| Pyrrhocoricin | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 The firebug Pyrrhocoris apterus | |||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Symbol | ? | ||||||
| CAS number | |||||||
| PDB | 5FDV | ||||||
| UniProt | P37362 | ||||||
| |||||||
Pyrrhocoricin is a 20-residue long antimicrobial peptide of the firebug Pyrrhocoris apterus . [1]
| Pyrrhocoricin | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 The firebug Pyrrhocoris apterus | |||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Symbol | ? | ||||||
| CAS number | |||||||
| PDB | 5FDV | ||||||
| UniProt | P37362 | ||||||
| |||||||
Pyrrhocoricin is a 20-residue long antimicrobial peptide of the firebug Pyrrhocoris apterus . [1]
Pyrrhocoricin is primarily active against Gram-negative bacteria. The peptide is proline-rich with proline-arginine repeats, as well a critical threonine residue, which is required for activity through O-glycosylation. Like the antimicrobial peptides drosocin and abaecin, pyrrhocoricin binds to the bacterial protein DnaK, inhibiting cell machinery and replication. [2] Only the L-enantiomer of pyrrhocoricin is active against bacteria. [3] The action of pyrrhocoricin-like peptides is potentiated by the presence of pore-forming peptides, which facilitates the entry of pyrrhocoricin-like peptides into the bacterial cell. [4] Proline-rich peptides like Pyrrhocoricin can also bind to microbe ribosomes, preventing protein translation. [5] In the absence of pore-forming peptides, pyrrhocoricin is taken into the bacteria by the action of bacterial uptake permeases. [6]

The macrolides are a class of natural products that consist of a large macrocyclic lactone ring to which one or more deoxy sugars, usually cladinose and desosamine, may be attached. The lactone rings are usually 14-, 15-, or 16-membered. Macrolides belong to the polyketide class of natural products. Some macrolides have antibiotic or antifungal activity and are used as pharmaceutical drugs. Macrolides are bacteriostatic in that they suppress or inhibit bacterial growth rather than killing bacteria completely.
Protein targeting or protein sorting is the biological mechanism by which proteins are transported to their appropriate destinations within or outside the cell. Proteins can be targeted to the inner space of an organelle, different intracellular membranes, the plasma membrane, or to the exterior of the cell via secretion. Information contained in the protein itself directs this delivery process. Correct sorting is crucial for the cell; errors have been linked to multiple disease-states.
Bacteriocins are proteinaceous or peptidic toxins produced by bacteria to inhibit the growth of similar or closely related bacterial strain(s). They are similar to yeast and paramecium killing factors, and are structurally, functionally, and ecologically diverse. Applications of bacteriocins are being tested to assess their application as narrow-spectrum antibiotics.
Lantibiotics are a class of polycyclic peptide antibiotics that contain the characteristic thioether amino acids lanthionine or methyllanthionine, as well as the unsaturated amino acids dehydroalanine, and 2-aminoisobutyric acid. They belong to ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides.

Polymyxins are antibiotics. Polymyxins B and E are used in the treatment of Gram-negative bacterial infections. They work mostly by breaking up the bacterial cell membrane. They are part of a broader class of molecules called nonribosomal peptides.

Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), also called host defence peptides (HDPs) are part of the innate immune response found among all classes of life. Fundamental differences exist between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that may represent targets for antimicrobial peptides. These peptides are potent, broad spectrum antibiotics which demonstrate potential as novel therapeutic agents. Antimicrobial peptides have been demonstrated to kill Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria, enveloped viruses, fungi and even transformed or cancerous cells. Unlike the majority of conventional antibiotics it appears that antimicrobial peptides frequently destabilize biological membranes, can form transmembrane channels, and may also have the ability to enhance immunity by functioning as immunomodulators.
Bacterial translation is the process by which messenger RNA is translated into proteins in bacteria.

Lincosamides are a class of antibiotics, which include lincomycin, clindamycin, and pirlimycin.
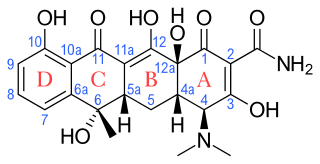
Tetracyclines are a group of broad-spectrum antibiotic compounds that have a common basic structure and are either isolated directly from several species of Streptomyces bacteria or produced semi-synthetically from those isolated compounds. Tetracycline molecules comprise a linear fused tetracyclic nucleus to which a variety of functional groups are attached. Tetracyclines are named for their four ("tetra-") hydrocarbon rings ("-cycl-") derivation ("-ine"). They are defined as a subclass of polyketides, having an octahydrotetracene-2-carboxamide skeleton and are known as derivatives of polycyclic naphthacene carboxamide. While all tetracyclines have a common structure, they differ from each other by the presence of chloride, methyl, and hydroxyl groups. These modifications do not change their broad antibacterial activity, but do affect pharmacological properties such as half-life and binding to proteins in serum.

