A check-raise in poker is a common deceptive play in which a player checks early in a betting round, hoping someone else will open. The player who checked then raises in the same round.
In poker, the strength of a hand is often called its value; however, in the context of poker strategy the term is more often used to describe a betting tactic, a bet for value. This bet is intended to increase the size of the pot, by inducing opponents to call. A bet for value is in contrast to a bluff or a protection bet.
Protection in poker is a bet made with a strong but vulnerable hand, such as top pair when straight or flush draws are possible. The bet forces opponents with draws to either call with insufficient pot odds, or to fold, both of which are profitable for the betting player. By contrast, if he failed to protect his hand, another player could draw out on him at no cost, meaning he gets no value from his made hand.
In the game of poker, opens and raises are considered aggressive plays, while calls and checks are considered passive. It is said that "aggression has its own value", meaning that often aggressive plays can make money with weak hands because of bluff value. In general, opponents must respond to aggressive play by playing more loosely, which offers more opportunities to make mistakes.
In the game of poker, the play largely centers on the act of betting, and as such, a protocol has been developed to speed up play, lessen confusion, and increase security while playing. Different games are played using different types of bets, and small variations in etiquette exist between cardrooms, but for the most part the following rules and protocol are observed by the majority of poker players.

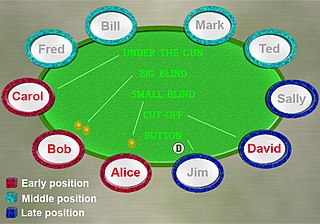
Texas hold 'em is a variation of the card game of poker. Two cards, known as hole cards, are dealt face down to each player, and then five community cards are dealt face up in three stages. The stages consist of a series of three cards, later an additional single card, and a final card. Each player seeks the best five card poker hand from any combination of the seven cards of the five community cards and their two hole cards. Players have betting options to check, call, raise, or fold. Rounds of betting take place before the flop is dealt and after each subsequent deal. The player who has the best hand and has not folded by the end of all betting rounds wins all of the money bet for the hand, known as the pot.
Slow playing is a deceptive play in poker where a player bets weakly or passively with a strong holding. It is the opposite of fast playing. A flat call can be a form of slow playing. The objective of slow playing is to lure opponents into a pot who might fold to a raise, or to cause them to bet more strongly than they would if the player had played aggressively. Slow playing sacrifices protection against hands that may improve and risks losing the pot-building value of a bet if the opponent also checks.
The fundamental theorem of poker is a principle first articulated by David Sklansky that he believes expresses the essential nature of poker as a game of decision-making in the face of incomplete information.

Jack "Treetop" Straus was an American professional poker player.
A big bet (BB) is the larger of two fixed bet amounts in a fixed-limit poker game. A big bet is used in the final rounds of a game to increase the pot amount and thereby enable the possibility of a bluff. Big bets are generally double the wager of the initial or small bet. Any multi-round poker game can use big bets to standardize wagers while maintaining a sufficient risk-ratio to encourage bluffing. Casino poker tables use big bets to set a limit to the amount of money a patron can lose in each wager.
Morton's theorem is a poker principle articulated by Andy Morton in a Usenet poker newsgroup. It states that in multi-way pots, a player's expectation may be maximized by an opponent making a correct decision.

Badugi is a draw poker variant similar to triple draw, with hand-values similar to lowball. The betting structure and overall play of the game is identical to a standard poker game using blinds, but, unlike traditional poker which involves a minimum of five cards, players' hands contain only four cards at any one time. During each of three drawing rounds, players can trade zero to four cards from their hands for new ones from the deck, in an attempt to form the best badugi hand and win the pot. Badugi is an often gambling game, with the object being to win money in the form of pots. The winner of the pot is the person with the best badugi hand at the conclusion of play. Badugi is played in cardrooms around the world, as well as online, in rooms such as PokerStars. Although it doesn’t have its own tournament per se at the WSOP, it is featured in the Dealers Choice events as well as in the Triple Draw Mix.

High Stakes Poker is a cash game poker television program, which was broadcast by the cable television network GSN in the United States. The poker variant played on the show is no limit Texas hold 'em. It premiered on January 16, 2006 and ended on December 17, 2007 for the first 4 seasons and the last 3 seasons ran from March 1, 2009 to May 21, 2011 and was simulcast in 3DTV on N3D.
Cash games, also sometimes referred to as ring games or live action games, are poker games played with "real" chips and money at stake, usually with no predetermined end time, with players able to enter and leave as they see fit. In contrast, a poker tournament is played with tournament chips worth nothing outside the tournament, with a definite end condition, and a specific roster of competitors.
Negative freeroll is a term used in poker. It refers to a situation, usually occurring in no-limit or pot-limit when contemplating an all-in wager, where the player acting first checks in a situation where they would be forced to call an opponent's final bet. If the opponent has a stronger hand, the opponent will most likely bet and the player will call and lose all their money regardless. However, if the opponent has a weaker hand, betting may be the only way to get the opponent's money into the pot, as checking allows the opponent the opportunity to check in turn.
The following is a glossary of poker terms used in the card game of poker. It supplements the glossary of card game terms. Besides the terms listed here, there are thousands of common and uncommon poker slang terms. This is not intended to be a formal dictionary; precise usage details and multiple closely related senses are omitted here in favor of concise treatment of the basics.
Poker is a popular card game that combines elements of chance and strategy. There are various styles of poker, all of which share an objective of presenting the least probable or highest-scoring hand. A poker hand is usually a configuration of five cards depending on the variant, either held entirely by a player or drawn partly from a number of shared, community cards. Players bet on their hands in a number of rounds as cards are drawn, employing various mathematical and intuitive strategies in an attempt to better opponents.






