
The characteristic impedance or surge impedance (usually written Z0) of a uniform transmission line is the ratio of the amplitudes of voltage and current of a single wave propagating along the line; that is, a wave travelling in one direction in the absence of reflections in the other direction. Alternatively, and equivalently, it can be defined as the input impedance of a transmission line when its length is infinite. Characteristic impedance is determined by the geometry and materials of the transmission line and, for a uniform line, is not dependent on its length. The SI unit of characteristic impedance is the ohm.

In electrical engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable or other structure designed to conduct electromagnetic waves in a contained manner. The term applies when the conductors are long enough that the wave nature of the transmission must be taken into account. This applies especially to radio-frequency engineering because the short wavelengths mean that wave phenomena arise over very short distances. However, the theory of transmission lines was historically developed to explain phenomena on very long telegraph lines, especially submarine telegraph cables.
In electrical engineering, the maximum power transfer theorem states that, to obtain maximum external power from a power source with internal resistance, the resistance of the load must equal the resistance of the source as viewed from its output terminals. Moritz von Jacobi published the maximum power (transfer) theorem around 1840; it is also referred to as "Jacobi's law".
In statistics, maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) is a method of estimating the parameters of an assumed probability distribution, given some observed data. This is achieved by maximizing a likelihood function so that, under the assumed statistical model, the observed data is most probable. The point in the parameter space that maximizes the likelihood function is called the maximum likelihood estimate. The logic of maximum likelihood is both intuitive and flexible, and as such the method has become a dominant means of statistical inference.
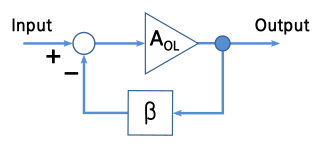
A negative-feedback amplifier is an electronic amplifier that subtracts a fraction of its output from its input, so that negative feedback opposes the original signal. The applied negative feedback can improve its performance and reduces sensitivity to parameter variations due to manufacturing or environment. Because of these advantages, many amplifiers and control systems use negative feedback.
In mathematical analysis, Hölder's inequality, named after Otto Hölder, is a fundamental inequality between integrals and an indispensable tool for the study of Lp spaces.

The output impedance of an electrical network is the measure of the opposition to current flow (impedance), both static (resistance) and dynamic (reactance), into the load network being connected that is internal to the electrical source. The output impedance is a measure of the source's propensity to drop in voltage when the load draws current, the source network being the portion of the network that transmits and the load network being the portion of the network that consumes.
In electrical engineering and electronics, a network is a collection of interconnected components. Network analysis is the process of finding the voltages across, and the currents through, all network components. There are many techniques for calculating these values; however, for the most part, the techniques assume linear components. Except where stated, the methods described in this article are applicable only to linear network analysis.
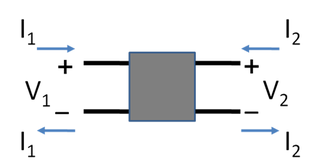
In electronics, a two-port network is an electrical network or device with two pairs of terminals to connect to external circuits. Two terminals constitute a port if the currents applied to them satisfy the essential requirement known as the port condition: the current entering one terminal must equal the current emerging from the other terminal on the same port. The ports constitute interfaces where the network connects to other networks, the points where signals are applied or outputs are taken. In a two-port network, often port 1 is considered the input port and port 2 is considered the output port.
In probability theory and statistics, the generalized extreme value (GEV) distribution is a family of continuous probability distributions developed within extreme value theory to combine the Gumbel, Fréchet and Weibull families also known as type I, II and III extreme value distributions. By the extreme value theorem the GEV distribution is the only possible limit distribution of properly normalized maxima of a sequence of independent and identically distributed random variables. Note that a limit distribution needs to exist, which requires regularity conditions on the tail of the distribution. Despite this, the GEV distribution is often used as an approximation to model the maxima of long (finite) sequences of random variables.
Scattering parameters or S-parameters describe the electrical behavior of linear electrical networks when undergoing various steady state stimuli by electrical signals.

In electronics, a current divider is a simple linear circuit that produces an output current (IX) that is a fraction of its input current (IT). Current division refers to the splitting of current between the branches of the divider. The currents in the various branches of such a circuit will always divide in such a way as to minimize the total energy expended.
Ripple in electronics is the residual periodic variation of the DC voltage within a power supply which has been derived from an alternating current (AC) source. This ripple is due to incomplete suppression of the alternating waveform after rectification. Ripple voltage originates as the output of a rectifier or from generation and commutation of DC power.

An attenuator is an electronic device that reduces the power of a signal without appreciably distorting its waveform.
The telegrapher's equations are a pair of coupled, linear partial differential equations that describe the voltage and current on an electrical transmission line with distance and time. The equations come from Oliver Heaviside who developed the transmission line model starting with an August 1876 paper, On the Extra Current. The model demonstrates that the electromagnetic waves can be reflected on the wire, and that wave patterns can form along the line.
Image impedance is a concept used in electronic network design and analysis and most especially in filter design. The term image impedance applies to the impedance seen looking into a port of a network. Usually a two-port network is implied but the concept can be extended to networks with more than two ports. The definition of image impedance for a two-port network is the impedance, Zi 1, seen looking into port 1 when port 2 is terminated with the image impedance, Zi 2, for port 2. In general, the image impedances of ports 1 and 2 will not be equal unless the network is symmetrical with respect to the ports.
Constant k filters, also k-type filters, are a type of electronic filter designed using the image method. They are the original and simplest filters produced by this methodology and consist of a ladder network of identical sections of passive components. Historically, they are the first filters that could approach the ideal filter frequency response to within any prescribed limit with the addition of a sufficient number of sections. However, they are rarely considered for a modern design, the principles behind them having been superseded by other methodologies which are more accurate in their prediction of filter response.
A quarter-wave impedance transformer, often written as λ/4 impedance transformer, is a transmission line or waveguide used in electrical engineering of length one-quarter wavelength (λ), terminated with some known impedance. It presents at its input the dual of the impedance with which it is terminated.

An RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.
Performance modelling is the abstraction of a real system into a simplified representation to enable the prediction of performance. The creation of a model can provide insight into how a proposed or actual system will or does work. This can, however, point towards different things to people belonging to different fields of work.













