Related Research Articles

The Lower Mainland is a geographic and cultural region of the mainland coast of British Columbia that generally comprises the regional districts of Metro Vancouver and the Fraser Valley. Home to approximately 3.05 million people as of the 2021 Canadian census, the Lower Mainland contains sixteen of the province's 30 most populous municipalities and approximately 60% of the province's total population.

Delta is a city in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia, Canada, as part of Greater Vancouver. Located on the Fraser Lowland south of Fraser River's south arm, it is bordered by the city of Richmond on the Lulu Island to the north, New Westminster to the northeast, Surrey to the east, the Boundary Bay and the American pene-exclave Point Roberts to the south, and the Strait of Georgia to the west.
Highway 17 is a provincial highway in British Columbia, Canada. It comprises two separate sections connected by a ferry link. The Vancouver Island section is known as the Patricia Bay Highway and connects Victoria to the Swartz Bay ferry terminal in North Saanich. The Lower Mainland section is known as the South Fraser Perimeter Road and connects the Tsawwassen ferry terminal to Delta and Surrey, terminating at an interchange with Highway 1 in the Fraser Valley.

Halkomelem is a language of various First Nations peoples of the British Columbia Coast. It is spoken in what is now British Columbia, ranging from southeastern Vancouver Island from the west shore of Saanich Inlet northward beyond Gabriola Island and Nanaimo to Nanoose Bay and including the Lower Mainland from the Fraser River Delta upriver to Harrison Lake and the lower boundary of the Fraser Canyon.

The Stó꞉lō, alternately written as Sto꞉lo, Stó:lô, or Stó:lõ, historically as Staulo or Stahlo, and historically known and commonly referred to in ethnographic literature as the Fraser River Indians or Lower Fraser Salish, are a group of First Nations peoples inhabiting the Fraser Valley and lower Fraser Canyon of British Columbia, Canada, part of the loose grouping of Coast Salish nations. Stó꞉lō is the Halqemeylem word for "river", so the Stó꞉lō are the river people. The first documented reference to these people as "the Stó꞉lō" occurs in Catholic Oblate missionary records from the 1880s. Prior to this, references were primarily to individual tribal groups such as Matsqui, Ts’elxweyeqw, or Sumas.
First Nations in British Columbia constitute many First Nations governments and peoples in the province of British Columbia. Many of these Indigenous Canadians are affiliated in tribal councils. Ethnic groups include the Haida, Coast Salish, Kwakwaka'wakw, Gitxsan, Tsimshian, Nisga'a and other examples of the Pacific Northwest Coast cultures, and also various Interior Salish and Athapaskan peoples, and also the Ktunaxa.

The Pattullo Bridge is a through arch bridge that crosses the Fraser River and links the cities of New Westminster and Surrey in Metro Vancouver, British Columbia. It was named in honour of Thomas Dufferin Pattullo, the 22nd Premier of British Columbia. A key link between Surrey and the rest of Greater Vancouver, the Pattullo Bridge handles an average of 75,700 cars and 3840 trucks daily, or roughly 20% of vehicle traffic across the Fraser River as of 2013.

The Musqueam Nation is a First Nation whose traditional territory encompasses the western half of what is now Greater Vancouver, in British Columbia, Canada. It is governed by a band council and is known officially as the Musqueam Indian Band under the Indian Act. "Musqueam" is an anglicization of the Hunquminum name xʷməθkʷəy̓əm, which means "place of the river grass" or "place where the river grass grows".

