
Belfast is the capital and largest city of Northern Ireland, standing on the banks of the River Lagan on the east coast. It is the 12th-largest city in the United Kingdom and the second-largest on the island of Ireland. It had a population of 343,542 in 2019. Belfast suffered greatly during the violence that accompanied the partition of Ireland, and especially during the more recent conflict known as the Troubles.

Queen's University Belfast, officially The Queen's University of Belfast, is a public research university in Belfast, Northern Ireland, United Kingdom. The university received its charter in 1845 as "Queen's College, Belfast" and opened four years later.

The River Lagan is a major river in Northern Ireland which runs 53.5 miles (86 km) from the Slieve Croob mountain in County Down to Belfast where it enters Belfast Lough, an inlet of the Irish Sea. The Lagan forms much of the border between County Antrim and County Down in the east of Ulster. It rises as a tiny, fast-moving stream near to the summit of Slieve Croob; Transmitter Road runs nearby. It runs to Belfast through Dromara, Donaghcloney and Dromore. On the lower slopes of the mountain, it combines with a branch from Legananny Mountain, just opposite Slieve Croob. The river then turns east to Magheralin into a broad plain between the plateaus of Antrim and Down.
Belfast City Centre is the central business district of Belfast, Northern Ireland.

The Malone Road is a radial road in Belfast, Northern Ireland, leading from the university quarter southwards to the affluent suburbs of Malone and Upper Malone, each a separate electoral ward. The road runs parallel to the Lisburn Road and is linked by over a dozen side streets, while at its northern end, the Stranmillis Road rejoins the Malone Road to form University Road, which in turn joins with the Lisburn Road to become Bradbury Place. Most of the road is in the BT9 postcode district.

St Thomas' Church is a church of the Church of Ireland in south Belfast, Northern Ireland. It is located at the end of Eglantine Avenue at the junction with the Lisburn Road and holds regular services. The parish extends from Elmwood Avenue to Adelaide Park, and from the Malone Road to the Lisburn Road.

Sir Charles Lanyon DL, JP was an English architect of the 19th century. His work is most closely associated with Belfast, Northern Ireland.

The Belfast–Newry line operates from Lanyon Place station in County Antrim to Newry in County Down, Northern Ireland. The manager for this line is based at Portadown railway station, although the line extends to the border to include the Scarva and Poyntzpass halts and Newry. Newry is on the fringe of the network, being the last stop before the border with the Republic of Ireland. The line follows the route of the northern half of the main Dublin–Belfast line, with the exception of calling at Belfast Great Victoria Street.

Botanic Gardens is a public garden in Belfast, Northern Ireland.

Botanic railway station serves the Botanic area in south Belfast, Northern Ireland and students for Queen's University Belfast; it is also near Shaftesbury Square which is along Botanic Avenue. It is named after the nearby Belfast Botanic Gardens. It is one of the four stations located in the city centre, the others being City Hospital, Great Victoria Street, and Lanyon Place.

Stranmillis is an area in south Belfast, Northern Ireland. It is also an electoral ward for Belfast City Council, part of the Laganbank district electoral area. As part of the Queen's Quarter, it is the location for prominent attractions such as the Ulster Museum and Botanic Gardens. The area is located on Stranmillis Road, with Malone Road to the west and the River Lagan to the east. Its name, meaning "the sweet stream" in Irish, refers to the Lagan, whose waters are still fresh at this point, before becoming brackish as the river flows onward toward its mouth in Belfast Lough.

Lisburn Road is a main arterial route linking Belfast and Lisburn, Northern Ireland.

The Belfast quarters are distinctive cultural zones within the city of Belfast, Northern Ireland, whose identities have been developed as a spur to tourism and urban regeneration. These "quarters" differ from the traditional districts into which Belfast is divided.
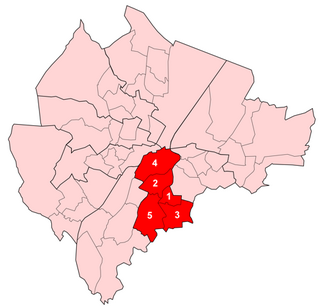
Laganbank was one of the nine district electoral areas in Belfast, Northern Ireland which existed from 1985 to 2014. Located in the south of the city, the district elected five members to Belfast City Council and contained the wards of Ballynafeigh, Botanic, Shaftesbury, Stranmillis, and Rosetta. Laganbank, along with neighbouring Balmoral, formed the greater part of the Belfast South constituencies for the Northern Ireland Assembly and UK Parliament.

The Lagan Canal was a 44-kilometre (27 mi) canal built to connect Belfast to Lough Neagh. The first section, which is a river navigation, was opened in 1763, and linked Belfast to Lisburn. The second section from Lisburn to Lough Neagh includes a small amount of river navigation, but was largely built as a canal. At its peak it was one of the most successful of the Irish canals, but ultimately it was unable to compete with road and rail transport, and the two sections were closed in 1954 and 1958. The central section from Sprucefield to Moira was destroyed by the construction of the M1 motorway in the 1960s. Responsibility for most of its remains passed first to the Department of Agriculture and then to the Department of Culture, Arts and Leisure, although the section between Aghalee Bridge and Lough Neagh, including the final ten locks, passed into private ownership. There is an active campaign to re-open the canal, including reinstatement of the central section.
Botanic is one of the ten district electoral areas (DEA) in Belfast, Northern Ireland. The district elects five members to Belfast City Council and contains the wards of Blackstaff; Central; Ormeau; Stranmillis and Windsor. Botanic, along with neighbouring Balmoral, forms the greater part of the Belfast South constituencies for the Northern Ireland Assembly and UK Parliament. It covers large parts of the centre and southern parts of the city.
The architecture of Belfast comprises architectural styles ranging from Georgian through to modernist buildings such as the Waterfront Hall and Titanic Belfast. The city's Victorian and Edwardian buildings are notable for their display of a large number of sculptures. Many of Belfast's Victorian era landmarks, including the main Lanyon Building at Queens University, were designed by Sir Charles Lanyon.























