Related Research Articles

Gene therapy is a medical field which focuses on the genetic modification of cells to produce a therapeutic effect or the treatment of disease by repairing or reconstructing defective genetic material. The first attempt at modifying human DNA was performed in 1980, by Martin Cline, but the first successful nuclear gene transfer in humans, approved by the National Institutes of Health, was performed in May 1989. The first therapeutic use of gene transfer as well as the first direct insertion of human DNA into the nuclear genome was performed by French Anderson in a trial starting in September 1990. It is thought to be able to cure many genetic disorders or treat them over time.

In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell in a cell lineage. They are found in both embryonic and adult organisms, but they have slightly different properties in each. They are usually distinguished from progenitor cells, which cannot divide indefinitely, and precursor or blast cells, which are usually committed to differentiating into one cell type.
Anti-thymocyte globulin (ATG) is an infusion of horse or rabbit-derived antibodies against human T cells and their precursors (thymocytes), which is used in the prevention and treatment of acute rejection in organ transplantation and therapy of aplastic anemia due to bone marrow insufficiency.
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood in order to replicate inside of a patient and to produce additional normal blood cells. It may be autologous, allogeneic or syngeneic.

Graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) is a syndrome, characterized by inflammation in different organs. GvHD is commonly associated with bone marrow transplants and stem cell transplants.
Metachromatic leukodystrophy (MLD) is a lysosomal storage disease which is commonly listed in the family of leukodystrophies as well as among the sphingolipidoses as it affects the metabolism of sphingolipids. Leukodystrophies affect the growth and/or development of myelin, the fatty covering which acts as an insulator around nerve fibers throughout the central and peripheral nervous systems. MLD involves cerebroside sulfate accumulation. Metachromatic leukodystrophy, like most enzyme deficiencies, has an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern.

Cell therapy is a therapy in which viable cells are injected, grafted or implanted into a patient in order to effectuate a medicinal effect, for example, by transplanting T-cells capable of fighting cancer cells via cell-mediated immunity in the course of immunotherapy, or grafting stem cells to regenerate diseased tissues.
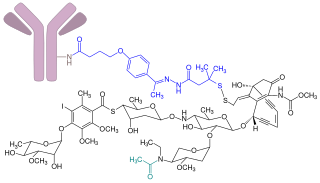
Gemtuzumab ozogamicin, sold under the brand name Mylotarg, is an antibody-drug conjugate that is used to treat acute myeloid leukemia.
Stem-cell therapy is the use of stem cells to treat or prevent a disease or condition. As of 2016, the only established therapy using stem cells is hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. This usually takes the form of a bone-marrow transplantation, but the cells can also be derived from umbilical cord blood. Research is underway to develop various sources for stem cells as well as to apply stem-cell treatments for neurodegenerative diseases and conditions such as diabetes and heart disease.

Plerixafor, sold under the brand name Mozobil, is an immunostimulant used to mobilize hematopoietic stem cells in cancer patients into the bloodstream. The stem cells are then extracted from the blood and transplanted back to the patient. The drug was developed by AnorMED, which was subsequently bought by Genzyme.

Ruxolitinib, sold under the brand name Jakafi among others, is a medication used for the treatment of intermediate or high-risk myelofibrosis, a type of myeloproliferative neoplasm that affects the bone marrow; polycythemia vera, when there has been an inadequate response to or intolerance of hydroxyurea; and steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease. Ruxolitinib is a Janus kinase inhibitor. It was developed and marketed by Incyte Corp in the US under the brand name Jakafi, and by Novartis elsewhere in the world, under the brand name Jakavi.

Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) also known as mesenchymal stromal cells or medicinal signaling cells are multipotent stromal cells that can differentiate into a variety of cell types, including osteoblasts, chondrocytes, myocytes and adipocytes.
Adult mesenchymal stem cells are being used by researchers in the fields of regenerative medicine and tissue engineering to artificially reconstruct human tissue which has been previously damaged. Mesenchymal stem cells are able to differentiate, or mature from a less specialized cell to a more specialized cell type, to replace damaged tissues in various organs.

Pluri Inc., formerly Pluristem Therapeutics, is an Israeli company engaged in the development of human placental adherent stromal cells for commercial use in disease treatment. According to the company's website, it extracts adult stem cells exclusively from postnatal placentas.
Osiris Therapeutics, Inc. was founded in March 1993 following the identification of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) by Dr. Arnold Caplan and colleagues at Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland Ohio. This was years before Geron and Advanced Cell Sciences appeared and garnered massive public attention for their stem cell work. Dr. Caplan contributed a license to the technology and joined Kevin Kimberlin, James S. Burns, a biotech venture capitalist, and Peter Friedli, a "high-tech financier" and lead investor, to launch Osiris; Caplan and Burns had named the company after the Egyptian god of the "lower world". Early financing was provided by a number of entities, including Three Arch Bay Health Sciences Fund of Mountain View, California, Burns and a New York-based acquaintance of Burns. Almost immediately the company tried launching an initial public offering (IPO), but the petition was withdrawn due to low investor interest. By 1994, the state of Maryland had determined that they wanted Osiris to be based in their state, and state officials engineered a loan and equity investment which successfully lured the company from Ohio by 1995.
TK is an experimental cell therapy which may be used to treat high-risk leukemia. It is currently undergoing a Phase III clinical trial to determine efficacy and clinical usefulness.
Mesoblast Limited is an Australian-based regenerative medicine company. It seeks to provide treatments for inflammatory ailments, cardiovascular disease and back pain. The company is led by Silviu Itescu, who founded the company in 2004.

Venetoclax, sold under the brand names Venclexta and Venclyxto, is a medication used to treat adults with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), or acute myeloid leukemia (AML).

Shimon Slavin, M.D., is an Israeli professor of medicine. Slavin pioneered the use of immunotherapy mediated by allogeneic donor lymphocytes and innovative methods for stem cell transplantation for the cure of hematological malignancies and solid tumors, and using hematopoietic stem cells for induction of transplantation tolerance to bone marrow and donor allografts.

Selinexor sold under the brand name Xpovio among others, is a selective inhibitor of nuclear export used as an anti-cancer medication. It works by blocking the action of exportin 1 and thus blocking the transport of several proteins involved in cancer-cell growth from the cell nucleus to the cytoplasm, which ultimately arrests the cell cycle and leads to apoptosis. It is the first drug with this mechanism of action.
References
- 1 2 "Prochymal - First Stem Cell Drug Approved". 22 May 2012.
- ↑ Waltz, Emily (2013-12-01). "Mesoblast acquires Osiris' stem cell business". Nature Biotechnology. 31 (12): 1061. doi: 10.1038/nbt1213-1061 . ISSN 1546-1696. S2CID 32036070.
- ↑ Caplan, Arnold I. (2017-04-28). "Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Time to Change the Name!". Stem Cells Translational Medicine. 6 (6): 1445–1451. doi:10.1002/sctm.17-0051. ISSN 2157-6564. PMC 5689741 . PMID 28452204.
- ↑ "A Stem-Cell-Based Drug Gets Approval in Canada". 17 May 2012.
- ↑ Osiris Therapeutics, Inc. Form S-1 Registration Statement under the Securities Act of 1933. May 12, 2020.
- ↑ Sheikh, Knvul and Thomas, Katie. More Coronavirus Vaccines and Treatments Head Toward Human Trials. April 8, 2020, May 2, 2020
- ↑ "Osiris Therapeutics Announces Preliminary Results for Prochymal Phase III GvHD Trials". 8 Sep 2009.