
Rhys ap Gruffydd, commonly known as The Lord Rhys, in Welsh Yr Arglwydd Rhys was the ruler of the Welsh kingdom of Deheubarth in south Wales from 1155 to 1197 and native Prince of Wales.

Stephen, often referred to as Stephen of Blois, was King of England from 22 December 1135 to his death in 1154. He was Count of Boulogne jure uxoris from 1125 until 1147 and Duke of Normandy from 1135 until 1144. His reign was marked by the Anarchy, a civil war with his cousin and rival, the Empress Matilda, whose son, Henry II, succeeded Stephen as the first of the Angevin kings of England.
William I, usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England, reigning from 1066 until his death in 1087. A descendant of Rollo, he was Duke of Normandy from 1035 onward. By 1060, following a long struggle to establish his throne, his hold on Normandy was secure. In 1066, following the death of Edward the Confessor, William invaded England, leading an army of Normans to victory over the Anglo-Saxon forces of Harold Godwinson at the Battle of Hastings, and suppressed subsequent English revolts in what has become known as the Norman Conquest. The rest of his life was marked by struggles to consolidate his hold over England and his continental lands, and by difficulties with his eldest son, Robert Curthose.

Pope Gregory VII, born Hildebrand of Sovana, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 22 April 1073 to his death in 1085. He is venerated as a saint in the Catholic Church.

James IV was King of Scotland from 11 June 1488 until his death at the Battle of Flodden in 1513. He inherited the throne at the age of fifteen on the death of his father, James III, at the Battle of Sauchieburn, following a rebellion in which the younger James was the figurehead of the rebels. James IV is generally regarded as the most successful of the Stewart monarchs. He was responsible for a major expansion of the Scottish royal navy, which included the founding of two royal dockyards and the acquisition or construction of 38 ships, including the Michael, the largest warship of its time.
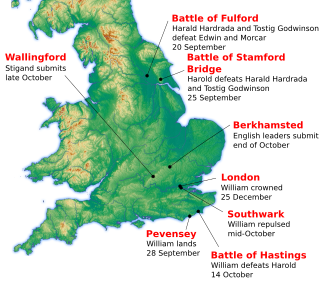
The Norman Conquest was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Normans, Bretons, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Conqueror.

The Anarchy was a civil war in England and Normandy between 1138 and 1153, which resulted in a widespread breakdown in law and order. The conflict was a war of succession precipitated by the accidental death of William Adelin, the only legitimate son of King Henry I, who drowned in the sinking of the White Ship in 1120. Henry sought to be succeeded by his daughter, known as Empress Matilda, but was only partially successful in convincing the nobility to support her. On Henry's death in 1135, his nephew Stephen of Blois seized the throne, with the help of Stephen's brother Henry of Blois, who was the Bishop of Winchester. Stephen's early reign saw fierce fighting with disloyal English barons, rebellious Welsh leaders, and Scottish invaders. Following a major rebellion in the south-west of England, Matilda invaded in 1139 with the help of her half-brother Robert of Gloucester.

James III was King of Scots from 1460 until his death at the Battle of Sauchieburn in 1488. He inherited the throne as a child following the death of his father, King James II, at the siege of Roxburgh Castle. James III's reign began with a minority that lasted almost a decade, during which Scotland was governed by a series of regents and factions who struggled for possession of the young king, before his personal rule began in 1469.

Maine is one of the traditional provinces of France. It corresponds to the former County of Maine, whose capital was also the city of Le Mans. The area, now divided into the departments of Sarthe and Mayenne, counts about 857,000 inhabitants.

The term Norman architecture is used to categorise styles of Romanesque architecture developed by the Normans in the various lands under their dominion or influence in the 11th and 12th centuries. In particular the term is traditionally used for English Romanesque architecture. The Normans introduced large numbers of castles and fortifications including Norman keeps, and at the same time monasteries, abbeys, churches and cathedrals, in a style characterised by the usual Romanesque rounded arches and especially massive proportions compared to other regional variations of the style.
The Revolt of the Earls in 1075 was a rebellion of three earls against William I of England. It was the last serious act of resistance against William in the Norman Conquest.

Romanesque Revival is a style of building employed beginning in the mid-19th century inspired by the 11th- and 12th-century Romanesque architecture. Unlike the historic Romanesque style, Romanesque Revival buildings tended to feature more simplified arches and windows than their historic counterparts.
Philaretos Brachamios or Vahram Varajnuni was a distinguished Byzantine general and warlord of Armenian heritage, and for a time was a usurper against emperor Michael VII. Philaretos is attested on seals as taxiarches, as well as protospatharios and topoteretes of the Tagmata of Cappadocia, then as magistros and doux (duke), and finally as kouropalates and doux.

Listowel Castle, located near the town of Listowel, County Kerry in Ireland, was built in the 15th century. It was the last bastion against Queen Elizabeth I in the First Desmond Rebellion, and was the last fortress of the Geraldines to be subdued. It fell after 28 days siege to Sir Charles Wilmot on 5 November 1600, who had the castle's garrison executed in the following days. The castle is a noted example of Anglo-Norman architecture in County Kerry, and has been the subject of several restoration projects. It is now protected as a national monument, and is open to the public for tours on a daily basis.

Le comte Ory is a comic opera written by Gioachino Rossini in 1828. Some of the music originates from his opera Il viaggio a Reims written three years earlier for the coronation of Charles X. The French libretto was by Eugène Scribe and Charles-Gaspard Delestre-Poirson adapted from a comedy they had first written in 1817.

The Norman conquest of southern Italy lasted from 999 to 1139, involving many battles and independent conquerors.
Philip de Braose, 2nd Lord of Bramber was an Anglo-Norman nobleman and Marcher Lord.

The Normans were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Franks and Gallo-Romans. The term is also used to denote emigrants from the duchy who conquered other territories such as England and Sicily. The Norse settlements in West Francia followed a series of raids on the French northern coast mainly from Denmark, although some also sailed from Norway and Sweden. Said settlements were finally legitimized when Rollo, a Scandinavian Viking leader, agreed to swear fealty to King Charles III of West Francia following the siege of Chartres in 911 AD. The intermingling in Normandy produced an ethnic and cultural "Norman" identity in the first half of the 10th century, an identity which continued to evolve over the centuries.
Peter II was the third Italo-Norman count of Trani. He was the youngest of three sons of Peter I; his elder brothers were Amico and Geoffrey.
Jean-Yves Stephane Marcel Raimbaud was a French animator and screenwriter. He is best known for creating the animated series, Oggy and the Cockroaches that officially debuted posthumously on 6 September 1998, on France 3. He also created Space Goofs, the first show he made co-produced by Gaumont Multimedia and Xilam.













