Related Research Articles

Huntington's disease (HD), also known as Huntington's chorea, is an incurable neurodegenerative disease that is mostly inherited. The earliest symptoms are often subtle problems with mood or mental/psychiatric abilities. A general lack of coordination and an unsteady gait often follow. It is also a basal ganglia disease causing a hyperkinetic movement disorder known as chorea. As the disease advances, uncoordinated, involuntary body movements of chorea become more apparent. Physical abilities gradually worsen until coordinated movement becomes difficult and the person is unable to talk. Mental abilities generally decline into dementia, depression, apathy, and impulsivity at times. The specific symptoms vary somewhat between people. Symptoms usually begin between 30 and 50 years of age, and can start at any age but are usually seen around the age of 40. The disease may develop earlier in each successive generation. About eight percent of cases start before the age of 20 years, and are known as juvenile HD, which typically present with the slow movement symptoms of Parkinson's disease rather than those of chorea.

Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is a genetic neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by mild-to-moderate intellectual disability. The average IQ in males with FXS is under 55, while about two thirds of affected females are intellectually disabled. Physical features may include a long and narrow face, large ears, flexible fingers, and large testicles. About a third of those affected have features of autism such as problems with social interactions and delayed speech. Hyperactivity is common, and seizures occur in about 10%. Males are usually more affected than females.
Repeated sequences are short or long patterns that occur in multiple copies throughout the genome. In many organisms, a significant fraction of the genomic DNA is repetitive, with over two-thirds of the sequence consisting of repetitive elements in humans. Some of these repeated sequences are necessary for maintaining important genome structures such as telomeres or centromeres.
In genetics, anticipation is a phenomenon whereby as a genetic disorder is passed on to the next generation, the symptoms of the genetic disorder become apparent at an earlier age with each generation. In most cases, an increase in the severity of symptoms is also noted. Anticipation is common in trinucleotide repeat disorders, such as Huntington's disease and myotonic dystrophy, where a dynamic mutation in DNA occurs. All of these diseases have neurological symptoms. Prior to the understanding of the genetic mechanism for anticipation, it was debated whether anticipation was a true biological phenomenon or whether the earlier age of diagnosis was related to heightened awareness of disease symptoms within a family.

Non-Mendelian inheritance is any pattern in which traits do not segregate in accordance with Mendel's laws. These laws describe the inheritance of traits linked to single genes on chromosomes in the nucleus. In Mendelian inheritance, each parent contributes one of two possible alleles for a trait. If the genotypes of both parents in a genetic cross are known, Mendel's laws can be used to determine the distribution of phenotypes expected for the population of offspring. There are several situations in which the proportions of phenotypes observed in the progeny do not match the predicted values.

Spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA) is a progressive, degenerative, genetic disease with multiple types, each of which could be considered a neurological condition in its own right. An estimated 150,000 people in the United States have a diagnosis of spinocerebellar ataxia at any given time. SCA is hereditary, progressive, degenerative, and often fatal. There is no known effective treatment or cure. SCA can affect anyone of any age. The disease is caused by either a recessive or dominant gene. In many cases people are not aware that they carry a relevant gene until they have children who begin to show signs of having the disorder. Currently, research is being conducted at Universities, such as the University of Minnesota, to elucidate many of the unknown characteristics of the disease.
In genetics, trinucleotide repeat disorders, a subset of microsatellite expansion diseases, are a set of over 30 genetic disorders caused by trinucleotide repeat expansion, a kind of mutation in which repeats of three nucleotides increase in copy numbers until they cross a threshold above which they cause developmental, neurological or neuromuscular disorders. In addition to the expansions of these trinucleotide repeats, expansions of one tetranucleotide (CCTG), five pentanucleotide, three hexanucleotide, and one dodecanucleotide (CCCCGCCCCGCG) repeat cause 13 other diseases. Depending on its location, the unstable trinucleotide repeat may cause defects in a protein encoded by a gene; change the regulation of gene expression; produce a toxic RNA, or lead to production of a toxic protein. In general, the larger the expansion the faster the onset of disease, and the more severe the disease becomes.
The Sherman paradox was a term used to describe the anomalous pattern of inheritance found in fragile X syndrome. The phenomenon is also referred to as anticipation or dynamic mutation.

