Related Research Articles

In the United Kingdom, a scheduled monument is a nationally important archaeological site or historic building, given protection against unauthorised change.
A national scenic area (NSA) is a conservation designation used in several countries.
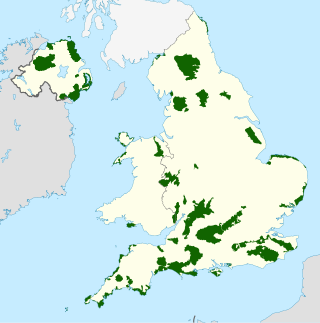
An Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty is one of 46 areas of countryside in England, Wales, or Northern Ireland that has been designated for conservation due to its significant landscape value. Since 2023, the areas in England and Wales have also adopted the name National Landscapes.
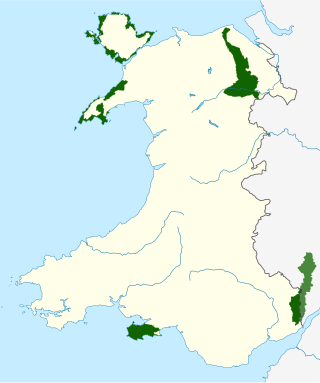
There are five Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONBs) in Wales, known from November 2023 as National Landscapes. AONBs are areas of countryside that have been designated for statutory protection, due to their significant landscape value, by initially the Government of the United Kingdom and later Welsh devolved bodies. Of the current five areas designated, four are wholly in Wales, with another spanning the Wales-England border, and in total AONBs account for 4% of Wales' land area.

The Bristol Channel is a major inlet in the island of Great Britain, separating South Wales and South West England. It extends from the smaller Severn Estuary of the River Severn to the North Atlantic Ocean. It takes its name from the English city and port of Bristol.
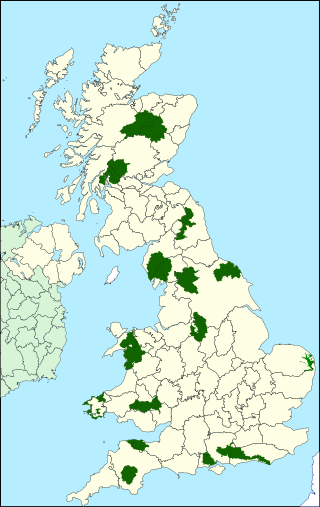
National parks of the United Kingdom are 15 areas of relatively undeveloped and scenic landscape across the country. Despite their name, they are quite different from national parks in many other countries, which are usually owned and managed by governments as protected community resources, and which do not usually include permanent human communities. In the United Kingdom, an area designated as a national park may include substantial settlements and human land uses that are often integral parts of the landscape. Land within national parks remains largely in private ownership. These parks are therefore not "national parks" according to the internationally accepted standard of the IUCN but they are areas of outstanding landscape where planning controls are a little more restrictive than elsewhere.

The Blackdown Hills, or Blackdowns, are a range of hills along the Somerset-Devon border in south-western England. The plateau is dominated by hard chert bands of Upper Greensand with some remnants of chalk, and is cut through by river valleys.
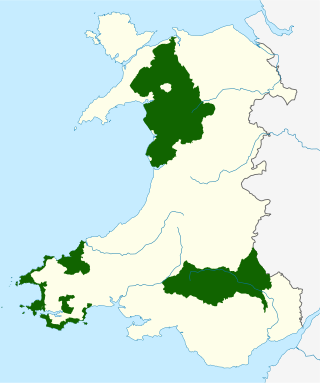
The national parks of Wales are managed areas of outstanding landscape in Wales, United Kingdom where some forms of development are restricted to preserve the landscape and natural environment. Together, they cover 20% of the land surface of Wales and have a resident population of over 80,000 people. Each National Park Authority is a free-standing body within the local government framework.

The Wye Valley is a valley in Wales and England. The River Wye is the fourth-longest river in the United Kingdom.

The North Devon Coast is a designated Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty in Devon, England, designated in September 1959. The AONB contributes to a family of protected landscapes in the Southwest of England and a total of 38% of the region is classified by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as Category V Protected Landscapes. The twelve Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty extend to 30% of the region, twice the proportion covered by AONBs in England as a whole and a further two National Parks, Dartmoor and Exmoor, cover an additional 7%.