Kwantlen First Nation is a First Nations band government in British Columbia, Canada, located primarily on McMillan Island near Fort Langley. The Kwantlen people traditionally speak hən̓q̓əmin̓əm̓, the Downriver dialect of Halkomelem, one of the Salishan family languages.
McMillan Island is an island in the Fraser River, British Columbia, Canada, also known as McMillan Slough..
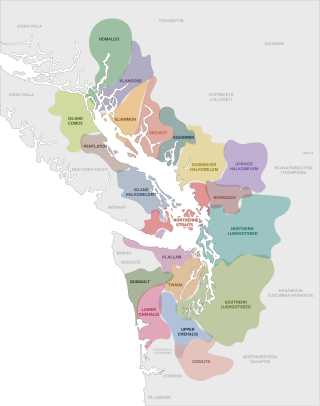
The Coast Salish are a group of ethnically and linguistically related Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast, living in the Canadian province of British Columbia and the U.S. states of Washington and Oregon. They speak one of the Coast Salish languages. The Nuxalk nation are usually included in the group, although their language is more closely related to Interior Salish languages.

The Tsawwassen First Nation is a First Nations government whose lands are located in the Greater Vancouver area of the Lower Mainland of British Columbia, Canada, close to the South Arm of the Fraser River and just north of the international boundary with the United States at Point Roberts, Washington. Tsawwassen First Nation lists its membership at 491 people, nearly half of whom live on the lands.

The Katzie First Nation or Katzie Nation is a First Nation whose traditional territory lies in the Lower Fraser Valley of British Columbia, Canada. According to their oral tradition, the Katzie people are the descendants of the Oe'lecten and Swaneset communities, two of five established by the Creator in present-day Greater Vancouver.
The New Westminster Indian Band is an Indian Act band government based at suite 105 – 3680 Rae Avenue in Vancouver, British Columbia. The band administration uses the unofficial name "Qayqayt First Nation" in its public communication. The New Westminster Indian Band is one of the smallest First Nations in Canada and the only one registered without a land base.

The Salish peoples are indigenous peoples of the American and Canadian Pacific Northwest, identified by their use of the Salishan languages which diversified out of Proto-Salish between 3,000 and 6,000 years ago.

The Marpole Midden, also known by archaeologists as the Great Fraser Midden or Eburne site, is a 4000-year-old midden at the mouth of the Fraser River, in the Marpole neighbourhood of Vancouver, British Columbia. The site was the location of the ancient Musqueam village of c̓əsnaʔəm and a sacred burial ground.
Brownsville was a former community in what is now the City of Surrey, British Columbia, Canada. Also known as South Westminster, it was located where the city ran a small ferry across the Fraser River, today approximately where the east footing of the Skytrain bridge is, this was also the former site of qiqéyt (Qayqayt), one of the main summer villages of the Kwantlen people and later, also the Musqueam people
Susan Point is a Musqueam Coast Salish artist from Canada, who works in the Coast Salish tradition. Her sculpture, prints and public art works include pieces installed at the Vancouver International Airport, the National Museum of the American Indian in Washington D.C., Stanley Park in Vancouver, the Museum of Anthropology at UBC, the Penn Museum in Philadelphia, and the city of Seattle.
The Hwlitsum First Nation is an organization representing the group historically known as the Lamalchi or Lamalcha but properly called Hwlitsum. The Hwlitsum are the descendants of the Lamalchi people and changed their name to Hwlitsum when they moved to Hwlitsum in 1892. Hul'qumi'num custom names groups based on the location of their winter village. Changing location of their winter village changed the name of the people. The Hwlitsum are a Hulquminum-speaking people whose home region is in the Southern Gulf Islands. The Hwlitsum were never granted reserves or band status and are currently seeking recognition as a band government from the governments of British Columbia and Canada.
References
- ↑ "Pattullo Bridge Replacement Project" (PDF).
- ↑ "BC Geographical Names". apps.gov.bc.ca. Retrieved 24 July 2022.
- ↑ Fraser, Simon (30 May 2007). The Letters and Journals of Simon Fraser, 1806-1808. Dundurn. ISBN 978-1-55002-713-6.
- ↑ "Kwantlen of the Coast Salish: A Halkomelem tribe". www.surreyhistory.ca. Retrieved 24 July 2022.
- ↑ Brett, David Howe (14 November 2024). "Does New Westminster's Qayqayt First Nation Exist?". The New Westminster Times. Archived from the original on 6 June 2024. Retrieved 6 June 2024.