
Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) class of memory integrated circuits used in computers. DDR SDRAM, also retroactively called DDR1 SDRAM, has been superseded by DDR2 SDRAM, DDR3 SDRAM, DDR4 SDRAM and DDR5 SDRAM. None of its successors are forward or backward compatible with DDR1 SDRAM, meaning DDR2, DDR3, DDR4 and DDR5 memory modules will not work in DDR1-equipped motherboards, and vice versa.

Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) is a local computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer and is part of the PCI Local Bus standard. The PCI bus supports the functions found on a processor bus but in a standardized format that is independent of any given processor's native bus. Devices connected to the PCI bus appear to a bus master to be connected directly to its own bus and are assigned addresses in the processor's address space. It is a parallel bus, synchronous to a single bus clock. Attached devices can take either the form of an integrated circuit fitted onto the motherboard or an expansion card that fits into a slot. The PCI Local Bus was first implemented in IBM PC compatibles, where it displaced the combination of several slow Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) slots and one fast VESA Local Bus (VLB) slot as the bus configuration. It has subsequently been adopted for other computer types. Typical PCI cards used in PCs include: network cards, sound cards, modems, extra ports such as Universal Serial Bus (USB) or serial, TV tuner cards and hard disk drive host adapters. PCI video cards replaced ISA and VLB cards until rising bandwidth needs outgrew the abilities of PCI. The preferred interface for video cards then became Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP), a superset of PCI, before giving way to PCI Express.

Static random-access memory is a type of random-access memory (RAM) that uses latching circuitry (flip-flop) to store each bit. SRAM is volatile memory; data is lost when power is removed.

Dynamic random-access memory is a type of random-access semiconductor memory that stores each bit of data in a memory cell, usually consisting of a tiny capacitor and a transistor, both typically based on metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) technology. While most DRAM memory cell designs use a capacitor and transistor, some only use two transistors. In the designs where a capacitor is used, the capacitor can either be charged or discharged; these two states are taken to represent the two values of a bit, conventionally called 0 and 1. The electric charge on the capacitors gradually leaks away; without intervention the data on the capacitor would soon be lost. To prevent this, DRAM requires an external memory refresh circuit which periodically rewrites the data in the capacitors, restoring them to their original charge. This refresh process is the defining characteristic of dynamic random-access memory, in contrast to static random-access memory (SRAM) which does not require data to be refreshed. Unlike flash memory, DRAM is volatile memory, since it loses its data quickly when power is removed. However, DRAM does exhibit limited data remanence.

Synchronous dynamic random-access memory is any DRAM where the operation of its external pin interface is coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal.

A DIMM, commonly called a RAM stick, comprises a series of dynamic random-access memory integrated circuits. These memory modules are mounted on a printed circuit board and designed for use in personal computers, workstations, printers, and servers. They are the predominant method for adding memory into a computer system. The vast majority of DIMMs are standardized through JEDEC standards, although there are proprietary DIMMs. DIMMs come in a variety of speeds and sizes, but generally are one of two lengths - PC which are 133.35 mm (5.25 in) and laptop (SO-DIMM) which are about half the size at 67.60 mm (2.66 in).

Double Data Rate 2 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) interface. It superseded the original DDR SDRAM specification, and was itself superseded by DDR3 SDRAM. DDR2 DIMMs are neither forward compatible with DDR3 nor backward compatible with DDR.
The Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) is a synchronous serial communication interface specification used for short-distance communication, primarily in embedded systems. The interface was developed by Motorola in the mid-1980s and has become a de facto standard. Typical applications include Secure Digital cards and liquid crystal displays.

In computing, a computer bus operating with double data rate (DDR) transfers data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal. This is also known as double pumped, dual-pumped, and double transition. The term toggle mode is used in the context of NAND flash memory.
Semiconductor memory is a digital electronic semiconductor device used for digital data storage, such as computer memory. It typically refers to devices in which data is stored within metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) memory cells on a silicon integrated circuit memory chip. There are numerous different types using different semiconductor technologies. The two main types of random-access memory (RAM) are static RAM (SRAM), which uses several transistors per memory cell, and dynamic RAM (DRAM), which uses a transistor and a MOS capacitor per cell. Non-volatile memory uses floating-gate memory cells, which consist of a single floating-gate transistor per cell.
Column Address Strobe (CAS) latency, or CL, is the delay in clock cycles between the READ command and the moment data is available. In asynchronous DRAM, the interval is specified in nanoseconds. In synchronous DRAM, the interval is specified in clock cycles. Because the latency is dependent upon a number of clock ticks instead of absolute time, the actual time for an SDRAM module to respond to a CAS event might vary between uses of the same module if the clock rate differs.

The Intel 8253 and 8254 are programmable interval timers (PITs), which perform timing and counting functions using three 16-bit counters.
XDR DRAM is a high-performance dynamic random-access memory interface. It is based on and succeeds RDRAM. Competing technologies include DDR2 and GDDR4.
In the fields of digital electronics and computer hardware, multi-channel memory architecture is a technology that increases the data transfer rate between the DRAM memory and the memory controller by adding more channels of communication between them. Theoretically, this multiplies the data rate by exactly the number of channels present. Dual-channel memory employs two channels. The technique goes back as far as the 1960s having been used in IBM System/360 Model 91 and in CDC 6600.
Memory refresh is the process of periodically reading information from an area of computer memory and immediately rewriting the read information to the same area without modification, for the purpose of preserving the information. Memory refresh is a background maintenance process required during the operation of semiconductor dynamic random-access memory (DRAM), the most widely used type of computer memory, and in fact is the defining characteristic of this class of memory.

Pumping, when referring to computer systems, is an informal term for transmitting a data signal more than one time per clock signal.

Quad data rate is a communication signaling technique wherein data are transmitted at four points in the clock cycle: on the rising and falling edges, and at two intermediate points between them. The intermediate points are defined by a second clock that is 90° out of phase from the first. The effect is to deliver four bits of data per signal line per clock cycle.

Random-access memory is a form of computer memory that can be read and changed in any order, typically used to store working data and machine code. A random-access memory device allows data items to be read or written in almost the same amount of time irrespective of the physical location of data inside the memory, in contrast with other direct-access data storage media, where the time required to read and write data items varies significantly depending on their physical locations on the recording medium, due to mechanical limitations such as media rotation speeds and arm movement.
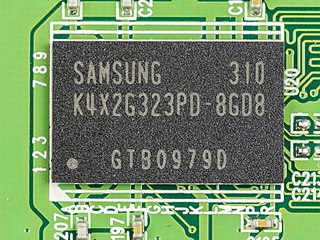
Low-Power Double Data Rate (LPDDR), also known as LPDDR SDRAM, is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory that consumes less power and is targeted for mobile computers and devices such as mobile phones. Older variants are also known as Mobile DDR, and abbreviated as mDDR.

Double Data Rate 5 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory. Compared to its predecessor DDR4 SDRAM, DDR5 was planned to reduce power consumption, while doubling bandwidth. The standard, originally targeted for 2018, was released on July 14, 2020.