FMR1 is a human gene that codes for a protein called fragile X messenger ribonucleoprotein, or FMRP. This protein, most commonly found in the brain, is essential for normal cognitive development and female reproductive function. Mutations of this gene can lead to fragile X syndrome, intellectual disability, premature ovarian failure, autism, Parkinson's disease, developmental delays and other cognitive deficits. The FMR1 premutation is associated with a wide spectrum of clinical phenotypes that affect more than two million people worldwide.
Slipped strand mispairing is a mutation process which occurs during DNA replication. It involves denaturation and displacement of the DNA strands, resulting in mispairing of the complementary bases. Slipped strand mispairing is one explanation for the origin and evolution of repetitive DNA sequences.
A trinucleotide repeat expansion, also known as a triplet repeat expansion, is the DNA mutation responsible for causing any type of disorder categorized as a trinucleotide repeat disorder. These are labelled in dynamical genetics as dynamic mutations. Triplet expansion is caused by slippage during DNA replication, also known as "copy choice" DNA replication. Due to the repetitive nature of the DNA sequence in these regions, 'loop out' structures may form during DNA replication while maintaining complementary base pairing between the parent strand and daughter strand being synthesized. If the loop out structure is formed from the sequence on the daughter strand this will result in an increase in the number of repeats. However, if the loop out structure is formed on the parent strand, a decrease in the number of repeats occurs. It appears that expansion of these repeats is more common than reduction. Generally, the larger the expansion the more likely they are to cause disease or increase the severity of disease. Other proposed mechanisms for expansion and reduction involve the interaction of RNA and DNA molecules.
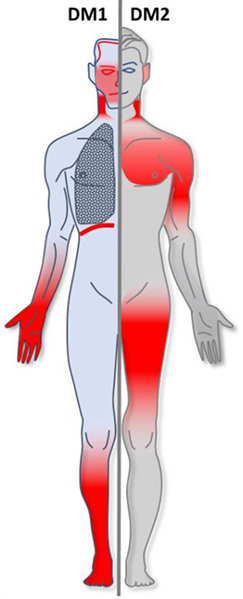
Myotonic dystrophy (DM) is a type of muscular dystrophy, a group of genetic disorders that cause progressive muscle loss and weakness. In DM, muscles are often unable to relax after contraction. Other manifestations may include cataracts, intellectual disability and heart conduction problems. In men, there may be early balding and infertility. While myotonic dystrophy can occur at any age, onset is typically in the 20s and 30s.
In genetics, a dynamic mutation is an unstable heritable element where the probability of expression of a mutant phenotype is a function of the number of copies of the mutation. That is, the replication product (progeny) of a dynamic mutation has a different likelihood of mutation than its predecessor. These mutations, typically short sequences repeated many times, give rise to numerous known diseases, including the trinucleotide repeat disorders.
A polyglutamine tract or polyQ tract is a portion of a protein consisting of a sequence of several glutamine units. A tract typically consists of about 10 to a few hundred such units.
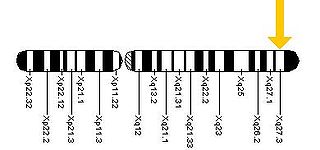
Fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS) is a late-onset neurodegenerative disorder most frequently seen in male premutation carriers of Fragile X syndrome (FXS) over the age of 50. The main clinical features of FXTAS include problems of movement with cerebellar gait ataxia and action tremor. Associated features include parkinsonism, cognitive decline, and dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. FXTAS is found in Fragile X "premutation" carriers, which is defined as a trinucleotide repeat expansion of 55-200 CGG repeats in the Fragile X mental retardation-1 (FMR1) gene. 4-40 CGG repeats in this gene is considered normal, while individual with >200 repeats have full Fragile X Syndrome.
Fragile X-associated primary ovarian insufficiency (FXPOI) is the most common genetic cause of premature ovarian failure in women with a normal karyotype 46,XX. The expansion of a CGG repeat in the 5' untranslated region of the FMR1 gene from the normal range of 5-45 repeats to the premutation range of 55-199 CGGs leads to risk of FXPOI for ovary-bearing individuals. About 1:150-1:200 women in the US population carry a premutation. Women who carry an FMR1 premutation have a roughly 20% risk of being diagnosed with FXPOI, compared to 1% for the general population, and an 8-15% risk of developing the neurogenerative tremor/ataxia disorder (FXTAS). FMR1 premutation women are also at increased risk of having a child with a CGG repeat that is expanded to >200 repeats. Individuals with a full mutation, unlike the premutation, produce little to no mRNA or protein from the FMR1 gene and have fragile X syndrome as a result.
Ying-Hui Fu is a Taiwanese-American biologist and human geneticist who has made important contributions to understanding the genetics of many neurological disorders. Her chief discoveries include describing Mendelian sleep phenotypes, identifying causative genes and mutations for circadian rhythm disorders, and characterizing genetic forms of demyelinating degenerative disorders. Fu is currently a professor of neurology at the University of California, San Francisco. She was elected to the US National Academy of Sciences in 2018.
Nagwa Abdel Meguid is an Egyptian geneticist and 2002 winner of the L’Oreal UNESCO Award for Women in Science for Africa and the Middle East. Her research has "identified several genetic mutations that cause common syndromes such as the fragile X syndrome and Autism".
David L. Nelson is an American human geneticist, currently an associate director at the Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities Research Center (1995), and professor at the Department of Molecular and Human Genetics at Baylor College of Medicine BCM since 1999. Since 2018, he is the director at the Cancer and Cell Biology Ph.D program, and the director of Integrative Molecular and Biomedical Sciences Ph.D since 2015 at BCM.
Unstable DNA sequence are segments of genetic material that exhibit high rates of mutation or variation over time, resulting in significant genetic diversity within populations or even individual organisms.
References
- ↑ Gersen, Steven L.; Keagle, Martha B. (2008). The Principles of Clinical Cytogenetics. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 505. ISBN 9781592598335.
- ↑ "fragile X syndrome". Genetics Home Reference. April 2012. Archived from the original on 9 October 2016. Retrieved 7 October 2016.
- ↑ Walker FO (January 2007). "Huntington's disease". Lancet. 369 (9557): 218–28. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60111-1. PMID 17240289. S2CID 46151626.