The history of Guyana begins about 35,000 years ago with the arrival of humans coming from Eurasia. These migrants became the Carib and Arawak tribes, who met Alonso de Ojeda's first expedition from Spain in 1499 at the Essequibo River. In the ensuing colonial era, Guyana's government was defined by the successive policies of the French, Dutch, and British settlers. During the colonial period, Guyana's economy was focused on plantation agriculture, which initially depended on slave labor. Guyana saw major slave rebellions in 1763 and 1823. Following the Slavery Abolition Act of 1833, 800,000 enslaved Africans in the Caribbean and South Africa were freed, resulting in plantations contracting indentured workers, mainly from India. Eventually, these Indians joined forces with Afro-Guyanese descendants of slaves to demand equal rights in government and society. After the Second World War, the British Empire pursued policy decolonization of its overseas territories, with independence granted to British Guiana on May 26, 1966. Following independence, Forbes Burnham rose to power, quickly becoming an authoritarian leader, pledging to bring socialism to Guyana. His power began to weaken following international attention brought to Guyana in wake of the Jonestown mass murder suicide in 1978.
Essequibo is the largest traditional region of Guyana but not an administrative region of Guyana today. It may also refer to:

The Guianas, also spelled Guyanas or Guayanas, is a region in north-eastern South America. Strictly, the term refers to the three Guyanas: Guyana, Suriname and French Guiana, formerly British, Dutch and French Guyana. Broadly it refers to the South American coast from the mouth of the Oronoco to the mouth of the Amazon.

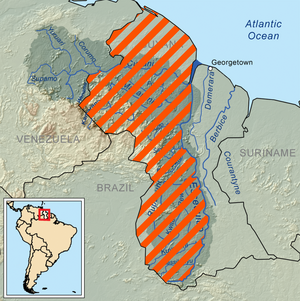
The Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela is a federation made up of twenty-three states, a Capital District and the Federal Dependencies, which consist of many islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. Venezuela claims the disputed Essequibo territory as one of its states, which it calls Guayana Esequiba, but the territory is controlled by Guyana as part of six of its regions.

Potaro-Siparuni is a region of Guyana. It borders the region of Cuyuni-Mazaruni to the north, the regions of Upper Demerara-Berbice and East Berbice-Corentyne to the east, the region of Upper Takutu-Upper Essequibo to the south and Brazil to the west.

Essequibo was a Dutch colony in the Guianas and later a county on the Essequibo River in the Guiana region on the north coast of South America. It was a colony of the Dutch West India Company between 1616 and 1792 and a colony of the Dutch state from 1792 until 1815. It was merged with Demerara in 1812 by the British who took control. It formally became a British colony in 1815 until Demerara-Essequibo was merged with Berbice to form the colony of British Guiana in 1831. In 1838, it became a county of British Guiana till 1958. In 1966, British Guiana gained independence as Guyana and in 1970 it became a republic as the Co-operative Republic of Guyana. It was located around the lower course of the Essequibo River.

Ankoko Island is an island located at the confluence of the Cuyuni River and Wenamu River, at 6°43′N61°8′W, on the border between Venezuela and Guyana.

The Rupununi uprising was a secessionist insurrection in Guyana that began on 2 January 1969 led by cattle ranchers who sought to control 22,300 square miles (58,000 km2) of land. Occurring less than two years after Guyana's independence from the United Kingdom, it constituted the country's earliest and most severe test of statehood and social solidarity. The rebels were ultimately dispersed by the Guyana Defence Force, with the group's leaders fleeing to Venezuela.

The Guyana–Venezuela territorial dispute is an ongoing territorial dispute between Guyana and Venezuela over the Essequibo region, also known as Esequibo or Guayana Esequiba in Spanish, a 159,500 km2 (61,600 sq mi) area west of the Essequibo River. The territory, excluding the Venezuelan-controlled Ankoko Island, is controlled by Guyana as part of six of its regions, based on the 1899 Paris Arbitral Award. It is also claimed by Venezuela as the Guayana Esequiba State. The boundary dispute was inherited from the colonial powers and has persisted following the independence of Venezuela and Guyana.

