
Aerodynamics, from Ancient Greek: ἀήρ aero (air) + Ancient Greek: δυναμική (dynamics), is the study of the motion of air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It involves topics covered in the field of fluid dynamics and its subfield of gas dynamics. The term aerodynamics is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, the difference being that "gas dynamics" applies to the study of the motion of all gases, and is not limited to air. The formal study of aerodynamics began in the modern sense in the eighteenth century, although observations of fundamental concepts such as aerodynamic drag were recorded much earlier. Most of the early efforts in aerodynamics were directed toward achieving heavier-than-air flight, which was first demonstrated by Otto Lilienthal in 1891. Since then, the use of aerodynamics through mathematical analysis, empirical approximations, wind tunnel experimentation, and computer simulations has formed a rational basis for the development of heavier-than-air flight and a number of other technologies. Recent work in aerodynamics has focused on issues related to compressible flow, turbulence, and boundary layers and has become increasingly computational in nature.

Wind tunnels are large tubes with air blowing through them which are used to replicate the interaction between air and an object flying through the air or moving along the ground. Researchers use wind tunnels to learn more about how an aircraft will fly. NASA uses wind tunnels to test scale models of aircraft and spacecraft. Some wind tunnels are large enough to contain full-size versions of vehicles. The wind tunnel moves air around an object, making it seem as if the object is flying.

Transonic flow is air flowing around an object at a speed that generates regions of both subsonic and supersonic airflow around that object. The exact range of speeds depends on the object's critical Mach number, but transonic flow is seen at flight speeds close to the speed of sound, typically between Mach 0.8 and 1.2.

The Langley Research Center, located in Hampton, Virginia, United States of America, is the oldest of NASA's field centers. Near the Chesapeake Bay front of Langley Air Force Base. LaRC has focused primarily on aeronautical research but has also tested space hardware such as the Apollo Lunar Module. In addition, many of the earliest high-profile space missions were planned and designed on-site. Langley was also considered a potential site for NASA's Manned Spacecraft Center prior to the eventual selection of Houston, Texas.

The Arnold Engineering Development Complex (AEDC), Arnold Engineering Development Center before July 2012, is an Air Force Materiel Command facility under the control of the Air Force Test Center (AFTC). Headquartered at Arnold Air Force Base, Tennessee, the Complex also operates from geographically separated units at Ames Research Center, Mountain View and Edwards AFB, California; Peterson AFB, Colorado; Eglin AFB, Florida; the Federal Research Center at White Oak, Maryland; Holloman AFB, Kirtland AFB, and White Sands Missile Range, New Mexico; Wright-Patterson AFB, Ohio, and Hill AFB, Utah. AEDC operates more than 68 test facilities, including, but not limited to, aerodynamic and propulsion wind tunnels, rocket and turbine engine test cells, environmental chambers, arc heaters, ballistic ranges, sled tracks, centrifuges, and other specialized test units.
Arnold Air Force Base is a United States Air Force base located in Coffee and Franklin counties, Tennessee, adjacent to the city of Tullahoma. It is named for General Henry "Hap" Arnold, the father of the U.S. Air Force.
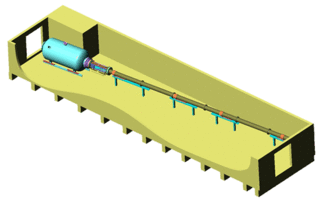
A Ludwieg tube is a cheap and efficient way of producing supersonic flow. Mach numbers up to 4 in air are easily obtained without any additional heating of the flow. With heating, Mach numbers of up to 11 can be reached.

The Unitary Plan Wind Tunnel, located at the NASA Ames Research Center in Moffett Federal Airfield, Mountain View, California, United States, is a research facility used extensively to design and test new generations of aircraft, both commercial and military, as well as NASA space vehicles, including the Space Shuttle. The facility was completed in 1955 and is one of five facilities created after the 1949 Unitary Plan Act supporting aeronautics research.
The University of Texas at Arlington Aerodynamics Research Center (ARC) is a facility located in the southeast portion of the campus operated under the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering. It was established in 1986 as part of an expansion of UTA's College of Engineering. The ARC contributes to the vision of UTA and the University of Texas System to transform the university into a full-fledged research institution. It showcases the aerodynamics research activities at UTA and, in its history, has established itself as a unique facility at a university level. The wind tunnels and equipment in the facility were mainly built by scouting for and upgrading decommissioned equipment from the government and industry. Currently, Masters and Ph.D. students perform research in the fields of high-speed gas dynamics, propulsion, and Computational fluid dynamics among other projects related to aerodynamics.
In aeronautics, expansion and shock tunnels are aerodynamic testing facilities with a specific interest in high speeds and high temperature testing. Shock tunnels use steady flow nozzle expansion whereas expansion tunnels use unsteady expansion with higher enthalpy, or thermal energy. In both cases the gases are compressed and heated until the gases are released, expanding rapidly down the expansion chamber. The tunnels reach speeds from Mach 3 to Mach 30 to create testing conditions that simulate hypersonic to re-entry flight. These tunnels are used by military and government agencies to test hypersonic vehicles that undergo a variety of natural phenomenon that occur during hypersonic flight.
The Aeronautical/Astronautical Research Laboratory (AARL) is an aerospace engineering research facility operated by Ohio State University. It is the principal research facility of the College of Engineering's Department of Aerospace and Astronautical Engineering. It is located on the grounds of Ohio State University Airport, in Columbus, Ohio.

