Related Research Articles
The dollar coin is a United States coin with a face value of one United States dollar. Dollar coins have been minted in the United States in gold, silver, and base metal versions. Dollar coins were first minted in the United States in 1794.

Jean Baptiste Charbonneau was a Native American-French Canadian explorer, guide, fur trapper, trader, military scout during the Mexican–American War, alcalde (mayor) of Mission San Luis Rey de Francia and a gold digger and hotel operator in Northern California. His mother was Sacagawea, a Shoshone Native who worked as a guide and interpreter for the Lewis and Clark Expedition. Charbonneau spoke French and English and learned German and Spanish during his six years in Europe from 1823 to 1829. He spoke Shoshone and other western Native American languages, which he picked up during his years of trapping and guiding.
The Shoshone or Shoshoni are a Native American tribe with four large cultural/linguistic divisions:

The Indigenous peoples of the Great Basin are Native Americans of the northern Great Basin, Snake River Plain, and upper Colorado River basin. The "Great Basin" is a cultural classification of indigenous peoples of the Americas and a cultural region located between the Rocky Mountains and the Sierra Nevada, in what is now Nevada, and parts of Oregon, California, Idaho, Wyoming, and Utah. The Great Basin region at the time of European contact was ~400,000 sq mi (1,000,000 km2). There is very little precipitation in the Great Basin area which affects the lifestyles and cultures of the inhabitants.
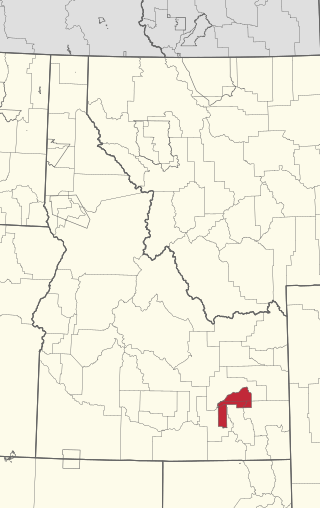
The Fort Hall Reservation is a Native American reservation of the federally recognized Shoshone-Bannock Tribes in the U.S. state of Idaho. This is one of five federally recognized tribes in the state. The reservation is located in southeastern Idaho on the Snake River Plain about 20 miles (32 km) north and west of Pocatello. It comprises 814.874 sq mi (2,110.51 km2) of land area in four counties: Bingham, Power, Bannock, and Caribou. To the east is the 60-mile-long (97 km) Portneuf Range; both Mount Putnam and South Putnam Mountain are located on the Fort Hall Reservation.
Glenna Maxey Goodacre was an American sculptor, best known for having designed the obverse of the Sacagawea dollar that entered circulation in the US in 2000, and the Vietnam Women's Memorial in Washington, D.C.
The Bannock War of 1878 was an armed conflict between the U.S. military and Bannock and Paiute warriors in Idaho and northeastern Oregon from June to August 1878. The Bannock totaled about 600 to 800 in 1870 because of other Shoshone peoples being included with Bannock numbers. they were led by Chief Buffalo Horn, who was killed in action on June 8, 1878. After his death, Chief Egan led the Bannocks. He and some of his warriors were killed in July by a Umatilla party that entered his camp in subterfuge.

The Bannock tribe were originally Northern Paiute but are more culturally affiliated with the Northern Shoshone. They are in the Great Basin classification of Indigenous People. Their traditional lands include northern Nevada, southeastern Oregon, southern Idaho, and western Wyoming. Today they are enrolled in the federally recognized Shoshone-Bannock Tribes of the Fort Hall Reservation of Idaho, located on the Fort Hall Indian Reservation.

The Sacagawea dollar is a United States dollar coin introduced in 2000, but subsequently minted only for niche circulation from 2002 onward. The coin generally failed to meet consumer and business demands.

The Institute of American Indian Arts (IAIA) is a public tribal land-grant college in Santa Fe, New Mexico, United States. The college focuses on Native American art. It operates the Museum of Contemporary Native Arts (MoCNA), which is housed in the historic Santa Fe Federal Building, a landmark Pueblo Revival building listed on the National Register of Historic Places as Federal Building. The museum houses the National Collection of Contemporary Indian Art, with more than 7,000 items.
Buhla is the name for a skeleton of a prehistoric (Paleo-Indian) woman found in a quarry near Buhl, Idaho, United States, in January 1989. The skeleton's age has been estimated by radiocarbon dating at 10,675 ± 95 BP, which confirms this as one of the oldest sets of human remains found in the Americas. The discovery was made by a quarry worker when he noticed what was found to be a thigh bone in the screen of a rock crusher. The nearly complete skeleton was subsequently unearthed nearby.
Grand Targhee Resort is a ski resort in the western United States, located in western Wyoming in the Caribou-Targhee National Forest, near Alta, the closest town to the resort. It is 42 miles (68 km) northwest of Jackson and is accessible only from the west, through Driggs, Idaho. The border with Idaho is less than five miles due west.

Sacagawea was a Lemhi Shoshone woman who, in her teens, helped the Lewis and Clark Expedition in achieving their chartered mission objectives by exploring the Louisiana Territory. Sacagawea traveled with the expedition thousands of miles from North Dakota to the Pacific Ocean, helping to establish cultural contacts with Native American people and contributing to the expedition's knowledge of natural history in different regions.

Eastern Shoshone are Shoshone who primarily live in Wyoming and in the northeast corner of the Great Basin where Utah, Idaho and Wyoming meet and are in the Great Basin classification of Indigenous People. They lived in the Rocky Mountains during the 1805 Lewis and Clark Expedition and adopted Plains horse culture in contrast to Western Shoshone that maintained a Great Basin culture.

Snake Indians is a collective name given to the Northern Paiute, Bannock, and Shoshone Native American tribes.

The Lemhi Shoshone are a tribe of Northern Shoshone, also called the Akaitikka, Agaidika, or "Eaters of Salmon". The name "Lemhi" comes from Fort Lemhi, a Mormon mission to this group. They traditionally lived in the Lemhi River Valley and along the upper Salmon River in Idaho. Bands were very fluid and nomadic, and they often interacted with and intermarried other bands of Shoshone and other tribes, such as the Bannock. Today most of them are enrolled in the Shoshone-Bannock Tribes of the Fort Hall Reservation of Idaho.
Benedicte Marie Wrensted was a notable Danish-American photographer, who emigrated to the United States after running a studio for a few years in Horsens, Denmark. She was an obscure photographer who is most notably remembered for her documentation of the Northern Shoshone, Lemhi, and Bannock tribes in Idaho between 1895-1912.

The Lemhi Reservation was a United States Indian Reservation for the Lemhi Shoshone from 1875 to 1907. During almost all this time their main chief was Tendoy.
LaNada War Jack, also known as LaNada Boyer and LaNada Means, is an American writer and activist. She was the first Native American student admitted to the University of California at Berkeley in 1968. She led the drive to create the Native American Student Organization and became its chair. As a leader of the Third World Strike at UC Berkeley in 1969, she was arrested but succeeded in obtaining approval for the first ethnic studies courses to be included in the university's curricula. A few months later, she became one of the organizers of the Occupation of Alcatraz in 1969. After the occupation, she completed her bachelor's degree at the University of California, Berkeley and went on to study law at Antioch School of Law in Washington, D.C. While in Washington, she participated in the takeover of the Bureau of Indian Affairs office in 1972.