The nuclear Overhauser effect (NOE) is the transfer of nuclear spin polarization from one population of spin-active nuclei to another via cross-relaxation. A phenomenological definition of the NOE in nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) is the change in the integrated intensity of one NMR resonance that occurs when another is saturated by irradiation with an RF field. The change in resonance intensity of a nucleus is a consequence of the nucleus being close in space to those directly affected by the RF perturbation.

Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy or magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), is a spectroscopic technique to observe local magnetic fields around atomic nuclei. This spectroscopy is based on the measurement of absorption of electromagnetic radiations in the radio frequency region from roughly 4 to 900 MHz. Absorption of radio waves in the presence of magnetic field is accompanied by a special type of nuclear transition, and for this reason, such type of spectroscopy is known as Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. The sample is placed in a magnetic field and the NMR signal is produced by excitation of the nuclei sample with radio waves into nuclear magnetic resonance, which is detected with sensitive radio receivers. The intramolecular magnetic field around an atom in a molecule changes the resonance frequency, thus giving access to details of the electronic structure of a molecule and its individual functional groups. As the fields are unique or highly characteristic to individual compounds, in modern organic chemistry practice, NMR spectroscopy is the definitive method to identify monomolecular organic compounds.

Solid-state NMR (ssNMR) spectroscopy is a technique for characterizing atomic level structure in solid materials e.g. powders, single crystals and amorphous samples and tissues using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The anisotropic part of many spin interactions are present in solid-state NMR, unlike in solution-state NMR where rapid tumbling motion averages out many of the spin interactions. As a result, solid-state NMR spectra are characterised by larger linewidths than in solution state NMR, which can be utilized to give quantitative information on the molecular structure, conformation and dynamics of the material. Solid-state NMR is often combined with magic angle spinning to remove anisotropic interactions and improve the resolution as well as the sensitivity of the technique.
In physics, Larmor precession is the precession of the magnetic moment of an object about an external magnetic field. The phenomenon is conceptually similar to the precession of a tilted classical gyroscope in an external torque-exerting gravitational field. Objects with a magnetic moment also have angular momentum and effective internal electric current proportional to their angular momentum; these include electrons, protons, other fermions, many atomic and nuclear systems, as well as classical macroscopic systems. The external magnetic field exerts a torque on the magnetic moment,
In MRI and NMR spectroscopy, an observable nuclear spin polarization (magnetization) is created by a homogeneous magnetic field. This field makes the magnetic dipole moments of the sample precess at the resonance (Larmor) frequency of the nuclei. At thermal equilibrium, nuclear spins precess randomly about the direction of the applied field. They become abruptly phase coherent when they are hit by radiofrequency (RF) pulses at the resonant frequency, created orthogonal to the field. The RF pulses cause the population of spin-states to be perturbed from their thermal equilibrium value. The generated transverse magnetization can then induce a signal in an RF coil that can be detected and amplified by an RF receiver. The return of the longitudinal component of the magnetization to its equilibrium value is termed spin-latticerelaxation while the loss of phase-coherence of the spins is termed spin-spin relaxation, which is manifest as an observed free induction decay (FID).

Nuclear magnetic resonance quantum computing (NMRQC) is one of the several proposed approaches for constructing a quantum computer, that uses the spin states of nuclei within molecules as qubits. The quantum states are probed through the nuclear magnetic resonances, allowing the system to be implemented as a variation of nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. NMR differs from other implementations of quantum computers in that it uses an ensemble of systems, in this case molecules, rather than a single pure state.
Insensitive nuclei enhancement by polarization transfer (INEPT) is a signal enhancement method used in NMR spectroscopy. It involves the transfer of nuclear spin polarization from spins with large Boltzmann population differences to nuclear spins of interest with lower Boltzmann population differences. INEPT uses J-coupling for the polarization transfer in contrast to Nuclear Overhauser effect (NOE), which arises from dipolar cross-relaxation. This method of signal enhancement was introduced by Ray Freeman in 1979. Due to its usefulness in signal enhancement, pulse sequences used in heteronuclear NMR experiments often contain blocks of INEPT or INEPT-like sequences.
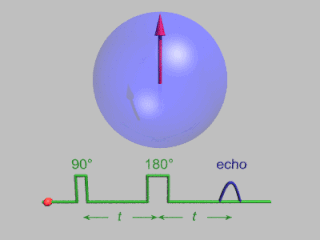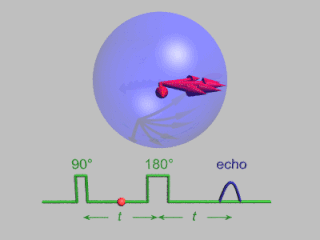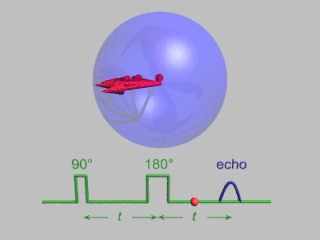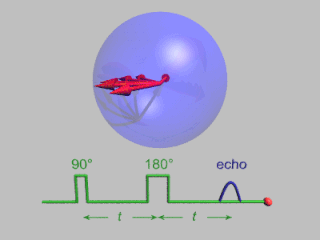
In magnetic resonance, a spin echo or Hahn echo is the refocusing of spin magnetisation by a pulse of resonant electromagnetic radiation. Modern nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) make use of this effect.

