
The Constitution of Canada is the supreme law in Canada. It outlines Canada's system of government and the civil and human rights of those who are citizens of Canada and non-citizens in Canada. Its contents are an amalgamation of various codified acts, treaties between the Crown and Indigenous Peoples, uncodified traditions and conventions. Canada is one of the oldest constitutional monarchies in the world.
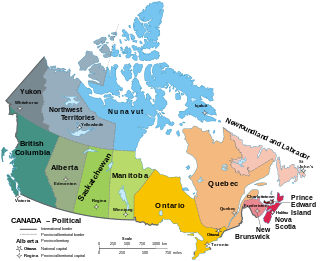
Canada has ten provinces and three territories that are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North America—New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and the Province of Canada —united to form a federation, becoming a fully independent country over the next century. Over its history, Canada's international borders have changed several times as it has added territories and provinces, making it the world's second-largest country by area.

Canadian Confederation was the process by which three British North American provinces—the Province of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick—were united into one federation called the Dominion of Canada, on July 1, 1867. Upon Confederation, Canada consisted of four provinces: Ontario and Quebec, which had been split out from the Province of Canada, and the provinces of Nova Scotia and New Brunswick. Over the years since Confederation, Canada has seen numerous territorial changes and expansions, resulting in the current number of ten provinces and three territories.
Canadian federalism involves the current nature and historical development of the federal system in Canada.

The Quebec Conference was held from October 10 to 24, 1864, to discuss a proposed Canadian confederation. It was in response to the shift in political ground when the United Kingdom and the United States had come very close to engaging in war with each other. Therefore, the overall goal of the conference was to elaborate on policies surrounding federalism and creating a single state, both of which had been discussed at the Charlottetown Conference around a month earlier. Canada West leader John A. Macdonald requested Governor-General Charles Monck to invite all representatives from the three Maritime provinces and Newfoundland to meet with the candidates who formed the United Canada to Quebec in October 1864. Although Newfoundland sent two observers, it did not participate directly in the proceedings.

The Canada Health Act, adopted in 1984, is the federal legislation in Canada for publicly-funded health insurance, commonly called "medicare", and sets out the primary objective of Canadian healthcare policy.
The Constitutional debate of Canada is an ongoing debate covering various political issues regarding the fundamental law of the country. The debate can be traced back to the Royal Proclamation, issued on October 7, 1763, following the signing of the Treaty of Paris (1763) wherein France ceded most of New France to Great Britain in favour of keeping Guadeloupe.

In macroeconomics and finance, a transfer payment is a redistribution of income and wealth by means of the government making a payment, without goods or services being received in return. These payments are considered to be non-exhaustive because they do not directly absorb resources or create output. Examples of transfer payments include welfare, financial aid, social security, and government subsidies for certain businesses.
Saskatchewan Government Insurance (SGI) is a Canadian insurance company and a Crown corporation wholly owned by the Government of Saskatchewan. SGI's operations consist of the Saskatchewan Auto Fund, the compulsory public auto insurance program for Saskatchewan, and its property and casualty insurance division sells additional automobile and property insurance products in five Canadian provinces under the trade name SGI Canada.
Regionalism is a political ideology that seeks to increase the political power, influence and self-determination of the people of one or more subnational regions. It focuses on the "development of a political or social system based on one or more" regions and/or the national, normative or economic interests of a specific region, group of regions or another subnational entity, gaining strength from or aiming to strengthen the "consciousness of and loyalty to a distinct region with a homogeneous population", similarly to nationalism. More specifically, "regionalism refers to three distinct elements: movements demanding territorial autonomy within unitary states; the organization of the central state on a regional basis for the delivery of its policies including regional development policies; political decentralization and regional autonomy".
There have been various movements within Canada for secession.
In Canada, a lieutenant governor is the representative of the King of Canada in the government of each province. The Governor General of Canada appoints the lieutenant governors on the advice of the Prime Minister of Canada to carry out most of the monarch's constitutional and ceremonial duties for an unfixed period of time—known as serving "At Her Excellency's pleasure"—though five years is the normal convention. Similar positions in Canada's three territories are termed "Commissioners" and are representatives of the federal government, not the monarch directly.
This is a list of leaders and office-holders of Canada. See also Canadian incumbents by year.

The monarchy of Canada forms the core of each Canadian provincial jurisdiction's Westminster-style parliamentary democracy, being the foundation of the executive, legislative, and judicial branches of government in each province. The monarchy has been headed since September 8, 2022 by King Charles III who as sovereign is shared equally with both the Commonwealth realms and the Canadian federal entity. He, his consort, and other members of the Canadian royal family undertake various public and private functions across the country. He is the only member of the royal family with any constitutional role.

Canada has access to all main sources of energy including oil and gas, coal, hydropower, biomass, solar, geothermal, wind, marine and nuclear. It is the world's second largest producer of uranium, third largest producer of hydro-electricity, fourth largest natural gas producer, and the fifth largest producer of crude oil. In 2006, only Russia, the People's Republic of China, the United States and Saudi Arabia produce more total energy than Canada.
Crown corporations in Canada are government organizations with a mixture of commercial and public-policy objectives. They are directly and wholly owned by the Crown.
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman provincia, which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outside Italy. The term province has since been adopted by many countries. In some countries with no actual provinces, "the provinces" is a metaphorical term meaning "outside the capital city".
The sovereignty of Canada is, in legal terms, the power of Canada to govern itself and its subjects; it is the ultimate source of Canada's law and order. Sovereignty is also a major cultural matter in Canada. Several matters currently define Canadian sovereignty: the Canadian monarchy, telecommunication, the autonomy of the provinces, and Canada's Arctic border.

Multiculturalism in Canada was officially adopted by the government during the 1970s and 1980s. The Canadian federal government has been described as the instigator of multiculturalism as an ideology because of its public emphasis on the social importance of immigration. The 1960s Royal Commission on Bilingualism and Biculturalism is often referred to as the origin of modern political awareness of multiculturalism, resulting in Canada being one of the most multicultural nations in the world. The official state policy of multiculturalism is often cited as one of Canada's significant accomplishments, and a key distinguishing element of Canadian identity and Canadian values.

Interprovincial migration in Canada is the movement by people from one Canadian province or territory to another with the intention of settling, permanently or temporarily, in the new province or territory; it is more-or-less stable over time. In fiscal year 2019–20, 278,316 Canadians migrated province, representing 0.729% of the population.








