
Bradycardia is a slow resting heart rate, commonly under 60 beats per minute (BPM) as determined by an electrocardiogram. It is considered to be a normal heart rate during sleep, in young and healthy or elderly adults, and in athletes.
Polymorphism, polymorphic, polymorph, polymorphous, or polymorphy may refer to:
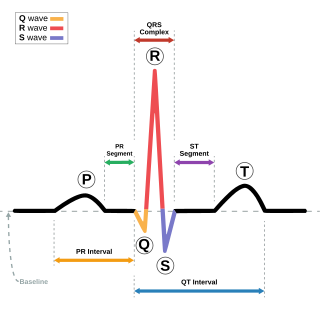
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram, a recording of the heart's electrical activity through repeated cardiac cycles. It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of the electrical activity of the heart using electrodes placed on the skin. These electrodes detect the small electrical changes that are a consequence of cardiac muscle depolarization followed by repolarization during each cardiac cycle (heartbeat). Changes in the normal ECG pattern occur in numerous cardiac abnormalities, including cardiac rhythm disturbances, inadequate coronary artery blood flow, and electrolyte disturbances.

A player piano is a self-playing piano containing a pneumatic or electro-mechanical mechanism that operates the piano action via programmed music recorded on perforated paper or metallic rolls, with more modern implementations using MIDI. The rise of the player piano grew with the rise of the mass-produced piano for the home, in the late 19th and early 20th century. Sales peaked in 1924 and subsequently declined as the improvement in phonograph recordings due to electrical recording methods developed in the mid-1920s. The advent of electrical amplification in home music reproduction via radio in the same period helped cause their eventual decline in popularity, and the stock market crash of 1929 virtually wiped out production.
ST, St, or St. may refer to:

Second-degree atrioventricular block is a disease of the electrical conduction system of the heart. It is a conduction block between the atria and ventricles. The presence of second-degree AV block is diagnosed when one or more of the atrial impulses fail to conduct to the ventricles due to impaired conduction. It is classified as a block of the AV node, falling between first-degree and third degree blocks.

Ventricular tachycardia is a fast heart rate arising from the lower chambers of the heart. Although a few seconds of VT may not result in permanent problems, longer periods are dangerous; and multiple episodes over a short period of time are referred to as an electrical storm. Short periods may occur without symptoms, or present with lightheadedness, palpitations, or chest pain. Ventricular tachycardia may result in ventricular fibrillation (VF) and turn into cardiac arrest. This conversion of the VT into VF is called the degeneration of the VT. It is found initially in about 7% of people in cardiac arrest.

Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is an umbrella term for fast heart rhythms arising from the upper part of the heart. This is in contrast to the other group of fast heart rhythms – ventricular tachycardia, which start within the lower chambers of the heart. There are four main types of SVT: atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT), and Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome. The symptoms of SVT include palpitations, feeling of faintness, sweating, shortness of breath, and/or chest pain.

In electrocardiography, the T wave represents the repolarization of the ventricles. The interval from the beginning of the QRS complex to the apex of the T wave is referred to as the absolute refractory period. The last half of the T wave is referred to as the relative refractory period or vulnerable period. The T wave contains more information than the QT interval. The T wave can be described by its symmetry, skewness, slope of ascending and descending limbs, amplitude and subintervals like the Tpeak–Tend interval.

A bundle branch block is a defect in one of the bundle branches in the electrical conduction system of the heart.

The QRS complex is the combination of three of the graphical deflections seen on a typical electrocardiogram. It is usually the central and most visually obvious part of the tracing. It corresponds to the depolarization of the right and left ventricles of the heart and contraction of the large ventricular muscles.
Monomorphic or Monomorphism may refer to:

Left bundle branch block (LBBB) is a conduction abnormality in the heart that can be seen on an electrocardiogram (ECG). In this condition, activation of the left ventricle of the heart is delayed, which causes the left ventricle to contract later than the right ventricle.
Lown–Ganong–Levine syndrome (LGL) is a pre-excitation syndrome of the heart. Those with LGL syndrome have episodes of abnormal heart racing with a short PR interval and normal QRS complexes seen on their electrocardiogram when in a normal sinus rhythm. LGL syndrome was originally thought to be due to an abnormal electrical connection between the atria and the ventricles, but is now thought to be due to accelerated conduction through the atrioventricular node in the majority of cases. The syndrome is named after Bernard Lown, William Francis Ganong, Jr., and Samuel A. Levine.
Q wave or Q-wave may refer to:

In electrocardiography, the ST segment connects the QRS complex and the T wave and has a duration of 0.005 to 0.150 sec.

Left anterior fascicular block (LAFB) is an abnormal condition of the left ventricle of the heart, related to, but distinguished from, left bundle branch block (LBBB).

In electrocardiography, left axis deviation (LAD) is a condition wherein the mean electrical axis of ventricular contraction of the heart lies in a frontal plane direction between −30° and −90°. This is reflected by a QRS complex positive in lead I and negative in leads aVF and II.
R peak, also written as R-peak and Rpeak, could refer to:
Quarry Siding railway station is a small railway station in Sundergarh district, Odisha. Its code is QRS. It serves Rourkela city as a secondary station. The station consists of two platforms. The platforms are not well sheltered. It lacks many facilities including water and sanitation. The station just 9 km from Rourkela city.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.









