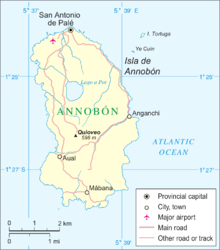
Quioveo is the extinct volcanic peak at the centre of the island of Annobón, Equatorial Guinea. It rises to a height of 598 metres. [1]

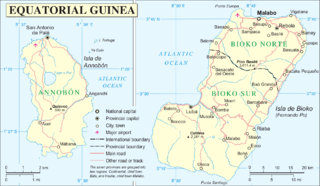
Annobón is a small province of Equatorial Guinea consisting of the island of Annobón and its associated islets in the Gulf of Guinea and Atlantic Ocean's Cameroon line. The provincial capital is San Antonio de Palé on the north side of the island; the other town is Mabana, formerly known as San Pedro. The roadstead is relatively safe, and some passing vessels take advantage of it in order to obtain water and fresh provisions, of which Annobon has offered an abundant supply. However, there is no regular shipping service to the rest of Equatorial Guinea, and ships call as infrequently as every few months. According to the 2015 census it had 5,232 inhabitants, a small population increase from the 5,008 registered by the 2001 census. The official language is Spanish but most of the inhabitants speak a creole form of Portuguese. The island's main industries are fishing and timbering.

Equatorial Guinea, officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea, is a country located on the west coast of Central Africa, with an area of 28,000 square kilometres (11,000 sq mi). Formerly the colony of Spanish Guinea, its post-independence name evokes its location near both the Equator and the Gulf of Guinea. Equatorial Guinea is the only sovereign African state in which Spanish is the official language. As of 2015, the country had an estimated population of 1,222,245.
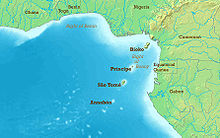
The island of Annobón is part of the Cameroon line of volcanoes, together with the islands of São Tomé Island, Príncipe, Bioko, and Mount Cameroon on the African mainland.

The Cameroon line is a 1,600 km (990 mi) chain of volcanoes. It includes islands in the Gulf of Guinea and mountains that extend along the border region of eastern Nigeria and western Cameroon, from Mount Cameroon on the Gulf of Guinea north and east towards Lake Chad. The islands, which span the equator, have tropical climates and are home to many unique plant and bird species. The mainland mountain regions are much cooler than the surrounding lowlands, and also contain unique and ecologically important environments.

São Tomé Island, at 854 km2 (330 sq mi), is the largest island of São Tomé and Príncipe and is home to about 157,000 or 96% of the nation's population. The island is divided into six districts. It is located 2 km north of the equator.

Príncipe is the smaller, northern major island of the country of São Tomé and Príncipe lying off the west coast of Africa in the Gulf of Guinea. It has an area of 136 square kilometres (53 sq mi) and a population of 7,324 (2012). The island is a heavily eroded volcano speculated to be over three million years old, surrounded by smaller islands including Ilheu Bom Bom, Ilhéu Caroço, Tinhosa Grande and Tinhosa Pequena. Part of the Cameroon Line archipelago, Príncipe rises in the south to 947 metres at Pico do Príncipe. The island is the main constituent of the Autonomous Region of Príncipe, established in 1995, and of the coterminous district of Pagué.