
Adhesive, also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non-metallic substance applied to one or both surfaces of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation.
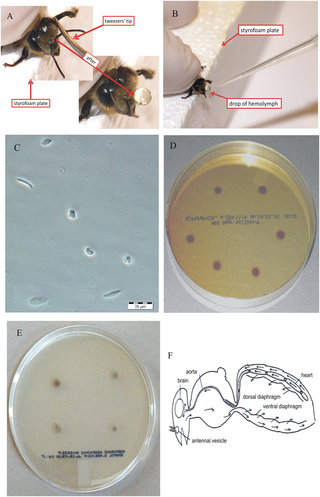
Hemolymph, or haemolymph, is a fluid, analogous to the blood in vertebrates, that circulates in the interior of the arthropod (invertebrate) body, remaining in direct contact with the animal's tissues. It is composed of a fluid plasma in which hemolymph cells called hemocytes are suspended. In addition to hemocytes, the plasma also contains many chemicals. It is the major tissue type of the open circulatory system characteristic of arthropods. In addition, some non-arthropods such as mollusks possess a hemolymphatic circulatory system.

Oriented strand board (OSB) is a type of engineered wood, formed by adding adhesives and then compressing layers of wood strands (flakes) in specific orientations. It was invented by Armin Elmendorf in California in 1963. OSB may have a rough and variegated surface with the individual strips of around 2.5 cm × 15 cm, lying unevenly across each other, and is produced in a variety of types and thicknesses.
In biology, setae are any of a number of different bristle- or hair-like structures on living organisms.

Solifugae is an order of arachnids known variously as solifuges, sun spiders, camel spiders, and wind scorpions. The order includes more than 1,000 described species in about 147 genera. Despite the common names, they are neither true scorpions nor true spiders. Because of this, it's less ambiguous to call them "solifuges". Most species of solifuge live in dry climates and feed opportunistically on ground-dwelling arthropods and other small animals. The largest species grow to a length of 12–15 cm (5–6 in), including legs. A number of urban legends exaggerate the size and speed of solifuges, and their potential danger to humans, which is negligible.

Carcinology is a branch of zoology that consists of the study of crustaceans. Crustaceans are a large class of arthropods classified by having a hard exoskeleton made of chitin or chitin and calcium, three body regions, and jointed, paired appendages. Crustaceans include lobsters, crayfish, shrimp, krill, copepods, barnacles and crabs. Most crustaceans are aquatic, but some can be terrestrial, sessile, or parasitic. Other names for carcinology are malacostracology, crustaceology, and crustalogy, and a person who studies crustaceans is a carcinologist or occasionally a malacostracologist, a crustaceologist, or a crustalogist.

Adhesion is the tendency of dissimilar particles or surfaces to cling to one another.

Surgical tape or medical tape is a type of pressure-sensitive adhesive tape used in medicine and first aid to hold a bandage or other dressing onto a wound. These tapes usually have a hypoallergenic adhesive which is designed to hold firmly onto skin, dressing materials, and underlying layers of tape, but to remove easily without damaging the skin. They allow air to reach the skin ("breathable"). Some breathable tapes such as kinesiology tape, and other elastic bandages with adhesive are made of cotton. Surgical tape is often white because it contains zinc oxide, which is added to help prevent infections. Tapes made of porous material, such as 3M Micropore, are widely used.

Arthropleura is a genus of massive millipedes that lived in what is now North America and Europe around 345 to 290 million years ago, from the Viséan stage of the lower Carboniferous Period to the Sakmarian stage of the lower Permian Period. The species of the genus are the largest known land invertebrates of all time, and would have had few, if any, predators.

Colobopsis saundersi, also called the Malaysian exploding ant, is a species of ant found in Malaysia and Brunei, belonging to the genus Colobopsis. A worker can explode suicidally and aggressively as an ultimate act of defense, an ability it has in common with several other species in this genus and a few other insects. The ant has an enormously enlarged mandibular gland, many times the size of other ants, which produces adhesive secretions for defense. According to a 2018 study, this species forms a species complex and is probably related to C. explodens, which is part of the C. cylindrica group.
The arthropod leg is a form of jointed appendage of arthropods, usually used for walking. Many of the terms used for arthropod leg segments are of Latin origin, and may be confused with terms for bones: coxa, trochanter, femur, tibia, tarsus, ischium, metatarsus, carpus, dactylus, patella.

The Entognatha are a class of wingless and ametabolous arthropods, which, together with the insects, makes up the subphylum Hexapoda. Their mouthparts are entognathous, meaning that they are retracted within the head, unlike the insects. Entognatha are apterous, meaning that they lack wings. The class contains three orders: Collembola, Diplura and Protura. These three groups were historically united with the now-obsolete order Thysanura to form the class Apterygota, but it has since been recognized that the hexapodous condition of these animals has evolved independently from that of insects, and independently within each order. The orders might not be closely related, and Entognatha is now considered to be a paraphyletic group.

Terrestrial animals are animals that live predominantly or entirely on land, as compared with aquatic animals, which live predominantly or entirely in the water, and semiaquatic animals, which rely on both aquatic and terrestrial habitats. Some groups of insects are terrestrial, such as ants, butterflies, earwigs, cockroaches, grasshoppers and many others, while other groups are partially aquatic, such as mosquitoes and dragonflies, which pass their larval stages in water.

The Worms of Kukumlima, written by Daniel Pinkwater, is a humorous book for all ages, first published in 1981.

Fuxianhuia is a genus of Lower Cambrian fossil arthropod known from the Chengjiang fauna in China. Its purportedly primitive features have led to its playing a pivotal role in discussions about the euarthropod stem group. Nevertheless, despite being known from many specimens, disputes about its morphology, in particular its head appendages, have made it one of the most controversial of the Chengjiang taxa, and it has been discussed extensively in the context of the arthropod head problem.

The Chaetonotida is an order of gastrotrichs. They generally have a tenpin or bottle-like shape.

Arthropods are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (metameric) segments, and paired jointed appendages. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. They form an extremely diverse group of up to ten million species.

Currency packaging includes several forms of packing cash for easy handling and counting. Many systems use standard color-coding or are marked to indicate the amount in the package.

Arthropods, including insects and spiders, make use of smooth adhesive pads as well as hairy pads for climbing and locomotion along non-horizontal surfaces. Both types of pads in insects make use of liquid secretions and are considered 'wet'. Dry adhesive mechanisms primarily rely on Van der Waals' forces and are also used by organisms other than insects. The fluid provides capillary and viscous adhesion and appears to be present in all insect adhesive pads. Little is known about the chemical properties of the adhesive fluids and the ultrastructure of the fluid-producing cells is currently not extensively studied. Additionally, both hairy and smooth types of adhesion have evolved separately numerous times in insects. Few comparative studies between the two types of adhesion mechanisms have been done, and there is a lack of information regarding the forces that can be supported by these systems in insects. Additionally, tree frogs and some mammals such as the arboreal possum and bats also make use of smooth adhesive pads. The use of adhesive pads for locomotion across non-horizontal surfaces is a trait that evolved separately in different species, making it an example of convergent evolution. The power of adhesion allows these organisms to be able to climb on almost any substance.
Berkshiria albistylum is a species of soldier fly in the family Stratiomyidae. Larvae can be found under the bark of poplar trees.

