Guyana, officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern coast of South America, part of the historic mainland British West Indies. Guyana is an indigenous word which means "Land of Many Waters". Georgetown is the capital of Guyana and is also the country's largest city. Guyana is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, Brazil to the south and southwest, Venezuela to the west, and Suriname to the east. With a land area of 214,969 km2 (83,000 sq mi), Guyana is the third-smallest sovereign state by area in mainland South America after Uruguay and Suriname, and is the second-least populous sovereign state in South America after Suriname; it is also one of the least densely populated countries on Earth. It has a wide variety of natural habitats and very high biodiversity. The country also hosts a part of the Amazon rainforest, the largest tropical rainforest in the world.

Guyana–Venezuela relations include diplomatic, economic and other interactions between the neighboring countries of the Co-operative Republic of Guyana and the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela.

The Venezuelan crisis of 1895 occurred over Venezuela's longstanding dispute with Great Britain about the territory of Essequibo, which Britain believed was part of British Guiana and Venezuela recognized as its own Guayana Esequiba. As the dispute became a crisis, the key issue became Britain's refusal to include in the proposed international arbitration the territory east of the "Schomburgk Line", which a surveyor had drawn half-a-century earlier as a boundary between Venezuela and the former Dutch territory ceded by the Dutch in the Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1814, later part of British Guiana. The crisis ultimately saw Britain accept the United States' intervention in the dispute to force arbitration of the entire disputed territory, and tacitly accept the US right to intervene under the Monroe Doctrine. A tribunal convened in Paris in 1898 to decide the matter, and in 1899 awarded the bulk of the disputed territory to British Guiana.

United Kingdom–Venezuela relations are the bilateral relations between the United Kingdom and Venezuela since 1821 when so-called "British Legions" of former British soldiers fought to defend the Second Republic of Venezuela against Spanish royalists in the Venezuelan War of Independence.

The Tigri Area is a wooded area that has been disputed by Guyana and Suriname since around 1840. It involves the area between the Upper Corentyne River, the Coeroeni River, and the Kutari River. This triangular area is known as the New River Triangle in Guyana. In 1969 the conflict ran high on, and since then it has been controlled by Guyana and claimed by Suriname. In 1971, both governments agreed that they would continue talks over the border issue and withdraw their military forces from the disputed triangle. Guyana has never held upon this agreement.

The Agreement to resolve the conflict between Venezuela and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland over the border between Venezuela and British Guiana, better known as the Geneva Agreement, is a treaty between Venezuela and the United Kingdom, along with its colony of British Guiana, that was signed in Geneva, Switzerland, on 17 February 1966. The treaty outlines the steps taken to resolve the territorial dispute between Venezuela and the United Kingdom, arising from Venezuela's contention to the UN in 1962 that the 1899 declaration by the Paris Tribunal of Arbitration awarding the territory to British Guiana was null and void, following the publication of Severo Mallet-Prevost's memorandums and other documents from the tribunal that called the decision into question.
Valerie Aurelia Hart was a Guyanese indigenous political leader from the Wapishana ethnic group and a member of Guyana's Amerindian Party, opposed to the Forbes Burnham government; she ran for the 1968 general elections, although she was not elected. She was exiled after participating in the Rupununi uprising.
Events in the year 2023 in Guyana.

A consultative referendum was initiated by the government of Nicolás Maduro regarding Venezuela's claim over the Guayana Esequiba, whose territory is disputed with, and controlled by, neighboring Guyana. The referendum took place on 3 December 2023 in Venezuela. The population of the territory in question was not consulted and did not vote as voting only took place within Venezuela.

The long-standing territorial dispute over the Essequibo region escalated into a crisis in 2023. The region is controlled by Guyana but is claimed by Venezuela. The dispute dates back many years and the current border was established by the Paris Arbitral Award in 1899. Venezuela renewed its claim in 1962 and the matter was referred to the International Court of Justice (ICJ) in 2018.

The Paris Arbitral Award is an arbitral award issued on 3 October 1899 by an arbitral tribunal convened in Paris, created two years earlier as established in the Arbitral Treaty of Washington D. C. on 2 February 1897, in which the United States on the one hand and the United Kingdom on the other, had agreed to submit to international arbitration the dispute over the border to the west of the British colony and the east of independent Venezuela, as a mechanism for an amicable solution to the territorial differendum.