A quadrilateral , in geometry, is a polygon with 4 sides.
Contents
Quadrilateral may also refer to:
A quadrilateral , in geometry, is a polygon with 4 sides.
Quadrilateral may also refer to:
Quadrangle or The Quadrangle may refer to:

In geometry a quadrilateral is a four-sided polygon, having four edges (sides) and four corners (vertices). The word is derived from the Latin words quadri, a variant of four, and latus, meaning "side". It is also called a tetragon, derived from Greek "tetra" meaning "four" and "gon" meaning "corner" or "angle", in analogy to other polygons. Since "gon" means "angle", it is analogously called a quadrangle, or 4-angle. A quadrilateral with vertices , , and is sometimes denoted as .

In Euclidean plane geometry, a rectangle is a rectilinear convex polygon or a quadrilateral with four right angles. It can also be defined as: an equiangular quadrilateral, since equiangular means that all of its angles are equal ; or a parallelogram containing a right angle. A rectangle with four sides of equal length is a square. The term "oblong" is used to refer to a non-square rectangle. A rectangle with vertices ABCD would be denoted as ABCD.

In Euclidean geometry, a kite is a quadrilateral with reflection symmetry across a diagonal. Because of this symmetry, a kite has two equal angles and two pairs of adjacent equal-length sides. Kites are also known as deltoids, but the word deltoid may also refer to a deltoid curve, an unrelated geometric object sometimes studied in connection with quadrilaterals. A kite may also be called a dart, particularly if it is not convex.
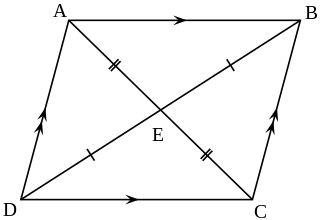
In Euclidean geometry, a parallelogram is a simple (non-self-intersecting) quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides. The opposite or facing sides of a parallelogram are of equal length and the opposite angles of a parallelogram are of equal measure. The congruence of opposite sides and opposite angles is a direct consequence of the Euclidean parallel postulate and neither condition can be proven without appealing to the Euclidean parallel postulate or one of its equivalent formulations.
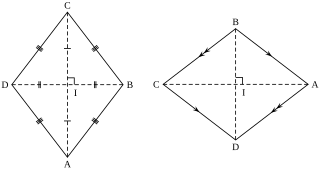
In plane Euclidean geometry, a rhombus is a quadrilateral whose four sides all have the same length. Another name is equilateral quadrilateral, since equilateral means that all of its sides are equal in length. The rhombus is often called a "diamond", after the diamonds suit in playing cards which resembles the projection of an octahedral diamond, or a lozenge, though the former sometimes refers specifically to a rhombus with a 60° angle, and the latter sometimes refers specifically to a rhombus with a 45° angle.

In Euclidean geometry, a cyclic quadrilateral or inscribed quadrilateral is a quadrilateral whose vertices all lie on a single circle. This circle is called the circumcircle or circumscribed circle, and the vertices are said to be concyclic. The center of the circle and its radius are called the circumcenter and the circumradius respectively. Other names for these quadrilaterals are concyclic quadrilateral and chordal quadrilateral, the latter since the sides of the quadrilateral are chords of the circumcircle. Usually the quadrilateral is assumed to be convex, but there are also crossed cyclic quadrilaterals. The formulas and properties given below are valid in the convex case.

In geometry, a trapezoid in North American English, or trapezium in British English, is a quadrilateral that has one pair of parallel sides.

In mathematics, hyperbolic geometry is a non-Euclidean geometry. The parallel postulate of Euclidean geometry is replaced with:
Quad as a word or prefix usually means four. It may refer to:
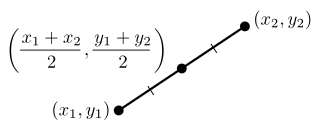
In geometry, the midpoint is the middle point of a line segment. It is equidistant from both endpoints, and it is the centroid both of the segment and of the endpoints. It bisects the segment.

