Administrative
Principal areas
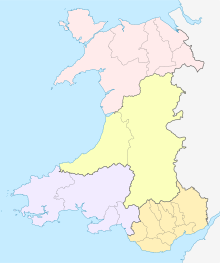
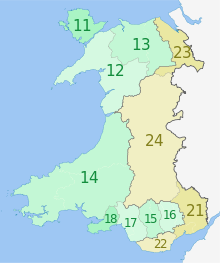
There are 22 principal areas of Wales. They were established on 1 April 1996 by the Local Government (Wales) Act 1994 (1994 c. 19). Eleven are styled "counties", including the cities of Cardiff and Swansea, and eleven are styled "county boroughs", including the cities of Newport and Wrexham. [1] [2] [3]
The location of each council headquarters is indicated by a yellow marker. County boroughs are marked by a dagger (†).
 |
|
| Areas marked † are county boroughs, while unmarked areas are counties. Welsh-language forms are given alongside the English where they differ. | |
Name changes
Some of the principal areas use different names to those given in the Local Government (Wales) Act 1994. In each case the council renamed the area immediately, with the changes taking effect on 2 April 1996. [4] The changes were:
- Conwy from "Aberconwy and Colwyn"
- Isle of Anglesey from "Anglesey"
- Gwynedd from "Caernarfonshire and Merionethshire"
- Ceredigion from "Cardiganshire"
Other smaller changes were also made, such as:
- Neath Port Talbot from "Neath and Port Talbot"
Communities
At the lowest level of administrative subdivision in Wales are the communities, into which each principal area is subdivided. They may have elected community councils which perform a number of roles, such as providing local facilities, and representing their communities to larger local government bodies. Community councils are the equivalent of English parish councils. A community council may call itself a "town council" if it so wishes. The councils of three communities with city status – Bangor, St Asaph, and St Davids – are known as "city councils". Communities which are too small to have a council may have a community meeting instead: an example of direct democracy. The communities in the urban areas of the cities of Cardiff, Swansea and Newport do not have community councils. [5] [6] [7]