Paul Felix Hoffman, FRSC, OC is a Canadian geologist and Sturgis Hooper Professor Emeritus of Geology at Harvard University. He specializes on the Precambrian era and is widely known for his research on Snowball Earth glaciation in the Neoproterozoic era particularly through his research on sedimentary rocks of Namibia.
James (Jim) W.H. Monger is an emeritus scientist of the Geological Survey of Canada and a world leader in the application of plate tectonics to the study of mountain chain formation.
Raymond (Ray) Thorsteinsson, was a Canadian geologist who focused on the geology of the high Arctic. He was a Fellow of The Arctic Institute of North America, primarily known for his contribution to the geology of the Proterozoic and Paleozoic rocks.
Robert John Wilson "Bob" Douglas FRSC (1920–1979) was a Canadian geologist who made contributions in the fields of structure stratigraphy, sedimentation, and petroleum geology.

Raymond Alexander Price, is an award winning Canadian geologist. He has used his research on the structure and tectonics of North America’s lithosphere to produce extensive geological maps. He has also provided guidance for nuclear fuel waste disposal and reports on the human contribution to Global warming.
Charles (Charlie) Richard Stelck, O.C., Ph.D., F.R.S.C., P.Geol. was an iconic Canadian petroleum geologist, paleontologist, stratigrapher, and university professor. He is known for his pioneering work on unraveling the stratigraphy of the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin, and his inspired use of biostratigraphy as an exploration tool for finding petroleum and natural gas fields.
Eric Walter Mountjoy was a Canadian geologist, who spent much of his career as a professor at McGill University. He was a foremost expert on sedimentology, Devonian reefs, carbonate diagenesis, porosity development and the structure of the Rocky Mountains. His research has provided useful applications to the petroleum industry.
Roger G. Walker, FRSC, MMR is a geologist and an award-winning Emeritus Professor at McMaster University.

The Scollard Formation is an Upper Cretaceous to lower Palaeocene stratigraphic unit of the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin in southwestern Alberta. Its deposition spanned the time interval from latest Cretaceous to early Paleocene, and it includes sediments that were deposited before, during, and after the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) extinction event. It is significant for its fossil record, and it includes the economically important coal deposits of the Ardley coal zone.

The Bluesky Formation is a stratigraphic unit of Lower Cretaceous age in the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin. It takes the name from the hamlet of Bluesky, and was first described in Shell's Bluesky No. 1 well by Badgley in 1952.
The Leduc Formation is a stratigraphic unit of Late Devonian (Frasnian) age in the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin. It takes its name from the city of Leduc, and it was formally described from the B.A. Pyrz No. 1 well in central Alberta, between the depths of 1,623.7 m (5,327 ft) and 1,807.5 m (5,930 ft), by Imperial Oil Limited in 1950. Supplementary information came from a complete section of the formation that was cored in Imperial Oil's Leduc No. 530 well between 1,633 m (5,358 ft) and 1,863 m (6,112 ft).

The Canadian Society of Petroleum Geologists (CSPG) is a professional geological society in Canada. The CSPG works to advance the science of geology, foster professional development of members and promote community awareness of the profession. The organization was founded on December 17, 1927 as the Alberta Society of Petroleum Geologists in Calgary and was modelled after the American Association of Petroleum Geologists. It is based in Calgary, Alberta.

Peter Alfred Ziegler was a Swiss geologist, who made contributions to the understanding of the geological evolution of Europe and the North Atlantic borderlands, of intraplate tectonics and of plate tectonic controls on the evolution and hydrocarbon potential of sedimentary basins. Ziegler's career consists of 33 years as exploration geologist with the petroleum industry, 30 of which with Shell, and 20 years of university teaching and research.

The Belt Supergroup is an assemblage of primarily fine-grained sedimentary rocks and mafic intrusive rocks of late Precambrian (Mesoproterozoic) age. It is more than 15 kilometres (10 mi) thick, covers an area of some 200,000 km2, and is considered to be one of the world's best-exposed and most accessible sequences of Mesoproterozoic rocks. It was named after the Big Belt Mountains in west-central Montana. It is present in western Montana and northern Idaho, with minor occurrences in northeastern Washington and western Wyoming. It extends into Canada where the equivalent rocks, which are called the Purcell Supergroup, are exposed in southeastern British Columbia and southwestern Alberta. The rocks of the Belt Supergroup contain economically significant deposits of lead, zinc, silver, copper, gold, and other metals in a number of areas, and some of the Belt rocks contain fossil stromatolites.
The Beaverhill Lake Group is a geologic unit of Middle Devonian to Late Devonian age in the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin that is present in the southwestern Northwest Territories, northeastern British Columbia and Alberta. It was named by the geological staff of Imperial Oil in 1950 for Beaverhill Lake, Alberta, based on the core from a well that they had drilled southeast of the lake, near Ryley, Alberta.
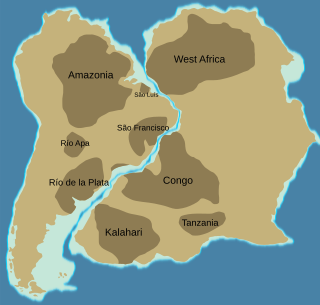
The country of Paraguay lies geologically at the borderzone between several cratons. Due to thick Cenozoic sediment cover and regolith development few outcrops are available in Paraguay. East of Paraguay River that Precambrian and Early Paleozoic crystalline basement crop out mainly in the heights of Caapucú and Apa. The geological processes that have shaped Paraguay's bedrock and sedimentary basins are diverse including rifting, marine sedimentation, metamorphism, eruption of flood basalts and alkaline potassic volcanism.

The Gog Group is a stratigraphic unit in the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin. It is present in the western main ranges of the Canadian Rockies in Alberta and British Columbia, and in the Cariboo Mountains and in the central Purcell Mountains in southwestern British Columbia. It was named by C.F. Deiss in 1940 for a type locality near Mount Assiniboine.

The Cairn Formation is a geologic formation of Late Devonian (Frasnian) age in the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin. It was named for the Cairn River near its junction with the Southesk River in Jasper National Park by D.J. McLaren in 1955.
The Purcell Supergroup is composed primarily of argillites, carbonate rocks, quartzites, and mafic igneous rocks of late Precambrian (Mesoproterozoic) age. It is present in an area of about 15,000 km2 in southwestern Alberta and southeastern British Columbia, Canada, and it extends into the northwestern United States where it is called the Belt Supergroup. It was named for the Purcell Mountains of British Columbia by R.A. Daly in 1912. Fossil stromatolites and algal structures are common in some of the Purcell Supergroup rocks, and the Sullivan ore body at Kimberley, British Columbia, a world-class deposit of lead, zinc, and silver, lies within the Alderidge Formation in the lower part of the Purcell.