Related Research Articles
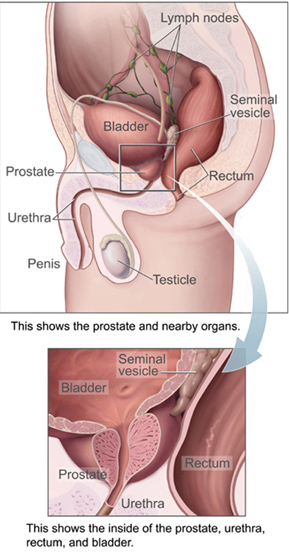
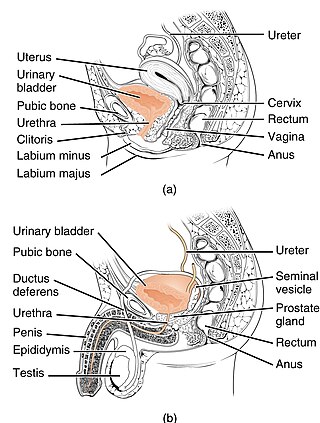
The prostate is an accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found in all male mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemically, and physiologically. Anatomically, the prostate is found below the bladder, with the urethra passing through it. It is described in gross anatomy as consisting of lobes and in microanatomy by zone. It is surrounded by an elastic, fibromuscular capsule and contains glandular tissue, as well as connective tissue.

Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), also called prostate enlargement, is a noncancerous increase in size of the prostate gland. Symptoms may include frequent urination, trouble starting to urinate, weak stream, inability to urinate, or loss of bladder control. Complications can include urinary tract infections, bladder stones, and chronic kidney problems.
Urinary incontinence (UI), also known as involuntary urination, is any uncontrolled leakage of urine. It is a common and distressing problem, which may have a large impact on quality of life. Urinary incontinence is common in older women and has been identified as an important issue in geriatric health care. The term enuresis is often used to refer to urinary incontinence primarily in children, such as nocturnal enuresis. UI is an example of a stigmatized medical condition, which creates barriers to successful management and makes the problem worse. People may be too embarrassed to seek medical help, and attempt to self-manage the symptom in secrecy from others.

A urethral stricture is a narrowing of the urethra, the tube connected to the bladder that allows urination. The narrowing reduces the flow of urine and makes it more difficult or even painful to empty the bladder.

Retrograde ejaculation occurs when semen which would be ejaculated via the urethra is redirected to the urinary bladder. Normally, the sphincter of the bladder contracts before ejaculation, inhibiting urination and preventing a reflux of semen into the bladder. The semen is forced to exit via the urethra, the path of least resistance. When the bladder sphincter does not function properly, retrograde ejaculation may occur. It can also be induced deliberately by a male as a primitive form of male birth control or as part of certain alternative medicine practices. The retrograde-ejaculated semen is excreted from the bladder during the next urination.

Urinary retention is an inability to completely empty the bladder. Onset can be sudden or gradual. When of sudden onset, symptoms include an inability to urinate and lower abdominal pain. When of gradual onset, symptoms may include loss of bladder control, mild lower abdominal pain, and a weak urine stream. Those with long-term problems are at risk of urinary tract infections.
Transurethral resection of the prostate is a urological operation. It is used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). As the name indicates, it is performed by visualising the prostate through the urethra and removing tissue by electrocautery or sharp dissection. It has been the standard treatment for BPH for many years, but recently alternative, minimally invasive techniques have become available. This procedure is done with spinal or general anaesthetic. A triple lumen catheter is inserted through the urethra to irrigate and drain the bladder after the surgical procedure is complete. The outcome is considered excellent for 80–90% of BPH patients. The procedure carries minimal risk for erectile dysfunction, moderate risk for bleeding, and a large risk for retrograde ejaculation.

Prostatectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the prostate gland. This operation is done for benign conditions that cause urinary retention, as well as for prostate cancer and for other cancers of the pelvis.
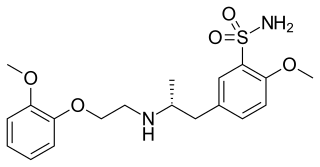
Tamsulosin, sold under the brand names including Flomax and Contiflo, is a medication used to treat symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and chronic prostatitis and to help with the passage of kidney stones. The evidence for benefit with a kidney stone is better when the stone is larger. Tamsulosin is taken by mouth.
Prostatic congestion is a medical condition of the prostate gland that happens when the prostate becomes swollen by excess fluid and can be caused by prostatitis. The condition often results in a person with prostatic congestion feeling the urge to urinate frequently. Prostatic congestion has been associated with prostate disease, which can progress due to age. Oftentimes, the prostate will grow in size which can lead to further problems, such as prostatitis, enlarged prostate, or prostate cancer.