In geometry, a set of points are said to be concyclic if they lie on a common circle. A polygon whose vertices are concyclic is called a cyclic polygon, and the circle is called its circumscribing circle or circumcircle. All concyclic points are equidistant from the center of the circle.

In Euclidean geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral, which means that it has four straight sides of equal length and four equal angles. It can also be defined as a rectangle with two equal-length adjacent sides. It is the only regular polygon whose internal angle, central angle, and external angle are all equal (90°), and whose diagonals are all equal in length. A square with vertices ABCD would be denoted ABCD.

The Wesleyan Quadrilateral, or Methodist Quadrilateral, is a methodology for theological reflection that is credited to John Wesley, leader of the Methodist movement in the late 18th century. The term itself was coined by 20th century American Methodist scholar Albert C. Outler.

In mathematics, specifically in incidence geometry and especially in projective geometry, a complete quadrangle is a system of geometric objects consisting of any four points in a plane, no three of which are on a common line, and of the six lines connecting the six pairs of points. Dually, a complete quadrilateral is a system of four lines, no three of which pass through the same point, and the six points of intersection of these lines. The complete quadrangle was called a tetrastigm by Lachlan (1893), and the complete quadrilateral was called a tetragram; those terms are occasionally still used.
In geometry, collinearity of a set of points is the property of their lying on a single line. A set of points with this property is said to be collinear. In greater generality, the term has been used for aligned objects, that is, things being "in a line" or "in a row".
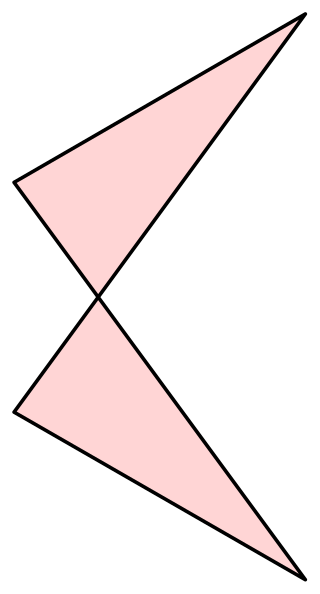
In geometry, an antiparallelogram is a type of self-crossing quadrilateral. Like a parallelogram, an antiparallelogram has two opposite pairs of equal-length sides, but these pairs of sides are not in general parallel. Instead, each pair of sides is antiparallel with respect to the other, with sides in the longer pair crossing each other as in a scissors mechanism. Whereas a parallelogram's opposite angles are equal and oriented the same way, an antiparallelogram's are equal but oppositely oriented. Antiparallelograms are also called contraparallelograms or crossed parallelograms.

In Euclidean geometry, Varignon's theorem holds that the midpoints of the sides of an arbitrary quadrilateral form a parallelogram, called the Varignon parallelogram. It is named after Pierre Varignon, whose proof was published posthumously in 1731.
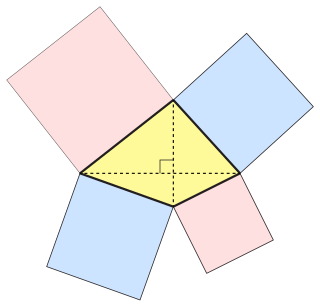
In Euclidean geometry, an orthodiagonal quadrilateral is a quadrilateral in which the diagonals cross at right angles. In other words, it is a four-sided figure in which the line segments between non-adjacent vertices are orthogonal (perpendicular) to each other.
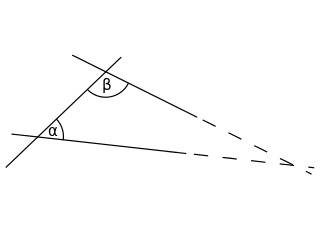
In geometry, the parallel postulate, also called Euclid's fifth postulate because it is the fifth postulate in Euclid's Elements, is a distinctive axiom in Euclidean geometry. It states that, in two-dimensional geometry:
If a line segment intersects two straight lines forming two interior angles on the same side that are less than two right angles, then the two lines, if extended indefinitely, meet on that side on which the angles sum to less than two right angles.