
Frauenzell Abbey was a Benedictine monastery situated in Frauenzell, which is part of Brennberg in Bavaria, Germany.
Metten Abbey, or St. Michael's Abbey at Metten is a house of the Benedictine Order in Metten near Deggendorf, situated between the fringes of the Bavarian Forest and the valley of the Danube, in Bavaria in Germany.

Ilmmünster Abbey was a collegiate foundation (Kollegiatstift) of canons, formerly a Benedictine monastery, in Ilmmünster, Bavaria, Germany. The church continues in use as a parish church.

Wessobrunn Abbey was a Benedictine monastery near Weilheim in Bavaria, Germany.

Oberalteich Abbey was a Benedictine monastery in Bogen, Bavaria, Germany.

Beuerberg Abbey, formerly a monastery of the Augustinian Canons, is now the Monastery of the Visitation, Beuerberg, a community of the Visitandines in Eurasburg in Bavaria, Germany.

Garsten Abbey is a former Benedictine monastery located in Garsten near Steyr in Upper Austria. Since 1851, the former monastery buildings have accommodated a prison.

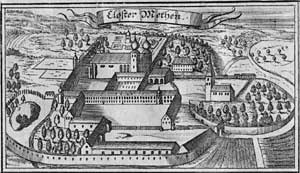
Seeon Abbey is a former Benedictine monastery in the municipality of Seeon-Seebruck in the rural district of Traunstein in Bavaria, Germany.

Wettenhausen Abbey was an Imperial Abbey of Augustinian Canons until its secularization in 1802–1803. Being one of the 40-odd self-ruling Imperial Abbeys of the Holy Roman Empire, Wettenhaussen Abbey was a virtually independent state. Its abbot had seat and voice in the Imperial Diet, where he sat on the Bench of the Prelates of Swabia. At the time of secularization, the Abbey's territory covered 56 square kilometers and it had about 5,400 subjects.

Aldersbach Abbey is a former Cistercian monastery in the community of Aldersbach in the district of Passau in the valley of the Vils, Lower Bavaria, Germany.

Schönau Abbey in Schönau in the Odenwald, in the Rhein-Neckar-Kreis in Baden-Württemberg, was a Cistercian monastery founded in 1142 from Eberbach Abbey. The present settlement of Schönau grew up round the monastery.

Baindt Abbey, otherwise the Imperial Abbey of Baindt, was a Cistercian nunnery in Baindt in the district of Ravensburg in Baden-Württemberg, Germany.

St. Mang's Abbey, Füssen or Füssen Abbey was a Benedictine monastery in Füssen in Bavaria, Germany. It was founded in the 9th century, and dissolved during the post-Napoleonic secularisation of Bavaria.
Roggenburg Abbey is a Premonstratensian canonry in Roggenburg near Neu-Ulm, Bavaria, in operation between 1126 and 1802, and again from its re-foundation in 1986. Since 1992 it has been a dependent priory of Windberg Abbey in Lower Bavaria. The monastery manages a training centre and a museum, and is widely known for its almost unchanged Baroque building and the organ concerts that are held in the church.

St. Burchard's Abbey was a Benedictine monastery in Würzburg, Germany, initially known as St. Andrew's Abbey. It was the first abbey established in Würzburg, founded ca. 750. In 1464, it was transformed into a Stift.

Michaelsberg Abbey or Michelsberg Abbey, also St. Michael's Abbey, Bamberg is a former Benedictine monastery in Bamberg in Bavaria, Germany. After its dissolution in 1803 the buildings were used for the almshouse Vereinigtes Katharinen- und Elisabethen-Spital, which is still there as a retirement home. The former abbey church remains in use as the Michaelskirche.

Weilheim in Oberbayern is a town in Germany, the capital of the district Weilheim-Schongau in the south of Bavaria. Weilheim has an old city-wall, historic houses and a museum.

The Liebenau monastery was a Dominican monastery. It was located outside the city gates of Worms in today's Worms-Hochheim district.

Franz Töpsl was an Augustinian Canon Regular, provost of Polling Abbey, historian and librarian.

Kloster Engelberg is a Franciscan monastery in Grossheubach in Bavaria, Germany. In the past, a pilgrimage dedicated to a figure of Mary, documented as far back as 1406, was administered by the Capuchins after 1630. Following secularization in the early 19th century, the Capuchins eventually left and the Franciscan order took over the abbey and caring for the pilgrims. The abbey is (partially) open to the public.



















