
Acrylic paint is a fast-drying paint made of pigment suspended in acrylic polymer emulsion and plasticizers, silicone oils, defoamers, stabilizers, or metal soaps. Most acrylic paints are water-based, but become water-resistant when dry. Depending on how much the paint is diluted with water, or modified with acrylic gels, mediums, or pastes, the finished acrylic painting can resemble a watercolor, a gouache, or an oil painting, or have its own unique characteristics not attainable with other media.

Oil painting is the process of painting with pigments with a medium of drying oil as the binder. It has been the most common technique for artistic painting on canvas or wood panel for several centuries, spreading from Europe to the rest of the world. The advantages of oil for painting images include "greater flexibility, richer and denser colour, the use of layers, and a wider range from light to dark". But the process is slower, especially when one layer of paint needs to be allowed to dry before another is applied.

Paint is a liquid pigment that, after application to a solid material, and allowed to dry, adds a film-like layer to protect, add color, or provide texture. Paint can be made in many colors—and in many different types. Most paints are either oil-based or water-based, and each has distinct characteristics.
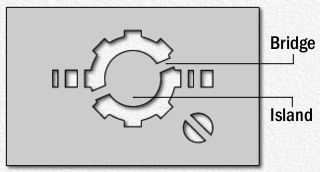
Stencilling produces an image or pattern on a surface, by applying pigment to a surface through an intermediate object, with designed holes in the intermediate object. The holes allow the pigment to reach only some parts of the surface creating the design. The stencil is both the resulting image or pattern and the intermediate object; the context in which stencil is used makes clear which meaning is intended. In practice, the (object) stencil is usually a thin sheet of material, such as paper, plastic, wood or metal, with letters or a design cut from it, used to produce the letters or design on an underlying surface by applying pigment through the cut-out holes in the material.

Tiles are usually thin, square or rectangular coverings manufactured from hard-wearing material such as ceramic, stone, metal, baked clay, or even glass. They are generally fixed in place in an array to cover roofs, floors, walls, edges, or other objects such as tabletops. Alternatively, tile can sometimes refer to similar units made from lightweight materials such as perlite, wood, and mineral wool, typically used for wall and ceiling applications. In another sense, a tile is a construction tile or similar object, such as rectangular counters used in playing games. The word is derived from the French word tuile, which is, in turn, from the Latin word tegula, meaning a roof tile composed of fired clay.

Slipware is pottery identified by its primary decorating process where slip is placed onto the leather-hard (semi-hardened) clay body surface before firing by dipping, painting or splashing. Slip is an aqueous suspension of a clay body, which is a mixture of clays and other minerals such as quartz, feldspar and mica. The slip placed onto a wet or leather-hard clay body surface by a variety of techniques including dipping, painting, piping or splashing. Slipware is the pottery on which slip has been applied either for glazing or decoration. Slip is liquified clay or clay slurry, with no fixed ratio of water and clay, which is used either for joining pottery pieces together by slip casting with mould, glazing or decorating the pottery by painting or dipping the pottery with slip.
Graining is the practice of imitating wood grain on a non-wood surface, or on relatively undesirable wood surface, in order to give it the appearance of a rare or higher quality wood, thereby increase that surface's aesthetic appeal. Graining was common in the 19th century, as people were keen on imitating hard, expensive woods by applying a superficial layer of paint onto soft, inexpensive woods or other hard surfaces. Graining can be accomplished using either rudimentary tools or highly specialized tools. A specialized thick brush used for graining is often called a mottler. Fan brushes, floggers, softening brushes, texture combs and even fingers are used to create various effects. The painting is carried out in layers, with the first layer being a base. Today that is usually done with latex paint in a gold or orange or tan tone, depending on the type of wood the artist is aiming to imitat. A second layer of tempera or thinned paint is applied over the dry base, by means of a sponge or large inexpensive brush. During the 19th century, however, brushes were more commonly used. It can also be applied on bricks and brass, as is more common today.

