuit if a dangerous voltage is detected. Once widely used, more recent installations instead use residual current circuit breakers which instead detect leakage current directly.
The media-independent interface (MII) was originally defined as a standard interface to connect a Fast Ethernet media access control (MAC) block to a PHY chip. The MII is standardized by IEEE 802.3u and connects different types of PHYs to MACs. Being media independent means that different types of PHY devices for connecting to different media can be used without redesigning or replacing the MAC hardware. Thus any MAC may be used with any PHY, independent of the network signal transmission media.

An overhead power line is a structure used in electric power transmission and distribution to transmit electrical energy along large distances. It consists of one or more conductors suspended by towers or poles. Since most of the insulation is provided by air, overhead power lines are generally the lowest-cost method of power transmission for large quantities of electric energy.
A duplex communication system is a point-to-point system composed of two or more connected parties or devices that can communicate with one another in both directions. Duplex systems are employed in many communications networks, either to allow for simultaneous communication in both directions between two connected parties or to provide a reverse path for the monitoring and remote adjustment of equipment in the field. There are two types of duplex communication systems: full-duplex (FDX) and half-duplex (HDX).
Most of the terms listed in Wikipedia glossaries are already defined and explained within Wikipedia itself. However, glossaries like this one are useful for looking up, comparing and reviewing large numbers of terms together. You can help enhance this page by adding new terms or writing definitions for existing ones.