Stress incontinence, also known as stress urinary incontinence (SUI) or effort incontinence is a form of urinary incontinence. It is due to inadequate closure of the bladder outlet by the urethral sphincter.
Saw palmetto extract is an extract of the fruit of the saw palmetto. It is marketed as a dietary supplement that may help with benign prostatic hyperplasia, but there is no clinical evidence that it is effective for this purpose.

A prostatic stent is a stent used to keep open the male urethra and allow the passing of urine in cases of prostatic obstruction and lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS). Prostatic obstruction is a common condition with a variety of causes. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is the most common cause, but obstruction may also occur acutely after treatment for BPH such as transurethral needle ablation of the prostate (TUNA), transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT), prostate cancer or after radiation therapy.
Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) refer to a group of clinical symptoms involving the bladder, urinary sphincter, urethra and, in men, the prostate. The term is more commonly applied to men – over 40% of older men are affected – but lower urinary tract symptoms also affect women. The condition is also termed prostatism in men, but LUTS is preferred.
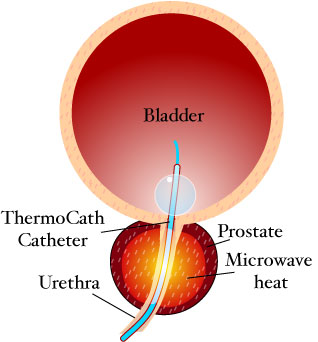
Transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT) is one of a number of effective and safe procedures used in the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms caused by benign prostatic hyperplasia. It is an alternative treatment to pharmacotherapy such as alpha blockers, transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), transurethral needle ablation of the prostate, photoselective vaporization of the prostate and prostatic removal or prostatectomy.

Prostatic artery embolization is a non-surgical technique for treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Urethral hypermobility is a condition of excessive movement of the female urethra due to a weakened urogenital diaphragm. It describes the instability of the urethra in relation to the pelvic floor muscles. A weakened pelvic floor muscle fails to adequately close the urethra and hence can cause stress urinary incontinence. This condition may be diagnosed by primary care providers or urologists. Treatment may include pelvic floor muscle exercises, surgery, or minimally invasive procedures.

If medical treatment is not effective, surgery may need to be performed for benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Aquablation therapy (AquaBeam) is a surgical procedure for men with lower urinary tract symptoms resulting from benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It is in the early stages of study. It is not categorized as minimally invasive as general anesthesia is required. The procedure was developed by PROCEPT BioRobotics and combines real-time visualization through a cystoscope and a bi-plane ultrasound, while using a high-velocity sterile saline heat-free waterjet and autonomous robotics to remove prostate tissue.
Prostate steam treatment (Rezum), also called water vapor thermal therapy (WVTT), is a minimally invasive surgical procedure for men with lower urinary tract symptoms resulting from prostate enlargement. It uses injections of steam to remove obstructive prostate tissue from the inside of the organ without injuring the prostatic part of the urinary tube.
References
- 1 2 Sountoulides, Petros; Karatzas, Anastasios; Gravas, Stavros (January 2019). "Current and emerging mechanical minimally invasive therapies for benign prostatic obstruction". Therapeutic Advances in Urology. 11: 1756287219828971. doi:10.1177/1756287219828971. ISSN 1756-2872. PMC 6376539 . PMID 30792821.
- ↑ Garcia, Cindy; Chin, Peter; Rashid, Prem; Woo, Henry H. (March 2015). "Prostatic urethral lift: A minimally invasive treatment for benign prostatic hyperplasia". Prostate International. 3 (1): 1–5. doi:10.1016/j.prnil.2015.02.002. ISSN 2287-8882. PMC 4494639 . PMID 26157759.
- 1 2 Jung, Jae Hung; Reddy, Balaji; McCutcheon, Karen Ann; Borofsky, Michael; Narayan, Vikram; Kim, Myung Ha; Dahm, Philipp (25 May 2019). "Prostatic urethral lift for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2019 (5): CD012832. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012832.pub2. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 6535104 . PMID 31128077.