The Culm Measures are a thick sequence of geological strata originating during the Carboniferous Period that occur in south-west England, principally in Devon and Cornwall, now known as the Culm Supergroup. Its estimated thickness varies between 3600 m and 4750 m though intense folding complicates it at outcrop. They are so called because of the occasional presence in the Barnstaple–Hartland area of a soft, often lenticular, sooty coal, which is known in Devon as culm. The word culm may be derived from the Old English word for coal col or from the Welsh word cwlwm meaning knot.

Tamar Valley National Landscape is a legally designated Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty in Devon and Cornwall in England. It includes an area of 75 square miles (190 km2) covering the lower parts of the valleys of the River Tamar, River Tavy and River Lynher to the north and west of Plymouth.

The South Devon National Landscape covers 337 square kilometres, including much of the South Hams area of Devon and the rugged coastline from Jennycliff Bay to Elberry Cove near Brixham. The purpose of an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty is to conserve and enhance the area's natural beauty. In South Devon this includes: undeveloped coastline, estuaries, geological and geomorphological features, expansive panoramic views, ancient agricultural field pattern, Devon banks, areas of high tranquility, dark night skies and natural nightscapes, historic features, green lanes, well known cultural associations, picturesque villages and hamlets. South Devon AONB was formally designated in August 1960 under the National Parks and Access to the Countryside Act 1949. The highest point in the AONB is Blackdown Camp at 199 metres above sea level.

The Solway Coast is a designated Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty in northern Cumbria, England. It incorporates two areas of coastline along the Solway Firth, the first running from just north of the city of Carlisle, at the estuary of the rivers Esk and Eden, in a westerly direction as far as Silloth-on-Solway, including the villages of Bowness-on-Solway, Burgh-by-Sands, Port Carlisle, and Skinburness. The second area begins just north of the hamlet of Beckfoot, and runs south down the coast to the southern end of Allonby Bay near the village of Crosscanonby. Included in this area are the villages of Mawbray and Allonby, and the hamlets of Dubmill, Hailforth and Salta. The hamlet of Wolsty lies just outside the AONB. Beginning at Silloth, the B5300 coast road runs in a south-westerly direction, entering the AONB just north of Beckfoot, and exiting near Crosscanonby.

Wales, a country that is part of the United Kingdom, contains protected areas under various designations. The largest designation by land area is Wales' three national parks, followed by the five Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty.

The Cornwall National Landscape covers 958 square kilometres (370 sq mi) in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom; that is, about 27% of the total area of the county. It comprises 12 separate areas, designated under the National Parks and Access to the Countryside Act 1949 for special landscape protection. Of the areas, eleven cover stretches of coastline; the twelfth is Bodmin Moor. The areas are together treated as a single Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB): all AONBs have been rebranded as National Landscapes since November 2023. Section 85 of the Countryside and Rights of Way Act 2000 places a duty on all relevant authorities when discharging any function affecting land within an AONB to have regard to the purpose of conserving and enhancing natural beauty. Section 89 places a statutory duty on Local Planning Authorities with an AONB within their administrative area to produce a 5-year management plan.

North Devon's Biosphere Reserve is a UNESCO biosphere reserve in North Devon. It covers 55 square miles (140 km2) and is centred on Braunton Burrows, the largest sand dune system (psammosere) in England. The boundaries of the reserve follow the edges of the conjoined catchment basin of the Rivers Taw and the Torridge and stretch out to sea to include the island of Lundy. The biosphere reserve is primarily lowland farmland, and includes many protected sites including 63 Sites of Special Scientific Interest which protect habitats such as culm grassland and broadleaved woodlands. The most populous settlements in its buffer area are Barnstaple, Bideford, Northam, Ilfracombe, and Okehampton.

The Clwydian Range and Dee Valley is a designated Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty located in north-east Wales, covering the Clwydian Range, and the valley of the River Dee.

Dorset National Landscape is a National Landscape area in Dorset, southern England, formerly known as and still legally designated as the Dorset Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB). The conservation designation means that the area is protected and promoted for its landscape value. The area was established in 1959, one of the early wave of National Landscapes to receive the designation.
References
- ↑ "Heritage coasts: definition, purpose and Natural England's role". GOV.UK. Retrieved 27 January 2017.
- ↑ "Heritage Coasts". Natural England. The National Archives. Archived from the original on 5 June 2014. Retrieved 27 January 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ↑ Natural England, East Riding of Yorkshire's National Nature Reserves (NNRs), updated 21 September 2023, accessed 27 May 2024