Related Research Articles

Remote work is the practice of working from one's home or another space rather than from an office.

Employment is a relationship between two parties regulating the provision of paid labour services. Usually based on a contract, one party, the employer, which might be a corporation, a not-for-profit organization, a co-operative, or any other entity, pays the other, the employee, in return for carrying out assigned work. Employees work in return for wages, which can be paid on the basis of an hourly rate, by piecework or an annual salary, depending on the type of work an employee does, the prevailing conditions of the sector and the bargaining power between the parties. Employees in some sectors may receive gratuities, bonus payments or stock options. In some types of employment, employees may receive benefits in addition to payment. Benefits may include health insurance, housing, and disability insurance. Employment is typically governed by employment laws, organisation or legal contracts.

Temporary work or temporary employment refers to an employment situation where the working arrangement is limited to a certain period of time based on the needs of the employing organization. Temporary employees are sometimes called "contractual", "seasonal", "interim", "casual staff", "outsourcing", "freelance"; or the words may be shortened to "temps". In some instances, temporary, highly skilled professionals refer to themselves as consultants. Increasingly, executive-level positions are also filled with interim executives or fractional executives.
Seniority is the state of being older or placed in a higher position of status relative to another individual, group, or organization. For example, one employee may be senior to another either by role or rank, or by having more years served within the organization. The term "seniority" can apply to either concept or both concurrently.
A layoff or downsizing is the temporary suspension or permanent termination of employment of an employee or, more commonly, a group of employees for business reasons, such as personnel management or downsizing an organization. Originally, layoff referred exclusively to a temporary interruption in work, or employment but this has evolved to a permanent elimination of a position in both British and US English, requiring the addition of "temporary" to specify the original meaning of the word. A layoff is not to be confused with wrongful termination.
Work-to-rule, also known as an Italian strike or a slowdown in United States usage, called in Italian a sciopero bianco meaning "white strike", is a job action in which employees do no more than the minimum required by the rules of their contract or job, and strictly follow time-consuming rules normally not enforced. This may cause a slowdown or decrease in productivity if the employer does not hire enough employees or pay the appropriate salary and consequently does not have the requirements needed to run normally.
Contingent work, casual work, or contract work, is an employment relationship with limited job security, payment on a piece work basis, typically part-time that is considered non-permanent. Although there is less job security, freelancers often report incomes higher than their former traditional jobs.
A furlough is a temporary cessation of paid employment that is intended to address the special needs of a company or employer; these needs may be due to economic conditions that affect a specific employer, or to those prevailing in society as a whole. Furloughs may be short-term or long-term. They are also known as temporary layoffs.

Employee engagement is a fundamental concept in the effort to understand and describe, both qualitatively and quantitatively, the nature of the relationship between an organization and its employees. An "engaged employee" is defined as one who is fully absorbed by and enthusiastic about their work and so takes positive action to further the organization's reputation and interests. An engaged employee has a positive attitude towards the organization and its values. In contrast, a disengaged employee may range from someone doing the bare minimum at work, up to an employee who is actively damaging the company's work output and reputation.

