Related Research Articles

All Souls' Day, also called The Commemoration of All the Faithful Departed, is a day of prayer and remembrance for the faithful departed, observed by Christians on 2 November. Through prayer, intercessions, alms and visits to cemeteries, people commemorate the poor souls in purgatory and give the departed their favorite indulgences.

The Mass of Paul VI, also known as the Ordinary Form or Novus Ordo, is the most commonly used liturgy in the Catholic Church. It was promulgated by Pope Paul VI in 1969 and its liturgical books were published in 1970; those books were then revised in 1975, they were revised again by Pope John Paul II in 2000, and a third revision was published in 2002.

The Tridentine Mass, also known as the Traditional Latin Mass or the Traditional Rite, is the liturgy in the Roman Missal of the Catholic Church codified in 1570 and published thereafter with amendments up to 1962. Celebrated almost exclusively in Ecclesiastical Latin, it was the most widely used Eucharistic liturgy in the world from its issuance in 1570 until the introduction of the Mass of Paul VI.

In the teaching of the Catholic Church, an indulgence is "a way to reduce the amount of punishment one has to undergo for (forgiven) sins". The Catechism of the Catholic Church describes an indulgence as "a remission before God of the temporal punishment due to sins whose guilt has already been forgiven, which the faithful Christian who is duly disposed gains under certain prescribed conditions…"

A Pontifical High Mass, also called Solemn Pontifical Mass, is a Solemn or High Mass celebrated by a bishop using certain prescribed ceremonies. Although in modern English the word "pontifical" is almost exclusively associated with the pope, any bishop may be properly called a pontiff. Thus, the celebrant of a Pontifical High Mass may be the pope, any bishop or any other prelate who is allowed to wear pontificals.
Low Mass is a Tridentine Mass defined officially in the Code of Rubrics included in the 1962 edition of the Roman Missal as a Mass in which the priest does not chant the parts that the rubrics assign to him. A sung Mass celebrated with the assistance of sacred ministers is a High or Solemn Mass; without them it is a Missa Cantata.

A Papal Mass is the Solemn Pontifical High Mass celebrated by the Pope. It is celebrated on such occasions as a papal coronation, an ex cathedra pronouncement, the canonization of a saint, on Easter or Christmas or other major feast days.

Episcopal sandals, also known as pontifical sandals, are a Catholic pontifical vestment worn by bishops when celebrating liturgical functions according to the pre–Vatican II rubrics, for example a Tridentine Solemn Pontifical Mass.

Divine Mercy Sunday is a feast day that is observed in the Roman Rite calendar, as well as some Anglo-Catholics of the Church of England. It is celebrated on the Second Sunday of Easter, which concludes the Octave of Easter. It is originally based on the Catholic devotion to the Divine Mercy that Faustina Kowalska reported as part of her encounter with Jesus, and is associated with special promises from Jesus and indulgences issued by the Catholic Church.

A tabernacle or a sacrament house is a fixed, locked box in which the Eucharist is stored as part of the "reserved sacrament" rite. A container for the same purpose, which is set directly into a wall, is called an aumbry.
A Catholic order liturgical rite is a variant of a Catholic liturgical rite distinct from the typical ones, such as the Roman Rite, but instead specific to a certain Catholic religious order.

The Mass is the central liturgical service of the Eucharist in the Catholic Church, in which bread and wine are consecrated and become the body and blood of Christ. As defined by the Church at the Council of Trent, in the Mass "the same Christ who offered himself once in a bloody manner on the altar of the cross, is present and offered in an unbloody manner". The Church describes the Mass as the "source and summit of the Christian life", and teaches that the Mass is a sacrifice, in which the sacramental bread and wine, through consecration by an ordained priest, become the sacrificial body, blood, soul, and divinity of Christ as the sacrifice on Calvary made truly present once again on the altar. The Catholic Church permits only baptised members in the state of grace to receive Christ in the Eucharist.
Purgatorial societies are Roman Catholic Church associations or confraternities which aim to assist souls in purgatory reach heaven. The doctrine concerning purgatory, the condition of the poor souls after death, the communion of saints, and the satisfactory value of our good works form the basis of these associations.

An ecclesiastical ring is a finger ring worn by clergy, such as a bishop's ring.

The altar in the Catholic Church is used for celebrating the Sacrifice of the Mass.
Bination, with reference to the liturgy of the Roman Catholic Church, is the offering up of the Holy Sacrifice of the Mass twice on the same day by the same celebrant.
In the liturgy of the Catholic Church, a votive Mass is a Mass offered for a votum, a special intention. Such a Mass does not correspond to the Divine Office for the day on which it is celebrated. Every day in the year has appointed to it a series of canonical hours and a Mass corresponding, containing, for instance, the same collect and the same Gospel. On most days, the Mass will correspond to the Office, but on occasion, other Masses may be celebrated. Votive Masses appear in the Roman and Gallican Rites. The Suffrage Mass is a type of votive Mass that is celebrated in favour to some dead people.
Indulgentarium Doctrina is an apostolic constitution about indulgences issued by Pope Paul VI on 1 January 1967. It responds to suggestions made at the Second Vatican Council, it substantially revised the practical application of the traditional doctrine relating to indulgences. The title is taken from the opening words of the original Latin text.
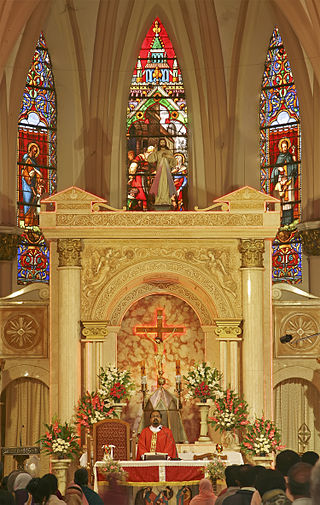
Versus populum is the liturgical stance of a priest who, while celebrating Mass, faces the people from the other side of the altar. The opposite stance, that of a priest facing in the same direction as the people, is today called ad orientem or ad apsidem.

In Roman Catholicism, the practice of Gregorian Masses is an ancient tradition in which it is believed that a continuous series of thirty consecutive Masses said in thirty days for the soul of a deceased person will release them from the punishments of Purgatory. Belief in the efficacy of the Gregorian Masses is based on a private revelation made to Pope Gregory the Great.
References
- ↑ Privileged Altar, Catholic Encyclopedia
- ↑ Gaetano Moroni (1840). Altare privilegiato (in Italian). Tipografia Emiliana. p. 280.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ↑ "Privilegium Altaris". McClintock and Strong Biblical Cyclopedia. Retrieved 27 July 2023.
- ↑ "EWTN.com - Privileged Altars" . Retrieved 21 February 2017.