Virus classification is the process of naming viruses and placing them into a taxonomic system similar to the classification systems used for cellular organisms.

Coxsackieviruses are a few related enteroviruses that belong to the Picornaviridae family of nonenveloped, linear, positive-sense single-stranded RNA viruses, as well as its genus Enterovirus, which also includes poliovirus and echovirus. Enteroviruses are among the most common and important human pathogens, and ordinarily its members are transmitted by the fecal–oral route. Coxsackieviruses share many characteristics with poliovirus. With control of poliovirus infections in much of the world, more attention has been focused on understanding the nonpolio enteroviruses such as coxsackievirus.

Bromoviridae is a family of viruses. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are six genera in the family.

The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) authorizes and organizes the taxonomic classification of and the nomenclatures for viruses. The ICTV has developed a universal taxonomic scheme for viruses, and thus has the means to appropriately describe, name, and classify every virus that affects living organisms. The members of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses are considered expert virologists. The ICTV was formed from and is governed by the Virology Division of the International Union of Microbiological Societies. Detailed work, such as delimiting the boundaries of species within a family, typically is performed by study groups of experts in the families.
Marnaviridae is a family of positive-stranded RNA viruses in the order Picornavirales. The first species of this family that was isolated is Heterosigma akashiwo RNA virus (HaRNAV) in the genus Marnavirus, that infects the toxic bloom-forming Raphidophyte alga, Heterosigma akashiwo. Using a sequence-based framework an additional twenty marine RNA viruses have been added to the family.

Benyvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Benyviridae. Plant serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: BNYVV: rhizomania.

Halspiviridae is a family of viruses that consists of a single genus, Salterprovirus, which consists of a single recognised species; Salterprovirus His1. This virus was isolated from hypersaline water in Australia and was able to be cultured on the halophilic archaeon Haloarcula hispanica. Like many other archaeoviruses, His1 has an approximately limoniform (lemon-shaped) virion.
Picobirnavirus is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses. It is the only genus in the family Picobirnaviridae. Although amniotes, especially mammals, were thought to serve as hosts, it has been recently suggested that these viruses might infect bacteria and possibly some other invertebrates. There are three species in this genus. Associated symptoms include gastroenteritis in animals and humans, though the disease association is unclear.

Aspiviridae, formerly Ophioviridae, is a family of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses which infect plants. Member viruses are characterized by an elongated and highly filamentous and flexible nucleocapsid with helical symmetry. It is a monotypic taxon containing only one genus, Ophiovirus. Aspiviridae is also the only family in the order Serpentovirales, which in turn is the only order in the class Milneviricetes.

Emaravirus is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses which infect plants. The plant virus group is the sole genus in the family Fimoviridae. The genus has 21 species.

Hantaviridae is a family of viruses in the order Bunyavirales. It is named for the Hantan River area in South Korea where an early outbreak of one of its species was observed.

Articulavirales is an order of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses which infect invertebrates and vertebrates. It includes the family of influenza viruses which infect humans. It is the only order of viruses in the monotypic class Insthoviricetes. The order contains two families and eight genera.

Peribunyaviridae is a family of viruses in the order Bunyavirales. Its name partially derives from Bunyamwera, Uganda, where the founding species was first isolated.
Caprine alphaherpesvirus 1 (CpHV-1) is a species of virus known to infect goats worldwide. It has been shown to produce systemic and respiratory symptoms in kids and to cause abortions in adult goats.
Panine gammaherpesvirus 1 (PnHV-1), commonly known as chimpanzee lymphocryptovirus, is a species of virus in the genus Lymphocryptovirus, subfamily Gammaherpesvirinae, family Herpesviridae, and order Herpesvirales.

Redondoviruses are a family of human-associated DNA viruses. Their name derives from the inferred circular structure of the viral genome . Redondoviruses have been identified in DNA sequence based surveys of samples from humans, primarily samples from the oral cavity and upper airway.
Pleolipoviridae is a family of DNA viruses that infect archaea.
Pisoniviricetes is a class of positive-strand RNA viruses which infect eukaryotes. A characteristic of the group is a conserved 3C-like protease from the PA clan of proteases for processing the translated polyprotein. The name of the group is a portmanteau of member orders "picornavirales, sobelivirales, nidovirales" and -viricetes which is the suffix for a virus class.
Thaspiviridae is a family of spindle-shaped viruses that is not assigned to any higher taxonomic ranks. The family contains a single genus, Nitmarvirus, which contains a single species, Nitmarvirus NSV1.
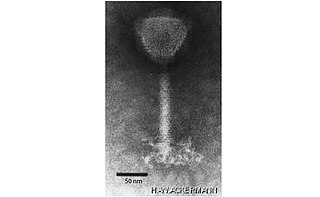
Herelleviridae is a family of bacterial viruses of the order Caudovirales infecting members of the phylum Firmicutes. The family has five subfamilies, 33 genera and 92 species.














