
The Mornington Peninsula National Park is a national park located in the Greater Melbourne region of Victoria, Australia. The 2,686-hectare (6,640-acre) national park is situated approximately 90 kilometres (56 mi) south of Melbourne on the Mornington Peninsula.

The Mornington Peninsula is a peninsula located south of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. It is surrounded by Port Phillip to the west, Western Port to the east and Bass Strait to the south, and is connected to the mainland in the north. Geographically, the peninsula begins its protrusion from the mainland in the area between Pearcedale and an area north of Frankston. The area was originally home to the Mayone-bulluk and Boonwurrung-Balluk clans, and formed part of the Boonwurrung nation's territory prior to European settlement.
Pulpit Rock may refer to:

Cape Schanck, or Tunnahan (Boonwurrung) is a locality at the southernmost tip of the Mornington Peninsula in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, approximately 72 km (45 mi) south of Melbourne's Central Business District, located within the Shire of Mornington Peninsula local government area. Cape Schanck recorded a population of 569 at the 2021 census.

Flinders is a seaside town on the Mornington Peninsula in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, 73 km (45 mi) south of Melbourne's Central Business District, located within the Shire of Mornington Peninsula local government area. Flinders recorded a population of 1,130 at the 2021 census.

Mornington is a seaside town of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia located on the Mornington Peninsula 46 km (29 mi) south-east of Melbourne's Central Business District. It is the most populous town in the Shire of Mornington Peninsula local government area. Mornington had a population of 25,759 at the 2021 census.

Arthur Merric Bloomfield Boyd was a leading Australian painter of the middle to late 20th century. Boyd's work ranges from impressionist renderings of Australian landscape to starkly expressionist figuration, and many canvases feature both. Several famous works set Biblical stories against the Australian landscape, such as The Expulsion (1947–48), now at the Art Gallery of New South Wales. Having a strong social conscience, Boyd's work deals with humanitarian issues and universal themes of love, loss and shame.

Laura is a rural town and locality in the Shire of Cook, Queensland, Australia. In the 2021 census, the locality of Laura had a population of 133 people.

Point Nepean marks the southern point of The Rip and the most westerly point of the Mornington Peninsula, in Victoria, Australia. It was named in 1802 after the British politician and colonial administrator Sir Evan Nepean by John Murray in HMS Lady Nelson. Its coast and adjacent waters are included in the Port Phillip Heads Marine National Park, while its land area is part of the Point Nepean National Park. The point includes Cheviot Beach on its southern side, notable as the site of the disappearance in 1967 of Australia's then-Prime Minister Harold Holt.

The Cape Schanck Lighthouse was built in 1859 as the second coastal lighthouse in the Australian state of Victoria. It is located on Cape Schanck, at the southernmost tip of the Mornington Peninsula. The 21 metres (69 ft) tall tower was built from limestone. The light's focal plane is situated 100 metres (330 ft) above sea level, the light characteristic is the Morse code letter "N", a long signal of 10.8 seconds followed by a flash. Depending on the bearing of the light, the colours are either white or red. Due to its powerful lantern of one million candela and a first order Fresnel lens, which was installed in 1915, the light has a range of 26 nmi (48 km).

SS Alert was a steamship that sank off Cape Schanck, Victoria, Australia on 28 December 1893. The ship was built for the gentle waters of Scottish lochs and was almost 51 m (167 ft) long and weighed 247 tonnes.

The Geelong Art Gallery, currently known as Geelong Gallery, is a major regional gallery in the city of Geelong in Victoria, Australia. The gallery has over 6,000 works of art in its collection. The Gallery forms Geelong's Cultural Precinct with the adjacent Geelong Library and Heritage Centre, Geelong Arts Centre, and the Geelong Courthouse.

South Channel Fort, also known as South Channel Island, is a 0.7 ha artificial island in southern Port Phillip, Victoria, Australia, 6 km north-east of the town of Sorrento. It was part of a network of fortifications protecting the narrow entrance to Port Phillip.
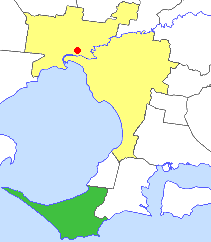
The Shire of Flinders was a local government area encompassing the extremity of the Mornington Peninsula, about 65 kilometres (40 mi) south of Melbourne, the state capital of Victoria, Australia. The shire covered an area of 324 square kilometres (125.1 sq mi), and existed from 1874 until 1994.

Alan McLeod McCulloch AO was one of Australia's foremost art critics for more than 60 years, an art historian and gallery director, cartoonist, and painter.

McCrae Homestead is an historic property located in McCrae, Victoria, Australia. It was built at the foot of Arthurs Seat, a small mountain, near the shores of Port Phillip in 1844 by Andrew McCrae, a lawyer, and his wife Georgiana Huntly McCrae, a portrait artist of note. The homestead is under the care of the National Trust of Australia, and is open to the public. Volunteers who are knowledgeable about the history of the house conduct tours and answer questions.
Dick Roughsey was an Australian Aboriginal artist from the Lardil language group on Mornington Island in the south-eastern Gulf of Carpentaria, Queensland. His tribal name was Goobalathaldin, meaning “the ocean, dancing”, describing a “rough sea”. He was an active and prominent figure involved in reviving and preserving the cultural life of the Lardil people. His best known works are a series of children's picture books that retell traditional Aboriginal stories including “The Rainbow Serpent”.

Aboriginal sites of Victoria form an important record of human occupation for probably more than 40,000 years. They may be identified from archaeological remains, historical and ethnographic information or continuing oral traditions and encompass places where rituals and ceremonies were performed, occupation sites where people ate, slept and carried out their day to day chores, and ephemeral evidence of people passing through the landscape, such as a discarded axe head or isolated artefact.

Mornington Peninsula Regional Gallery (MPRG) is a public art gallery on the Mornington Peninsula, south-east of Melbourne, Australia. The gallery opened in 1971, and holds both traditional and contemporary Australian art. The gallery is host to the National Works on Paper (NWOP) acquisitive art competition, established in 1998.

David Larwill (1956–2011) was an Australian artist recognisable by his distinctive and exuberant style based on bold colour, stylised figures and simplified form. Although best known as a figurative expressionist painter, Larwill was also a draughtsman and printmaker of note. He produced many drawings, watercolours, ceramics and sculptures as well as etchings, lithographs and screenprints. In a career that stretched over 30 years, Larwill held over 25 solo exhibitions and participated in scores of group shows.




