In physics, the spin–spin relaxation is the mechanism by which Mxy, the transverse component of the magnetization vector, exponentially decays towards its equilibrium value in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It is characterized by the spin–spin relaxation time, known as T2, a time constant characterizing the signal decay. It is named in contrast to T1, the spin–lattice relaxation time. It is the time it takes for the magnetic resonance signal to irreversibly decay to 37% (1/e) of its initial value after its generation by tipping the longitudinal magnetization towards the magnetic transverse plane. Hence the relation

In magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), k-space is the 2D or 3D Fourier transform of the image measured. It was introduced in 1979 by Likes and in 1983 by Ljunggren and Twieg.
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) in porous materials covers the application of using NMR as a tool to study the structure of porous media and various processes occurring in them. This technique allows the determination of characteristics such as the porosity and pore size distribution, the permeability, the water saturation, the wettability, etc.

Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon in which nuclei in a strong constant magnetic field are perturbed by a weak oscillating magnetic field and respond by producing an electromagnetic signal with a frequency characteristic of the magnetic field at the nucleus. This process occurs near resonance, when the oscillation frequency matches the intrinsic frequency of the nuclei, which depends on the strength of the static magnetic field, the chemical environment, and the magnetic properties of the isotope involved; in practical applications with static magnetic fields up to ca. 20 tesla, the frequency is similar to VHF and UHF television broadcasts (60–1000 MHz). NMR results from specific magnetic properties of certain atomic nuclei. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is widely used to determine the structure of organic molecules in solution and study molecular physics and crystals as well as non-crystalline materials. NMR is also routinely used in advanced medical imaging techniques, such as in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Electron nuclear double resonance (ENDOR) is a magnetic resonance technique for elucidating the molecular and electronic structure of paramagnetic species. The technique was first introduced to resolve interactions in electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectra. It is currently practiced in a variety of modalities, mainly in the areas of biophysics and heterogeneous catalysis.

The physics of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) concerns fundamental physical considerations of MRI techniques and technological aspects of MRI devices. MRI is a medical imaging technique mostly used in radiology and nuclear medicine in order to investigate the anatomy and physiology of the body, and to detect pathologies including tumors, inflammation, neurological conditions such as stroke, disorders of muscles and joints, and abnormalities in the heart and blood vessels among others. Contrast agents may be injected intravenously or into a joint to enhance the image and facilitate diagnosis. Unlike CT and X-ray, MRI uses no ionizing radiation and is, therefore, a safe procedure suitable for diagnosis in children and repeated runs. Patients with specific non-ferromagnetic metal implants, cochlear implants, and cardiac pacemakers nowadays may also have an MRI in spite of effects of the strong magnetic fields. This does not apply on older devices, and details for medical professionals are provided by the device's manufacturer.

Pulsed electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) is an electron paramagnetic resonance technique that involves the alignment of the net magnetization vector of the electron spins in a constant magnetic field. This alignment is perturbed by applying a short oscillating field, usually a microwave pulse. One can then measure the emitted microwave signal which is created by the sample magnetization. Fourier transformation of the microwave signal yields an EPR spectrum in the frequency domain. With a vast variety of pulse sequences it is possible to gain extensive knowledge on structural and dynamical properties of paramagnetic compounds. Pulsed EPR techniques such as electron spin echo envelope modulation (ESEEM) or pulsed electron nuclear double resonance (ENDOR) can reveal the interactions of the electron spin with its surrounding nuclear spins.

Gareth Alun Morris FRS is a Professor of Physical Chemistry, in the School of Chemistry at the University of Manchester.

Phase contrast magnetic resonance imaging (PC-MRI) is a specific type of magnetic resonance imaging used primarily to determine flow velocities. PC-MRI can be considered a method of Magnetic Resonance Velocimetry. It also provides a method of magnetic resonance angiography. Since modern PC-MRI is typically time-resolved, it provides a means of 4D imaging.
Adiabatic radio frequency (RF) pulses are used in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to achieve excitation that is insensitive to spatial inhomogeneities in the excitation field or off-resonances in the sampled object.
Mathias Nilsson is a Swedish chemist and a Professor in the Department of Chemistry at The University of Manchester. His research in general is based on physical chemistry and analytical chemistry, specifically on development and application of novel methods in Liquids NMR Spectroscopy

Cross-polarization (CP), originally published as proton-enhanced nuclear induction spectroscopy is a solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (ssNMR) technique to transfer nuclear magnetization from different types of nuclei via heteronuclear dipolar interactions. The 1H-X cross-polarization dramatically improves the sensitivity of ssNMR experiments of most experiments involving spin-1/2 nuclei, capitalizing on the higher 1H polarisation, and shorter T1(1H) relaxation times. It was developed by Michael Gibby, Alexander Pines and Professor John S. Waugh at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.










