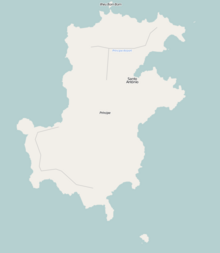
Pico de São Tomé is the highest mountain in São Tomé and Príncipe at 2,024 m (6,640 ft) elevation. It lies just west of the centre of São Tomé Island, in the Parque Natural Obô de São Tomé and in the Lembá District. The second highest point, Pico de Ana Chaves, lies about 3 km to its south east. The town Santa Catarina is 8 km to the west.

Ilhéu das Rolas is an islet in the African island nation of São Tomé and Príncipe. The island lies on the equator, off the southern tip of São Tomé Island, separated by Canal das Rolas. Its maximum elevation is 96 m. Its population is 76. It is part of the Caué District. Access is only by ferry departing from Ponta Baleia on São Tomé Island. There is a lighthouse on the islet, built in 1929. Its focal height is 106 meters and its range is 12 nmi. The island is home to a small resort, the Pestana Equador.

Ilhéu Bom Bom is an island in the Gulf of Guinea. The islet is located near the north coast of the island of Príncipe, one of the main islands of São Tomé and Príncipe and is almost completely forested. Its population is 15. There is a tourist resort near the island. There is a lighthouse on the island built in 1997. Its focal height is 64 meters and its range is 12 nmi.

Ilhéu das Cabras is an uninhabited island in the Gulf of Guinea. It is one of the smaller islands of São Tomé and Príncipe. The islet is located about 2 km off the northeast coast of the island of São Tomé, 8 km north of the city centre of São Tomé. The islet consists of two hills, about 90 metres high. There is a lighthouse on the northeastern summit, built in 1890; its focal height 97 metres and its range is 12 nmi. The islet was mentioned as "Mooro Caebres" in the 1665 map by Johannes Vingboons.

Ilhéu Caroço is an uninhabited islet in the Gulf of Guinea, part of São Tomé and Príncipe. The islet is located southeast of the island of Príncipe, about 3 km off the coast. Its area is about 0.4 km². The islet is steep, rocky and wooded, and rises to 305 metres elevation.

Tinhosa Grande is an uninhabited islet in São Tomé and Príncipe, located 23 km (14 mi) southwest of the island of Príncipe and 124 km (77 mi) northeast of the island of São Tomé. Together with the smaller islet Tinhosa Pequena, 4 kilometers to its north, it forms the Pedras Tinhosas group. It is 55 metres high, and its area is 20 hectares.

Tinhosa Pequena is an uninhabited islet in São Tomé and Príncipe, located 20 km (12 mi) southwest of the island of Príncipe and 127 km (79 mi) northeast of the island of São Tomé. Together with the larger islet Tinhosa Grande, 4 kilometers to its south, it forms the Pedras Tinhosas group. It is 64 metres high, and its area is 3 hectares.

São Sebastião Museum is a museum, housed in a 16th century fortress in the city of São Tomé, São Tomé and Príncipe. It lies in the northeastern part of the city centre, at the southeastern end of Ana Chaves Bay. It contains religious art and colonial-era artifacts. The fortress was built in 1566 by the Portuguese in order to protect the port and city of São Tomé against pirate attacks. A lighthouse was established in the fortress in 1866; it was rebuilt in 1928. The fortress was restored at the end of the 1950s.

Ana Chaves Bay is a bay on the northeast coast of São Tomé Island in São Tomé and Príncipe. The capital city of São Tomé and its port are situated by the bay. It stretches from the Ponta Oque del Rei in the north to Ponta São Sebastião in the south. Forte de São Sebastião, now part of São Sebastião Museum, occupies Ponta São Sebastião. The port of São Tomé was built at the end of the 1950s on reclaimed land that extends 0.2 miles (0.32 km) north of Ponta São Sebastião; there is a 200 m quay at its north end, with a depth of 3 metres alongside. It is the main port of the country for solid goods; the port of Neves is the main point of entry for liquid fuels. The bay is generally shallow, offering anchorage for small vessels in depths of less than 5 metres (16 ft).

Farol de Fontes Pereira de Melo is a lighthouse at the northeastern point of the island of Santo Antão in northwestern Cape Verde. It is situated on the headland Ponta de Tumbo, 2 km east of Janela, 6 km southeast of Pombas and 15 km northeast of Porto Novo. The lighthouse was named after Fontes Pereira de Melo, prime minister of Portugal for several times between 1871 and 1886. It is a white octagonal masonry tower, 16 meters high. Its focal height is 162 meters above sea level, and its range is 17 nautical miles. The adjacent building for the lighthouse keeper is abandoned and in poor condition.

São Sebastião Lighthouse is a lighthouse in the São Sebastião fortress at the southeastern end of Ana Chaves Bay in São Tomé, capital of São Tomé and Príncipe. The lighthouse is a 6 metres high white round tower with a red lantern. It was built in 1928. Its focal height is 14 metres.

Lagoa Azul Lighthouse is a lighthouse located on the headland of Lagoa Azul in the district of Lobata, northern São Tomé Island, São Tomé and Príncipe. It is 4.5 km northwest of Guadalupe and 15 km northwest of the city of São Tomé. The lighthouse was built in 1997. It is a 5 m high white tower with red bands, and its focal height is 34 m.

Vale da Custa is a village in the southeastern part of the island of Santiago, Cape Verde. It is situated 2 km northwest of São Francisco Bay, 6 km southeast of Ribeirão Chiqueiro and 9 kilometres northeast of the capital Praia. It is part of the municipality of São Domingos and the parish of Nossa Senhora da Luz. In 2010 its population was 378.

Fortaleza de Santo António da Ponta da Mina or Forte de Ponta da Mina is a ruined fort located east of the island capital Santo António in the island of Príncipe in São Tomé and Príncipe. It is located at the headland Ponta da Mina. The fortress consisted of two parts: the Bateria Real and the Bateria do Príncipe.

Pedra da Galé is an uninhabited islet in the Gulf of Guinea, part of São Tomé and Príncipe. It lies 3.7 km westnorthwest the north coast of the island of Príncipe. It is 190 meters long and up to 60 meters wide in its northern part, and four meters high. Since 2012, the islet forms a part of the Island of Príncipe Biosphere Reserve.

The Canal das Rolas is a strait of the Atlantic Ocean separating the small Ilhéu das Rolas from the southernmost point of the island of São Tomé, in São Tomé and Príncipe. It is 1.2 nautical miles wide. There is a ferry departing from Ponta Baleia on São Tomé Island to Ilhéu das Rolas.