AEDC Aerodynamic and Propulsion Test Unit (APTU) is a blowdown hypersonic wind tunnel driven by a combustion air heater (CAH). The facility is owned by the United States Air Force and operated by Aerospace Testing Alliance.

AEDC Hypervelocity Wind Tunnel 9 is a hypersonic wind tunnel owned by the United States Air Force and operated by National Aerospace Solutions The facility can generate high Mach numbers and high Reynolds for hypersonic ground testing and the validation of computational simulations for the Air Force and Department of Defense.

The High-Enthalpy Arc-Heated Facilities at Arnold Engineering Development Complex provide aerothermal ground test simulations of hypersonic flight over a wide range of velocities and pressure altitudes in support of materials and structures development. The facility is composed of three Arc Heaters: HEAT-H1, HEAT-H2, and Heat-H3 which can heat air up to 13,000 degrees Rankine through a controlled high voltage direct current electric arc discharge. The test unit is owned by the United States Air Force and operated by National Aerospace Solutions.
The von Karman Gas Dynamics Facility at Arnold Engineering Development Complex, Arnold Air Force Base, Tennessee, provide aerothermal ground test simulations of hypersonic flight over a wide range of velocities and pressure altitudes. The facility consists of three Hypersonic wind tunnels: Tunnel A, B, and C. The wind tunnels can be run for several hours at a time thanks to a 92,500 horsepower air compressor plant system. The test unit is owned by the United States Air Force and operated by National Aerospace Solutions.
The Aero-propulsion Systems Test Facility, located at Arnold Engineering Development Complex is a unique national facility designed to test aircraft propulsion systems in true mission environments without leaving the ground. The test unit is owned by the United States Air Force and operated by National Aerospace Solutions.
The AEDC Space Chambers Test Facility, located at Arnold Engineering Development Complex, contains several test units used for simulating space conditions. The facility has a variety of test cells to accommodate various sized test articles. Test articles range in size from the sensor level all the way up to full-scale space systems. All test units in the facility are owned by the United States Air Force and currently operated by Aerospace Testing Alliance.
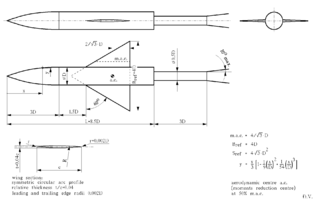
AGARD-B is a standard wind tunnel model that is used to verify, by comparison of test results with previously published data, the measurement chain in a wind tunnel. Together with its derivative AGARD-C it belongs to a family of AGARD standard wind tunnel models. Its origin dates to the year 1952, and the Second Meeting of the AGARD Wind Tunnel and Model Testing Panel in Rome, Italy, when it was decided to define two standard wind tunnel model configurations to be used for exchange of test data and comparison of test results of same models tested in different wind tunnels. The idea was to establish standards of comparison between wind tunnels and improve the validity of wind tunnel tests. Among the standard wind tunnel models, AGARD model configuration B (AGARD-B) has become by far the most popular. Initially intended for the supersonic wind tunnels, the AGARD-B configuration has since been tested in many wind tunnels at a wide range of Mach numbers, from low subsonic, through transonic to hypersonic. Therefore, a considerable database of test results is available.

The PHEDRA High Enthalpy low density Wind Tunnel, located at the ICARE Laboratory in Orléans, France, is a research facility used extensively for fundamental and applied research on non equilibrium plasma flows and planetary atmospheric entries. Its name is an acronym for soufflerie à Plasma Hors Equilibre de Rentreés Atmosphériques. Phedra wind tunnel takes part of the European Landscape Network portal MERIL.













