Well logging, also known as borehole logging is the practice of making a detailed record of the geologic formations penetrated by a borehole. The log may be based either on visual inspection of samples brought to the surface or on physical measurements made by instruments lowered into the hole. Some types of geophysical well logs can be done during any phase of a well's history: drilling, completing, producing, or abandoning. Well logging is performed in boreholes drilled for the oil and gas, groundwater, mineral and geothermal exploration, as well as part of environmental and geotechnical studies.
A mud engineer works on an oil well or gas well drilling rig, and is responsible for ensuring the properties of the drilling fluid, also known as drilling mud, are within designed specifications.

In geotechnical engineering, drilling fluid, also known as drilling mud, is used to aid the drilling of boreholes into the earth. Used while drilling oil and natural gas wells and on exploration drilling rigs, drilling fluids are also used for much simpler boreholes, such as water wells.

A derrickhand or derrickman is the person who sits atop the derrick on a drilling rig. Though the exact duties vary from rig to rig, they almost always report directly to the driller. Their job is to guide the stands of the drill pipe into the fingers at the top of the derrick. Other duties might include monitoring pH and calcium levels, viscosity and the mud weight (density), adding chemicals and oil based fluids, and being responsible for the shale shakers and mud pump.

Shale shakers are components of drilling equipment used in many industries, such as coal cleaning, mining, oil and gas drilling.They are the first phase of a solids control system on a drilling rig, and are used to remove large solids (cuttings) from the drilling fluid ("mud").

Drill cuttings are broken bits of solid material removed from a borehole drilled by rotary, percussion, or auger methods and brought to the surface in the drilling mud. Boreholes drilled in this way include oil or gas wells, water wells, and holes drilled for geotechnical investigations or mineral exploration.
The annulus of an oil well or water well is any void between any piping, tubing or casing and the piping, tubing, or casing immediately surrounding it. It is named after the corresponding geometric concept. The presence of an annulus gives the ability to circulate fluid in the well, provided that excess drill cuttings have not accumulated in the annulus, preventing fluid movement and possibly sticking the pipe in the borehole.
Spontaneous potential log, commonly called the self potential log or SP log, is a passive measurement taken by oil industry well loggers to characterise rock formation properties. The log works by measuring small electric potentials between depths with in the borehole and a grounded electrode at the surface. Conductive bore hole fluids are necessary to create a SP response, so the SP log cannot be used in nonconductive drilling muds or air filled holes.

A mud tank is an open-top container, typically made of square steel tube and steel plate, to store drilling fluid on a drilling rig. They are also called mud pits, as they were once simple pits in the earth.
A flow line, used on a drilling rig, is a large diameter pipe that is connected to the bell nipple and extends to the possum belly and acts as a return line, to the mud.
A Bell nipple is a section of large diameter pipe fitted to the top of the blowout preventers that the flow line attaches to via a side outlet, to allow the drilling fluid to flow back over the shale shakers to the mud tanks.
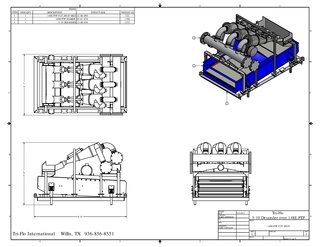
Desanders and desilters are solid control equipment with a set of hydrocyclones that separate sand and silt from the drilling fluids in drilling rigs. Desanders are installed on top of the mud tank following the shale shaker and the degasser, but before the desilter. The desander removes the abrasive solids from the drilling fluids which cannot be removed by shakers. Normally, the solid diameters for desanders to separate would be 45~74μm, and 15~44μm for desilters.
In oil or gas well drilling, lost circulation occurs when drilling fluid, known commonly as "mud", flows into one or more geological formations instead of returning up the annulus. Lost circulation can be a serious problem during the drilling of an oil well or gas well.

Effective solids control can be attributed to the overall performance of all the components of the mud systems. Conditioning the drilling fluid with the goal of dramatically lowering maintenance cost, avoiding excessive chemical treatment and maintaining mud systems volume will decrease the chance of equipment failure, unnecessary high mud costs, hole and drilling problems.

Mud Gas Separator is commonly called a gas-buster or poor boy degasser. It captures and separates the large volumes of free gas within the drilling fluid. If there is a "kick" situation, this vessel separates the mud and the gas by allowing it to flow over baffle plates. The gas then is forced to flow through a line, venting to a flare. A "kick" situation happens when the annular hydrostatic pressure in a drilling well temporarily falls below that of the formation, or pore, pressure in a permeable section downhole, and before control of the situation is lost.

Solids control is a process used in drilling rigs which use drilling fluid. It involves separating the "cuttings" from the fluid, allowing it to be recirculated or discharged to the environment.

Tight oil is light crude oil contained in unconventional petroleum-bearing formations of low permeability, often shale or tight sandstone. Economic production from tight oil formations requires the same hydraulic fracturing and often uses the same horizontal well technology used in the production of shale gas. While sometimes called "shale oil", tight oil should not be confused with oil shale or shale oil. Therefore, the International Energy Agency recommends using the term "light tight oil" for oil produced from shales or other very low permeability formations, while the World Energy Resources 2013 report by the World Energy Council uses the terms "tight oil" and "shale-hosted oil".

Fracking is a well stimulation technique involving the fracturing of formations in bedrock by a pressurized liquid. The process involves the high-pressure injection of "fracking fluid" into a wellbore to create cracks in the deep-rock formations through which natural gas, petroleum, and brine will flow more freely. When the hydraulic pressure is removed from the well, small grains of hydraulic fracturing proppants hold the fractures open.

Fracking in the United Kingdom started in the late 1970s with fracturing of the conventional oil and gas fields near the North Sea. It was used in about 200 British onshore oil and gas wells from the early 1980s. The technique attracted attention after licences use were awarded for onshore shale gas exploration in 2008. The topic received considerable public debate on environmental grounds, with a 2019 high court ruling ultimately banning the process. The two remaining high-volume fracturing wells were supposed to be plugged and decommissioned in 2022.