Class II bacteriocins are a class of small peptides that inhibit the growth of various bacteria.

A protein synthesis inhibitor is a compound that stops or slows the growth or proliferation of cells by disrupting the processes that lead directly to the generation of new proteins.

Cecropins are antimicrobial peptides. They were first isolated from the hemolymph of Hyalophora cecropia, whence the term cecropin was derived. Cecropins lyse bacterial cell membranes; they also inhibit proline uptake and cause leaky membranes.

OmpT is an aspartyl protease found on the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. OmpT is a subtype of the family of omptin proteases, which are found on some gram-negative species of bacteria.

Bottromycin is a macrocyclic peptide with antibiotic activity. It was first discovered in 1957 as a natural product isolated from Streptomyces bottropensis. It has been shown to inhibit methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE) among other Gram-positive bacteria and mycoplasma. Bottromycin is structurally distinct from both vancomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic, and methicillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic.

Lipid II is a precursor molecule in the synthesis of the cell wall of bacteria. It is a peptidoglycan, which is amphipathic and named for its bactoprenol hydrocarbon chain, which acts as a lipid anchor, embedding itself in the bacterial cell membrane. Lipid II must translocate across the cell membrane to deliver and incorporate its disaccharide-pentapeptide "building block" into the peptidoglycan mesh. Lipid II is the target of several antibiotics.
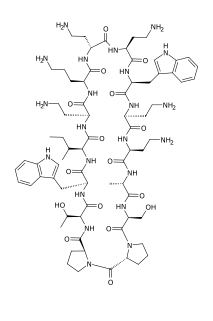
Murepavadin also known as POL7080 is a Pseudomonas specific peptidomimetic antibiotic. It is a synthetic cyclic beta hairpin peptidomimetic based on the cationic antimicrobial peptide protegrin I (PG-1) and the first example of an outer membrane protein-targeting antibiotic class with a novel, nonlytic mechanism of action, highly active and selective against the protein transporter LptD of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In preclinical studies the compound was highly active on a broad panel of clinical isolates including multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas bacteria with outstanding in vivo efficacy in sepsis, lung, and thigh infection models. Intravenous murepavadin is in development for the treatment of bacterial hospital-acquired pneumonia and bacterial ventilator-associated pneumonia due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa.

Diptericin is a 9 kDa antimicrobial peptide (AMP) of flies first isolated from the blowfly Phormia terranova. It is primarily active against Gram-negative bacteria, disrupting bacterial membrane integrity. The structure of this protein includes a proline-rich domain with similarities to the AMPs drosocin, pyrrhocoricin, and abaecin, and a glycine-rich domain with similarity to attacin. Diptericin is an iconic readout of immune system activity in flies, used ubiquitously in studies of Drosophila immunity. Diptericin is named after the insect order Diptera.

Drosocin is a 19-residue long antimicrobial peptide (AMP) of flies first isolated in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster, and later shown to be conserved throughout the genus Drosophila. Drosocin is regulated by the NF-κB Imd signalling pathway in the fly.

Metchnikowin is a 26-residue antimicrobial peptide of the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster that displays both antibacterial and antifungal properties. This peptide is expressed strongly in the Drosophila fat body, but is also expressed at surface epithelia in the trachea and gut. This is regulated by the NF-κB signalling pathways Toll and Imd. Metchnikowin is named after Russian immunologist Élie Metchnikoff, one of the founders of modern immunology.
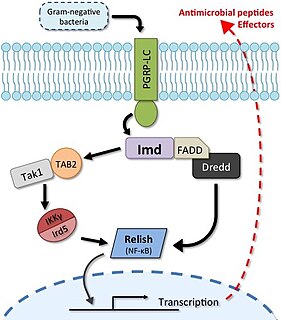
The Imd pathway is a broadly-conserved NF-κB immune signalling pathway of insects and some arthropods that regulates a potent antibacterial defence response. The pathway is named after the discovery of a mutation causing severe immune deficiency. The Imd pathway was first discovered in 1995 using Drosophila fruit flies by Bruno Lemaitre and colleagues, who also later discovered that the Drosophila Toll gene regulated defence against Gram-positive bacteria and fungi. Together the Toll and Imd pathways have formed a paradigm of insect immune signalling; as of September 2, 2019, these two landmark discovery papers have been cited collectively over 5000 times since publication on Google Scholar.