Related Research Articles
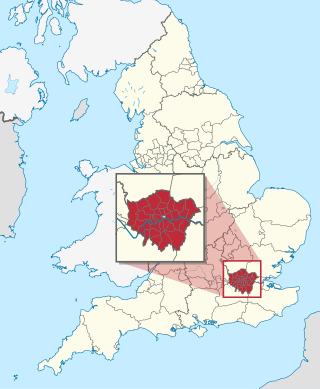
The London boroughs are the 32 local authority districts that together with the City of London make up the administrative area of Greater London, England; each is governed by a London borough council. The present London boroughs were all created at the same time as Greater London on 1 April 1965 by the London Government Act 1963 and are a type of local government district. Twelve were designated as Inner London boroughs and twenty as Outer London boroughs. The City of London, the historic centre, is a separate ceremonial county and sui generis local government district that functions quite differently from a London borough. However, the two counties together comprise the administrative area of Greater London as well as the London Region, all of which is also governed by the Greater London Authority, under the Mayor of London.
A unitary authority is a local authority responsible for all local government functions within its area or performing additional functions that elsewhere are usually performed by a higher level of sub-national government or the national government.
Local government in Wales is primarily undertaken by the twenty-two principal councils. The councils are unitary authorities, meaning they are responsible for providing local government services within their principal area, including education, social work, environmental protection, and most highway maintenance. The principal areas are divided into communities, most of which have an elected community council. The services provided by community councils vary, but they will typically maintain public spaces and facilities. Local councils in Wales are elected; the most recent local elections in Wales took place in 2022, and the next are due to take place in 2027.
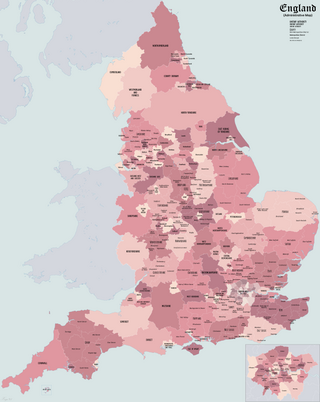
The subdivisions of England constitute a hierarchy of administrative divisions and non-administrative ceremonial areas.
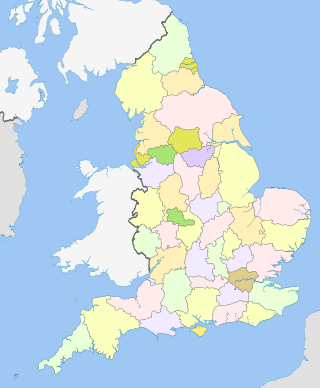
The counties of England are a type of subdivision of England. Counties have been used as administrative areas in England since Anglo-Saxon times. There are three definitions of county in England: the 48 ceremonial counties used for the purposes of lieutenancy; the 84 metropolitan and non-metropolitan counties for local government; and the 39 historic counties which were used for administration until 1974.

Ceremonial counties, formally known as counties for the purposes of the lieutenancies, are areas of England to which lord-lieutenants are appointed. They are one of the two main legal definitions of the counties of England in modern usage, the other being the counties for the purposes of local government legislation. A lord-lieutenant is the monarch's representative in an area. Shrieval counties have the same boundaries and serve a similar purpose, being the areas to which high sheriffs are appointed. High sheriffs are the monarch's judicial representative in an area.
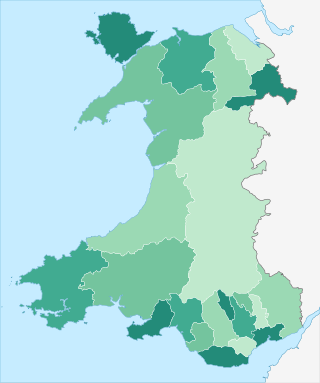
The principal areas of Wales, comprising the counties andcounty boroughs of Wales, are a form of subdivision in Wales. There are currently 22 principal areas in Wales, and they were established in 1996. They are a single-tier form of local government, each governed by a principal council. They replaced the previous two-tier system of eight counties and 32 districts that were in place in Wales from 1974 to 1996.

Local government in England broadly consists of three layers: civil parishes, local authorities, and regional authorities. Every part of England is governed by at least one local authority, but parish councils and regional authorities do not exist everywhere. In addition, there are 31 police and crime commissioners, four police, fire and crime commissioners, and ten national park authorities with local government responsibilities. Local government is not standardised across the country, with the last comprehensive reform taking place in 1974.

Colwyn was a local government district with borough status from 1974 to 1996, being one of six districts in the county of Clwyd, north-east Wales.

The Borough of Aberconwy was a local government district with borough status from 1974 to 1996, being one of five districts in the county of Gwynedd, north-west Wales.

The Borough of Arfon was local government district with borough status from 1974 to 1996, being one of five districts in the county of Gwynedd, north-west Wales.

Dwyfor was one of the five local government districts of Gwynedd, Wales from 1974 to 1996, covering the Llŷn peninsula. Its council was based in Pwllheli.

The Local Government Act 1972 is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974. It was one of the most significant Acts of Parliament to be passed by the Heath Government of 1970–74.

The Local Government (Wales) Act 1994 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which amended the Local Government Act 1972 to create the current local government structure in Wales of 22 unitary authority areas, referred to as principal areas in the Act, and abolished the previous two-tier structure of counties and districts. It came into effect on 1 April 1996.

The Lieutenancies Act 1997 is an Act of Parliament in the United Kingdom that defines areas that lord-lieutenants are appointed to in Great Britain. It came into force on 1 July 1997.

The Local Government Act 1933 was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that consolidated and revised existing legislation that regulated local government in England and Wales. It remained the principal legislation regulating local government until the Local Government Act 1972 took effect in 1974.

Gwynedd Council, which calls itself by its Welsh name Cyngor Gwynedd, is the governing body for the county of Gwynedd, one of the principal areas of Wales. The council administrates internally using the Welsh language.
The history of local government in Wales in a recognisably modern form emerged during the late 19th century. Administrative counties and county boroughs were first established in Wales in 1889. Urban and rural districts were formed in 1894. These were replaced in 1974 by a two-tier authority system across the country comprising eight counties and, within them, thirty-seven districts. This system was itself replaced by the introduction of 22 single-tier authorities in 1996.
The History of local government districts in Buckinghamshire began in 1835 with the formation of poor law unions. This was followed by the creation of various forms of local government body. In 1894 the existing arrangements were replaced with a system of municipal boroughs, urban and rural districts, which remained in place until 1974. Between 1974 and 2020 there were five non-metropolitan districts in the county, one of which became a unitary authority in 1997. The other four districts were abolished in 2020 when the rest of the county was placed under the Buckinghamshire Council unitary authority.
A principal council is a local government authority carrying out statutory duties in a principal area in England and Wales.