Craquelure is a fine pattern of dense cracking formed on the surface of materials. It can be a result of drying, aging, intentional patterning, or a combination of all three. The term is most often used to refer to tempera or oil paintings, but it can also develop in old ivory carvings or painted miniatures on an ivory backing. Recently, analysis of craquelure has been proposed as a way to authenticate art.
Visual design elements and principles describe fundamental ideas about the practice of visual design.
A glaze is a thin transparent or semi-transparent layer on a painting which modifies the appearance of the underlying paint layer. Glazes can change the chroma, value, hue and texture of a surface. Glazes consist of a great amount of binding medium in relation to a very small amount of pigment. Drying time will depend on the amount and type of paint medium used in the glaze. The medium, base, or vehicle is the mixture to which the dry pigment is added. Different media can increase or decrease the rate at which oil paints dry.

A wash is a term for a visual arts technique resulting in a semi-transparent layer of colour. A wash of diluted ink or watercolor paint applied in combination with drawing is called pen and wash, wash drawing, or ink and wash. Normally only one or two colours of wash are used; if more colours are used the result is likely to be classified as a full watercolor painting.

A color wash is a popular technique in faux painting using paint thinned out with glaze to create a subtle wash of color over walls or other surfaces.

Strié is a popular form of faux painting using glaze and paint brushes to create a soft natural striped texture.

Faux painting or faux finishing are terms used to describe decorative paint finishes that replicate the appearance of materials such as marble, wood or stone. The term comes from the French word faux, meaning false, as these techniques started as a form of replicating materials such as marble and wood with paint, but has subsequently come to encompass many other decorative finishes for walls and furniture including simulating recognisable textures and surfaces.
Hair highlighting/lowlighting is changing a person's hair color, using lightener or haircolor to lift the level or brightness of hair strands. There are four basic types of highlights: foil highlights, hair painting, frosting, and chunking. Highlights can be any color, as long as it is a lighter level than the surrounding hair. Hair lightened with bleach or permanent color will be permanent until new growth begins to show. Highlighted hair can make the hair appear fuller. Therefore, it is sometimes recommended for people with thin and fine hair. It also a recommended service for achieving better color balance with people that have at least 50% gray, and it also helps to diminish the line of demarcation once the new growth is showing from permanent hair color.
Acrylic painting techniques are different styles of manipulating and working with polymer-based acrylic paints. Acrylics differ from oil paints in that they have shorter drying times and are soluble in water. These types of paint eliminate the need for turpentine and gesso, and can be applied directly onto canvas. Aside from painting with concentrated color paints, acrylics can also be watered down to a consistency that can be poured or used for glazes.

Illusion knitting or shadow knitting is a form of textile art, in which the knitting is viewed as simply narrow stripes from one angle, and as an image when viewed from another angle. Illusion knitting has been recognised as an art form since 2010, largely due to the advances made by Steve Plummer who has created several large and detailed pieces. Similar effects occur in Tunisian crochet.

China painting, or porcelain painting, is the decoration of glazed porcelain objects such as plates, bowls, vases or statues. The body of the object may be hard-paste porcelain, developed in China in the 7th or 8th century, or soft-paste porcelain, developed in 18th-century Europe. The broader term ceramic painting includes painted decoration on lead-glazed earthenware such as creamware or tin-glazed pottery such as maiolica or faience.

The conservation and restoration of paintings is carried out by professional painting conservators. Paintings cover a wide range of various mediums, materials, and their supports. Painting types include fine art to decorative and functional objects spanning from acrylics, frescoes, and oil paint on various surfaces, egg tempera on panels and canvas, lacquer painting, water color and more. Knowing the materials of any given painting and its support allows for the proper restoration and conservation practices. All components of a painting will react to its environment differently, and impact the artwork as a whole. These material components along with collections care will determine the longevity of a painting. The first steps to conservation and restoration is preventive conservation followed by active restoration with the artist's intent in mind.
In visual arts, the ground is a prepared surface that covers the support of the picture and underlies the actual painting. Occasionally the term is also used in a broad sense to designate any surface used for painting, for example, paper for watercolor or plaster for fresco.