An employment agency is an organization which matches employers to employees. In developed countries, there are multiple private businesses which act as employment agencies and a publicly funded employment agency.
In human resources, turnover refers to employees who leave an organization. The turnover rate is the percentage of the total workforce who leave over a certain period. Organizations and wider industries may measure their turnover rate during a fiscal or calendar year.
The degree of labour market flexibility is the speed with which labour markets adapt to fluctuations and changes in society, the economy or production. This entails enabling labour markets to reach a continuous equilibrium determined by the intersection of the demand and supply curves.
The employee value proposition (EVP) is a part of employer branding, in that it is one of the ways companies attract the skills and employees they desire and keep them engaged. It is how companies market themselves to prospective talent, and also how they retain that talent in a competitive job market. The EVP is meant to communicate the values and culture of the organization, as well as take the focus off remuneration as the sole reason for working there. The benefits, when done correctly, are a more committed, happier, and productive workforce at a cheaper cost, which are the main goals of any employee-centered strategy. It may also have the side benefit of improving the company's perception in the eyes of consumers.
Employee retention is the ability of an organization to retain its employees and ensure sustainability. Employee retention can be represented by a simple statistic. Employee retention is also the strategies employers use to try to retain the employees in their workforce.
Work–life balance in the United States is having enough time for work and enough time to have a personal life in the United States. Related, though broader, terms include lifestyle balance and life balance. The most important thing in work and life is the personal ability to demonstrate and meet the needs of work and personal life in order to achieve goals. People should learn to deal with role engagement management, role conflict management and managing life needs to achieve balance. Balance is about how to properly achieve the desired work and life satisfaction and needs in a conflict situation.
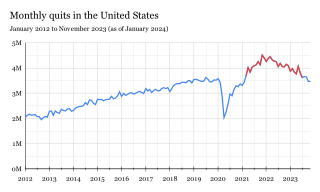
The Great Resignation, also known as the Big Quit and the Great Reshuffle, was a mainly American economic trend in which employees voluntarily resigned from their jobs en masse, beginning in early 2021 during the COVID-19 pandemic. Among the most cited reasons for resigning included wage stagnation amid rising cost of living, limited opportunities for career advancement, hostile work environments, lack of benefits, inflexible remote-work policies, and long-lasting job dissatisfaction. Most likely to quit were workers in hospitality, healthcare, and education. In addition, many of the resigning workers were retiring Baby Boomers, who are one of the largest demographic cohorts in the United States.
In human resources, resenteeism refers to a form of professional dissatisfaction wherein individuals choose to remain in unfulfilling jobs breeding resentment and a sense of entrapment. This is because they either unable to find a more applicable position, or are concerned about the perceived risks associated with changing employment. Individuals experiencing resenteeism will have poor employee engagement and may appear disillusioned, embittered, miserable, and unhappy. Resenteeism arose following the COVID-19 pandemic and the Great resignation where people reevaluated their work-life balance in the face of cost-of-living increases and is an extension of quiet quitting. Resenteeism is a form of occupational burnout.
Loud quitting refers to a type of employee disengagement in which individuals openly share their discontent, desire for change, and intention to leave. These individuals may refuse to do tasks that they deem unnecessary and by sharing their contempt with colleagues, may spread their disenchantment and disengagement. Loud quitting may arise from perceived workplace inequities, subpar compensation, and an unresponsive employer.
In human resources, quiet hiring refers to the practice of having an employee take on a new responsibilities or a role within their company due to need. The role may be temporary or permanent, and the reassignment may not align with employee interests. Quiet hiring often occurs during economic slowdowns as a cost-saving measure.
In human resources, rage applying refers to the application to a large number of jobs, typically online, when an employee is fed up with their current role. An individual may be prompted to begin rage applying after they've been denied a promotion or raise, feeling unrecognized, or under appreciated. Rage applying is a response to quiet quitting and may be felt as a form of empowerment or revenge against an employer. Rage applying can also allow an individual to understand their current market value.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Smith, Ray A. (August 28, 2023). "You've Heard of Quiet Quitting. Now Companies Are Quiet Cutting". WSJ. Retrieved October 14, 2023.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Thapa, Anuz (October 13, 2023). "Quiet cutting: How power in U.S. offices may be shifting back to bosses". CNBC. Retrieved October 14, 2023.
- 1 2 Mensik, Hailey (September 8, 2023). "WTF is quiet cutting?". WorkLife. Retrieved October 14, 2023.
- ↑ Mearian, Lucas (September 19, 2023). "Experts: 'Quiet cutting' employees makes no sense, and it's costly". Computerworld. Retrieved October 14, 2023.
- 1 2 Cerullo, Megan (August 29, 2023). "Companies are now "quiet cutting" workers. Here's what that means". CBS News. Retrieved October 14, 2023.
- ↑ Lucas, Suzanne (August 16, 2023). "What 'Quiet Cutting' Really Is and What It Looks Like Behind the Scenes" . Retrieved October 14, 2023.